Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Ten
Get insights from 63 questions on Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Ten, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Ten
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
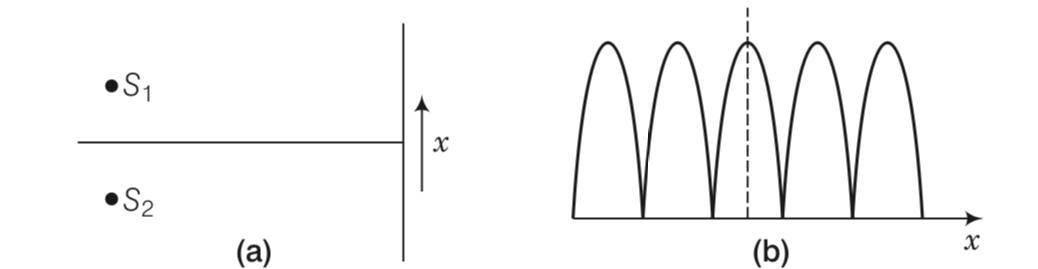
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (a, b, d)
Explanation-Consider the pattern of the intensity shown in the figure
(i) As intensities of all successive minima is zero, hence we can say that two sources S1 and S2 are having same intensities.
(ii) As width of the successive maxima (pulses) increases in continuous manner, we can say that the path difference (x) or phase difference varies in continuous manner.
(iii) We are using monochromatic light in YDSE to avoid overlapping and to have very clear pattern on the screen.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
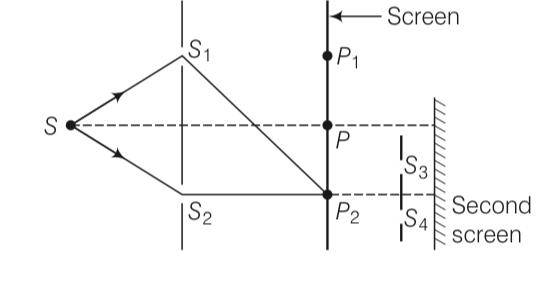
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- d
Explanation- According to question, there is a hole at point P2. From Huygen's principle, wave will propagates from the sources S1 and S2. Each point on the screen will acts as secondary sources of wavelets. Now, there is a hole at point P2 (minima). The hole will act as a source of fresh light for the slits S3 and S4.
Therefore, there will be a regular two slit pattern on the second screen
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer – (c)
Explanation- For the interference pattern to be formed on the screen, the sources should be coherent and emits lights of same frequency and wavelength. In a Young's double-slit experiment, when one of the holes is covered by a red filter and another by a blue filter. In this case due to filteration only red and blue lights are present. In YDSE monochromatic light is used for the formation of fringes on the screen. Hence, in this case there shall be no interference fringes.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- a
Explanation- due to refraction from the glass medium there is a phase change of
= =
According to snells law n= sin /sinr
Cosr =
= ( )
Phase difference = = = ( )
So net difference = = ( )-1/2+
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- ( a)
Explanation- given width of slit is 10410-10m= 10-6
Wavelength of sunlight varies from 4000A0 to 8000A0
As the width of slit is comparable to that of wavelength, hence diffraction occurs with maxima at centre. So, at the centre all colours appear i.e., mixing of colours form white patch at the centre.
New answer posted
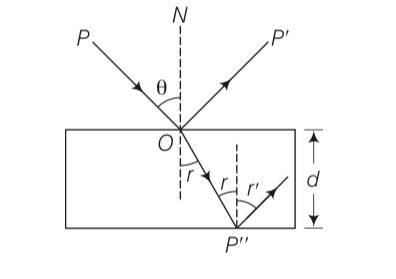
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (c)
Explanation-Consider the diagram the light beam incident from air to the glass slab at Brewster's angle (ip ). The incident ray is unpolarised and is represented by dot (.).
The reflected light is plane polarised represented by arrows.
As the emergent ray is unpolarised, hence intensity cannot be zero when passes through polaroid.
