Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Fourteen
Get insights from 70 questions on Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Fourteen, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Fourteen
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
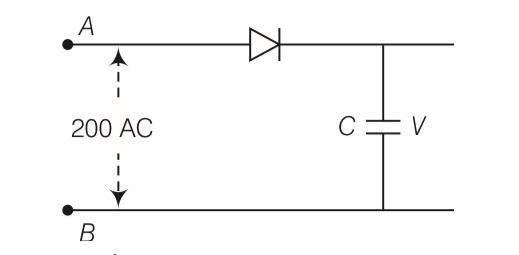
Answer- d
Explanation- as we know that Ev = Eo/ so E0= Ev so net voltage is 220 V
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
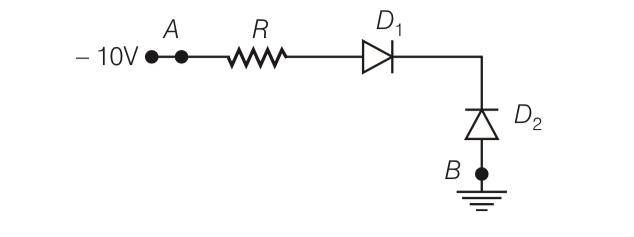
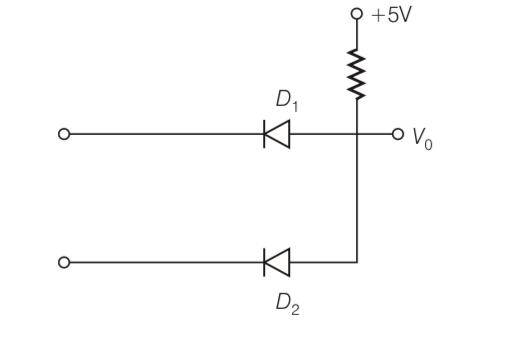
Answer-b
Explanation- from the figure we can say that diode D1 is reverse biased and diode D2 is forward biased so current will flow from B to A.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
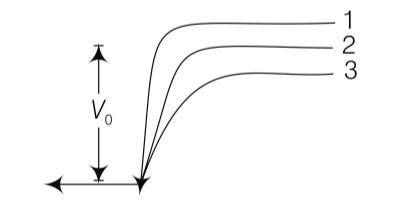
Explanation - When p-n junction is forward biased, it opposes the potential barrier junction, when p-n junction is reverse biased, it supports the potential barrier junction, resulting increase in potential barrier across the junction.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (d)
Explanation- when we increase temperature conductivity increases because number density is increasing after increasing temperature which decreases the relaxation time
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
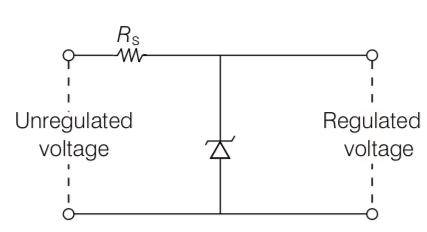
Explanation- power = 1W
Zener breakdown voltage = 5V
Minimum voltage = 3V
Maximum voltage = 7V
Current = power/voltage= 1/5=0.2A
The value of R for safe operation would be R = max voltage – Zener voltage/current
= 7- 5/0.2 = 2/0.2 = 10ohm
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
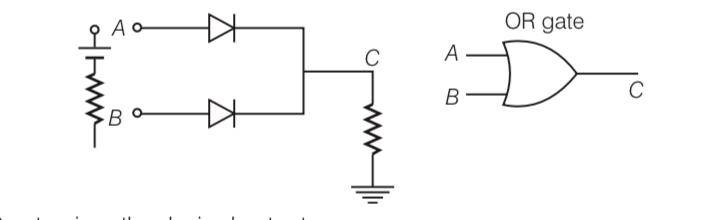
Explanation- this is AND GATE so truth table for this will be
A | B | A.B |
0 | 0 | |
0 | 1 | 0 |
1 | 0 | 1 |
1 | 1 |
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- In elemental semiconductor, the band gap is such that the emission are in infrared region and not in visible region.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- The NOT GATE is a device which has only one input and one output i.e., A'=Y means Y equals NOT A.
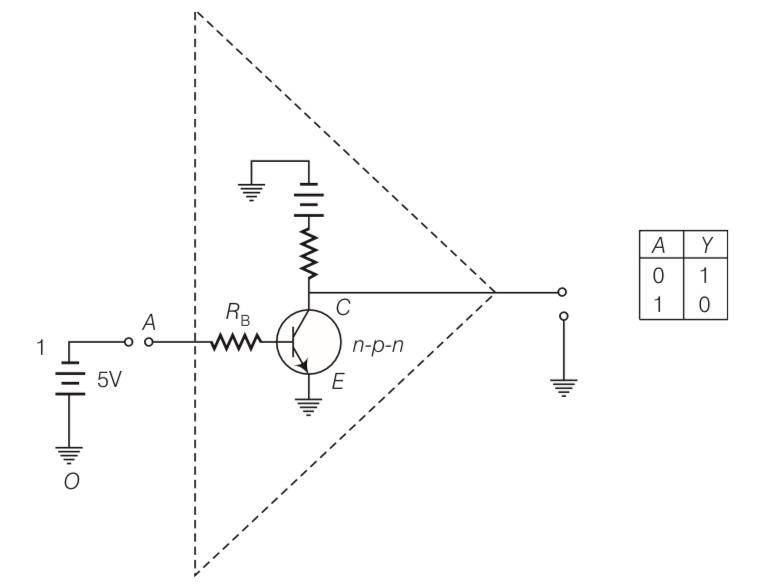
This GATE cannot be realised by using diodes. However it can be realised by making use of a
transistor. This can be seen in the figure given below.
A | Y |
0 | 1 |
1 | 0 |
Here, the base B of the transistor is connected to the input A through a resistance Rb and the emitter E is earthed. The collector is connected to 5 V battery. The output Y is the voltage at C w.r.t. earth.
The resistor Rb and Rc are so chosen that if emitter-base junction is unbiased, the transistor is in
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation-
OR GATE gives the desired output.
A | B | C |
0 | 0 | |
0 | 1 | 1 |
1 | 0 | 1 |
1 | 1 |
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
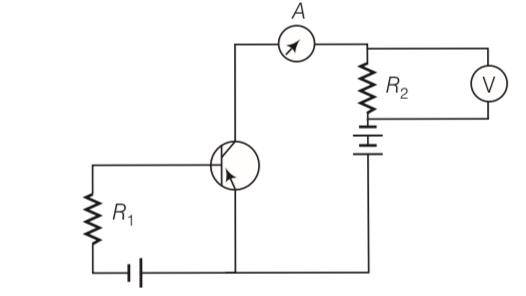
Explanation- as base current IB =
As Ri is increased IB is decreased.
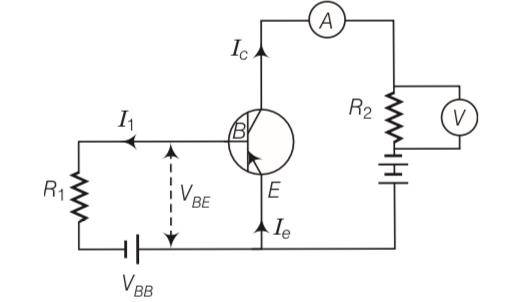
And collector current is Ic = IB as IB decreased Ic also decreased and the rading of voltmeter and ammeter also decreased.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 680k Reviews
- 1800k Answers