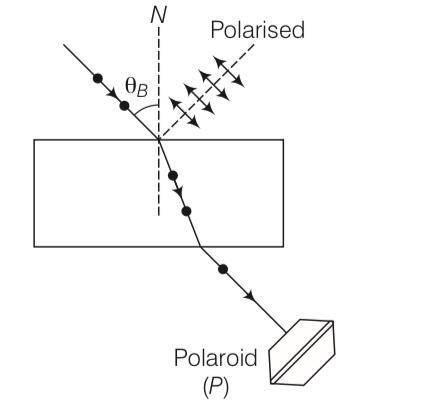
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
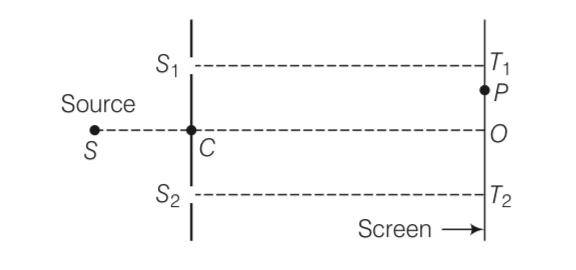
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- T2P= T2O+OP= D+x
T1P= T1O-OP= D-x
S1P =
S2P=
The minima will occur when S2P- S1P= (2n-1)
- =
[D2+4D2]1/2-[D2+0]1/2=
[5D2]1/2- [D2]1/2=
D-D=
we get D= 0.404
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- resolving power =1/d = = dmin= where is the wavelength of light
So dmin=
= = 0.12 10-9m
= = 0.2 10-3
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- When angle of incidence is equal to Brewster's angle, the transmitted light is unpolarised and reflected light is plane polarised.
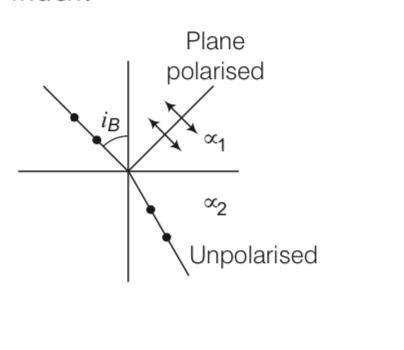
Consider the diagram in which unpolarised light is represented by dot and plane polarised light is represented By arrows.
Polarisation by reflection occurs when the angle of incidence Is the Brewster's angle
So tanib = where 2< 1
When the light rays travels in such a medium, the critical angle is
Sinic=
Where 2< 1
As tanib > sinic for large angles ib
Thus the polarisation by reflection occurs definitely.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- As per the given question, monochromatic light emerging from polaroid (I) is plane polarised. When polaroid (II) is placed infront of this polaroid (I), and rotated till no light passes through polaroid (II), then (I) and (II) are set in crossed positions, i.e., pass axes of I and II are at 90°.
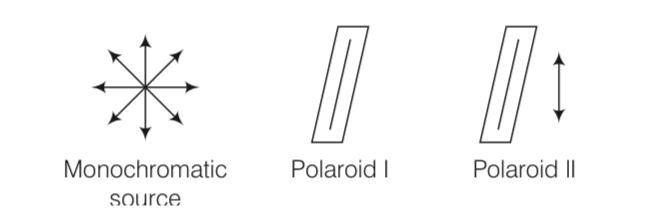
Consider the above diagram where a third polaroid (III) is placed between polaroid (I) and polaroid II.
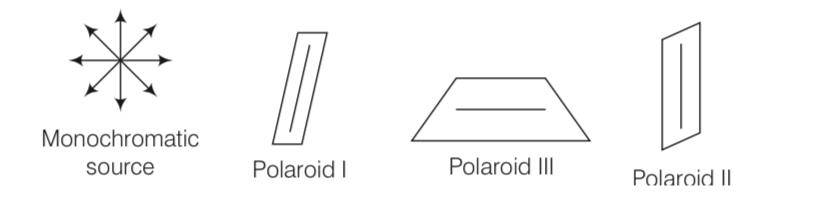
When a third polaroid (III) is placed in between (I) and (II), no light will emerge from (II), if pass axis of (III) is parallel to pass axis of (I) or (II). In
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers