Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Ten Wave Optics is great for Class 12 students who are preparing for the CBSE Board exam. By preparing from Shiksha's NCERT Exemplar, they can score high in their board exams as well as in the entrance exams such as NEET and JEE. The exemplar is prepared by the subject matter experts. It is reliable and accurate for exam preparation. This will help students develop their problem-solving skills and boost their exam confidence.
The students must download the Wave Optics Class 12 PDF from the Shiksha page. They can study from this PDF without any internet connection and can also take a printout of the PDF to practice on paper. The PDF includes various types of questions, including very short answer type questions, short answer type questions, long answer type questions and multiple choice questions. These are essential for exam preparation and deepening students' understanding of the key concepts of Physics Chapter 10. The Class 12th Chapter Ten Wave Optics Exemplar solutions include the solutions for all the questions of the Class 12 Physics NCERT exemplar book Chapter 10.
Students must also check the NCERT Solutions page on Shiksha and the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 10 Wave Optics.
- Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter Ten Wave Optics
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Wave Optics Short Answer Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Wave Optics Very Short Answer Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter 10 Long Answer Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Wave Optics Objective Type Questions
- 28th June 2022(First Shift)
- Important Formulas Related to Physics Chapter 10 NCERT Exemplar
- JEE Mains 2022
Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter Ten Wave Optics
The students can download the PDF of the Wave Optics Class 12. It contains well-structured solutions created by the subject matter experts. Students can study PDFs from anywhere without an internet connection. It contains all kinds of questions covering the key topics of Chapter 10 Class 12 Physics. The PDF includes VSA, SA, LA, and MCQs. These are all conceptual, application-based, and HOTS (Higher Order Thinking Skills) questions which help students prepare for the CBSE Board exam and entrance exam such as JEE and NEET. The PDF is available free of cost and provides a quick revision tool.
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Wave Optics Short Answer Type Questions
Following are the solutions:
Commonly asked questions
Consider a two slit interference arrangements (figure) such that the distance of the screen from the slits is. half the distance between the slits. Obtain the value of D in terms of X such that the first minima on the screen falls at a distance D from the centre O.
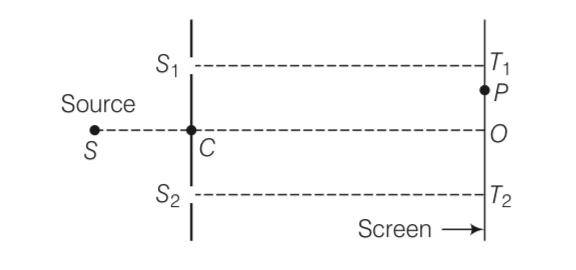
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- T2P= T2O+OP= D+x
T1P= T1O-OP= D-x
S1P =
S2P=
The minima will occur when S2P- S1P= (2n-1)
- =
[D2+4D2]1/2-[D2+0]1/2=
[5D2]1/2- [D2]1/2=
D-D=
we get D= 0.404
Can reflection result in plane polarised light if the light is incident on the interface from the side with higher refractive index?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- When angle of incidence is equal to Brewster’s angle, the transmitted light is unpolarised and reflected light is plane polarised.
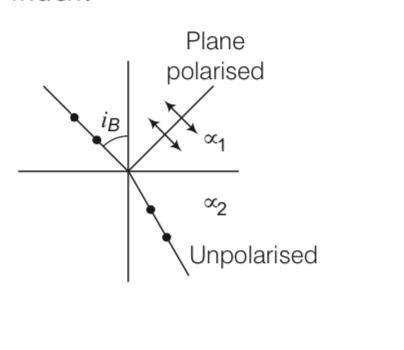
Consider the diagram in which unpolarised light is represented by dot and plane polarised light is represented By arrows.
Polarisation by reflection occurs when the angle of incidence Is the Brewster’s angle
So tanib = where 2< 1
When the light rays travels in such a medium, the critical angle is
Sinic=
Where 2< 1
As tanib > sinic for large angles ib
Thus the polarisation by reflection occurs definitely.
For the same objective, find the ratio of the least separation between two points to be distinguished by a microscope for light of 5000 Å and electrons accelerated through 100 V used as the illuminating substance.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- resolving power =1/d = = dmin= where is the wavelength of light
So dmin=
= = 0.12 10-9m
= = 0.2 10-3
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Wave Optics Very Short Answer Type Questions
Here are the solutions:
Commonly asked questions
Is Huygen’s principle valid for longitudinal sound waves?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- When we are considering a point source of sound wave. The disturbance due to the source propagates in spherical symmetry that is in all directions. The formation of
wavefront is in accordance with Huygen's principle.
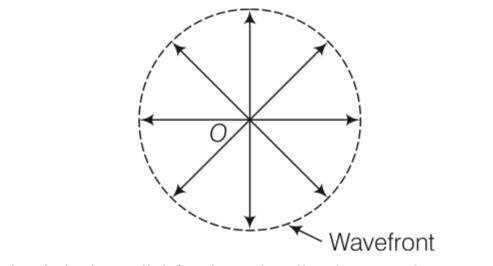
So, Huygen's principle is valid for longitudinal sound waves also.
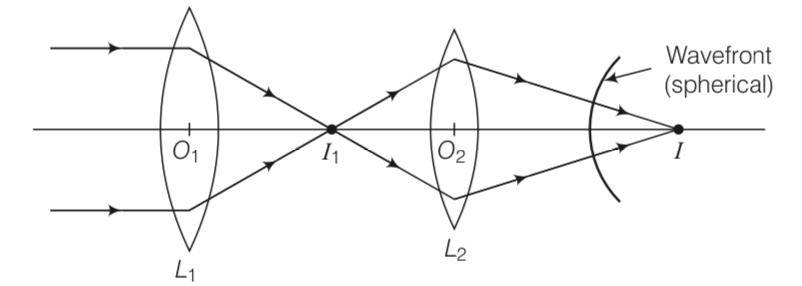
Consider a point at the focal point of a convergent lens. Another convergent lens of short focal length is placed on the other side. What is the nature of the wavefronts emerging from the final image?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- The point image I1, due to L1 is at the focal point. Now, due to the converging lens L2, let final image formed is I which is point image, hence the wavefront for this image will be of spherical symmetry.
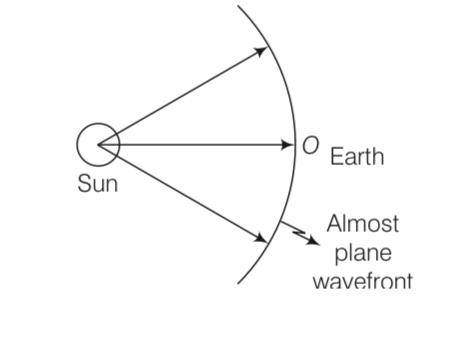
What is the shape of the wavefront on earth for sunlight?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- We know that the sun is at very large distance from the earth. Assuming sun as spherical, it can be considered as point source situated at infinity. Due to the large distance the radius of wavefront can be considered as large (infinity) and hence, wavefront is almost plane.
Why is the diffraction of Sound waves more evident in daily experience than that of light wave?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- As we know that the frequencies of sound waves lie between 20 Hz to 20 kHz so that their wavelength ranges between 15 m to 15 mm. The diffraction occur if the wavelength of waves is nearly equal to slit width.
As the wavelength of light waves is 7000 ×10-10 m to 4000 10-10m. The slit width is very near to the wavelength of sound waves as compared to light waves. Thus, the diffraction of sound waves is more evident in daily life than that of light waves.
The human eye has an approximate angular resolution of ɸ = 5.8 x 10-4rad and a typical photoprinter prints a minimum of 300 dpi (dots per inch, 1 inch = 2.54 cm). At what minimal distance z should a printed page be held so that one does not see the individual dots.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- angular resolution of the eye? = 5.8 x 10-4
linear distance between two dots is l= 2.54/300=0.84 10-2cm
? = l/z
z=l/? = = 14.5cm
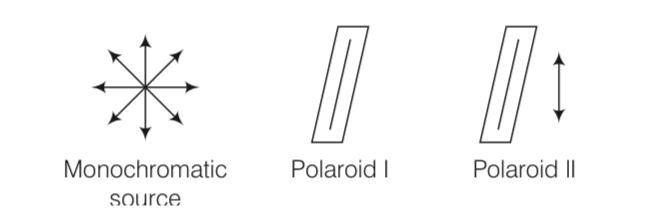
A polaroid (I) is placed in front,of a monochromatic source. Another polariod (II) is placed in front of this polaroid (I) and rotated till no light passes. A third polaroid (III) is now placed in between (I) and (II). In this case, will light emerge from (II). Explain
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- As per the given question, monochromatic light emerging from polaroid (I) is plane polarised. When polaroid (II) is placed infront of this polaroid (I), and rotated till no light passes through polaroid (II), then (I) and (II) are set in crossed positions, i.e., pass axes of I and II are at 90°.
Consider the above diagram where a third polaroid (III) is placed between polaroid (I) and polaroid II.
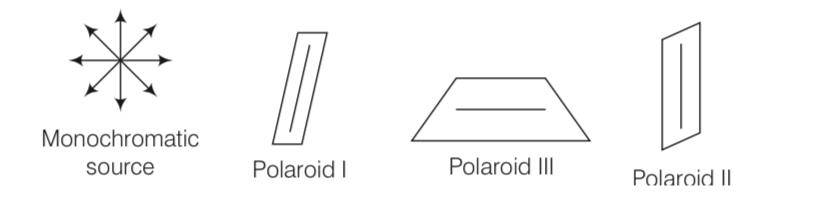
When a third polaroid (III) is placed in between (I) and (II), no light will emerge from (II), if pass axis of (III) is parallel to pass axis of (I) or (II). In all other cases, light will emerge from (II), as pass axis of (II)will no longer be at 90° to the pass axis of (III).
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter 10 Long Answer Type Questions
Find below the solutions:
Commonly asked questions
Figure shown a two slit arrangement with a source which emits unpolarised light. P is a polariser with axis whose direction is not given. If I 0 𝐼 0 is the intensity of the principal maxima when no polariser is present, calculte in the present case, the intensity of the principal maxima as well as the first minima.
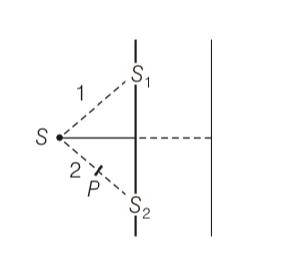
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- when polariser is not used
A=Aperp+A||
letA1= asinwt and A2=asin(wt+ )
now superposition principle for perpendicular polariser
AR= asinwt+ asin(wt+ )
AR=a(2cos sin(wt+ ))
AR=2acos sin(wt+ )
This eqn is also same for parallel polariser
AR=2acos sin(wt+ )
And we know that intensity is directly proportional to square of amplitude
(AR)2= (Aperp)2+(A||)2
So resultant intensity is
I=4(a)2cos2 dt + 4(a)2cos2 dt
I= 8(a)2cos2 (1/2) (after integrating sin value we got 1/2)
I= 4(a)2cos2
So I= 4(a)2
But when there is a polariser
Perpendicular polariser is blocked
I=2(a)2cos2 dt + (a)2
I=2(a)2cos2 1/2(a)2
When
Imax=2(a)2+1/2(a)2
Imax=5/2(a)2
Imax=5/2(I/4)=5I/8
At first minima it becomes I/8
A small transparent slab containing material of µ = 1.5 is placed along AS2(figure). What will be the distance from O of the principal maxima and of the first minima on either side of the principal maxima obtained in the absence of the glass slab?
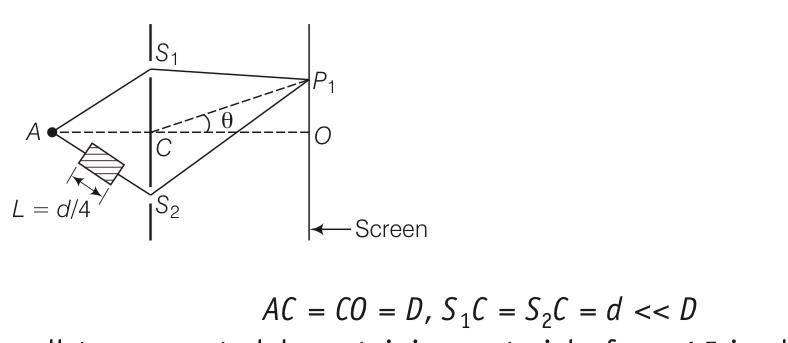
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- as the refractive index of the class , the path difference will be calculated as =2dsin +( )L
For principal maxima ,(path difference is zero)
2dsin 0+( )L=0
Sin 0= - =
Sin 0=-1/16
OP=Dtan 0= Dsin 0=-D/16
For pat h difference
2dsin 1+0.5L=
Sin 1= =
= = 1/4 -1/16
So two possible values and- =
Four identical monochromatic sources A, B, C, D as shown in the (figure)
produce waves of the same wavelength λ and are coherent. Two receiver
R1 and R2 are at great but equal distances from B.
(i) Which of the two receivers picks up the larger signal?
(ii) Which of the two receivers picks up the larger signal when B is turned off?
(iii) Which of the two receivers picks up the larger signal when D is turned off?
(iv) Which of the two receivers can distinguish which of the sources B or D has been turned off?
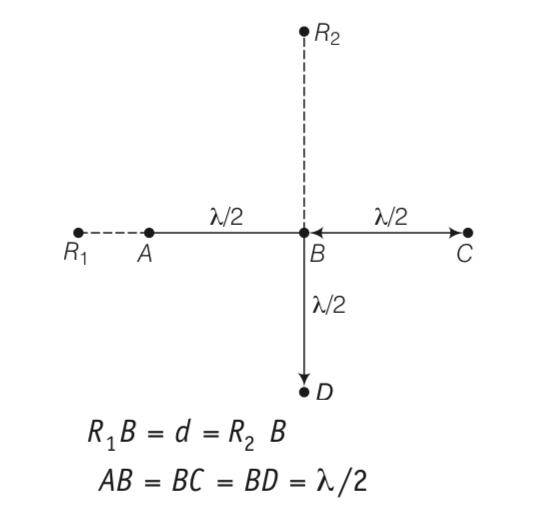
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation-consider the disturbance at the receiver R1 which is at a distance d from B
YA= acos(wt) and path difference is hence phase difference is .
Thus the wave R1 because of B
YB= acos(wt- )= - acoswt here path difference is and hence phase difference is
Thus R1 because of C
Yc= acos(wt-2 )= acoswt
(i)let the signal picked up at R2 from B be YB= a1cos(wt)
The path difference between signal at D and that B is
YD= -a1cos(wt)
The path difference between signal at A and that atB is
-d = d( -d =
therefore path difference os 0
A=a1cos(wt- )
C=a1cos(wt- )
Therefore signal picked up by R2 is
YA+Yb+Yc+Yd= y = 2a1cos(wt- )
|y|2 = 4a12cos2(wt- )
=2a12. Thus R1 picks up the larger signal.
(ii) if B is swiched off
R1 picks up y = acoswt
IR1= a2
R2 picks up y = a coswt
IR2= a2
(iii) thus R1 and R2 pick up the same signal
If D is switched off
R1 picks up by y = acoswt
IR1= a2
Y= 3acoswt
IR2=9a2/2
R2 picks up larger signal compared to R1
(iv) thus a signal at R1 indicates B has been switched off and an enhanced signal at R2 indicates D has been switched off.
The optical properties of a medium are governed by the relative permittivity (εr) and relative permeability (μr). The refractive index is defined as = n.For ordinary material εr > 0 and μr > 0 and the positive sign is taken for the square root. In 1964, a Russian scientist V. Veselago postulated the existence of material with εr < 0 and μr < 0. Since then such ‘metamaterials’ have been produced in the laboratories and their optical properties studied. For such materials n = – . As light enters a medium of such refractive index the phases travel away from the direction of propagation. (i) According to the description above show that if rays of light enter such a medium from air (refractive index =1) at an angle θ in 2nd quadrant, them the refracted beam is in the 3rd quadrant. (ii) Prove that Snell’s law holds for such a medium.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation-All points with the same optical path length must have the same phase.
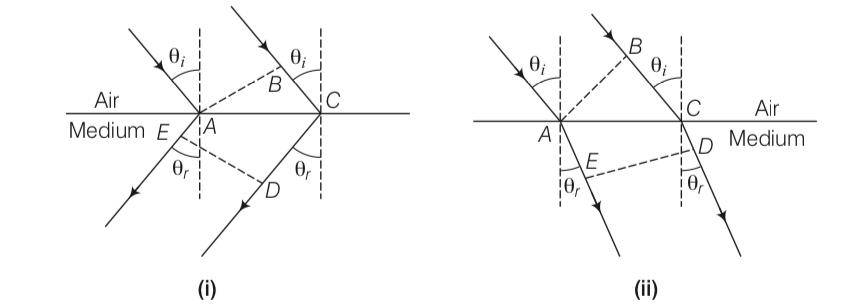
So – =BC-–
BC= (CD-AE)
BC>0, si must be greater than AD
But in other figure
–
So BC= –
But clearly here BE is less than zero
To proving snells law we know that
BC=ACsin and CD-AE=ACsin
So n= sini/sinr
To ensure almost 100% transmittivity, photographic lenses are often coated with a thin layer of dielectric material. The refractive index of this material is intermediated between that of air and glass (which makes the optical element of the lens). A typically used dielectric film is MgF2 (n=138). What should the thickness of the film be so that at the centre of the visible spectrum (5500 Å) there is maximum transmission.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- refractive index = 1.38 refractive index = 1.5
0
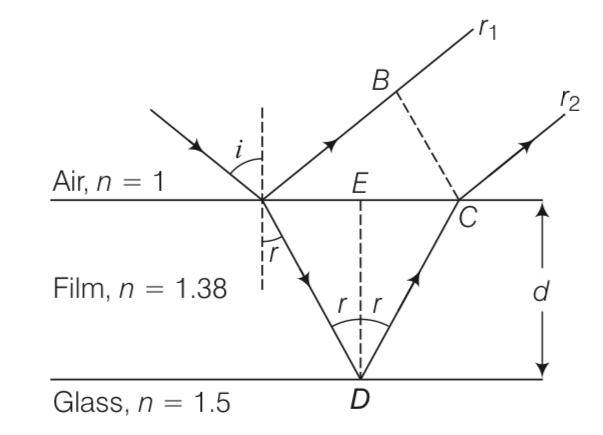
Consider a ray incident at an angle i. A part of this ray is reflected from the air-film interface And apart refracted inside.
This is partly reflected at the film-glass interface and a part transmitted. A part of the
reflected ray is reflected at the film-air interface and a part transmitted as r2 parallel to r 1. Of course successive reflections and transmissions will keep on decreasing the amplitude of the wave. Hence, rays r 1 and r2 shall dominate the behaviour. If incident light is to be transmitted through the lens, r 1 and r2 should interfere destructively. Both the reflections at A and D are from lower to higher refractive index and hence, there is no phase change on reflection. The optical path difference between r2 and r1 is
n(AD+CD)-AB
if d is the thickness of the film , then AD=CD=d/cosr
AB=AC sini
AC/2= d tanr
AC= 2dtanr
Hence AB= 2d tanr sini
Thus the optical path difference = -2dtanrsini
= 2. - 2d
= 2dsin{ }
= 2ndcosr
For path difference
2ndcosr=
ndcosr=
for photographic lenses, the sources are normally in vertical plane
i=r=00
ndcos0=
d= =5500/4 = 1000A0
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Wave Optics Objective Type Questions
Here are the questions and solutions:
Commonly asked questions
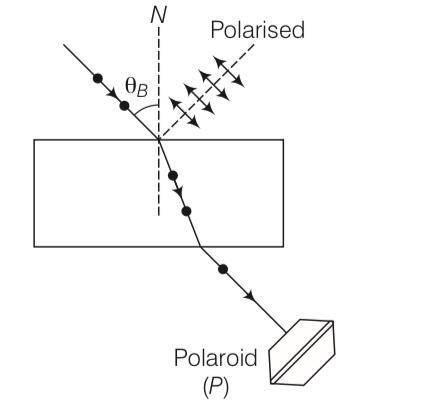
Consider a light beam incident from air to a glass slab at Brewster’s angle as shown in figure.
A Polaroid is placed in the path of the emergent ray at point P and rotated about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the polaroid.
(a) For a particular orientation, there shall be darkness as observed through the polaroid.
(b) The intensity of light as seen through the polaroid shall be independent of the rotation.
(c) The intensity of light as seen through the polaroid shall go minimum but not zero for two orientations of the polaroid.
(d) The intensity of light as seen through the polaroid shall go minimum for four orientations of the polaroid.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (c)
Explanation-Consider the diagram the light beam incident from air to the glass slab at Brewster's angle (ip ). The incident ray is unpolarised and is represented by dot (.).
The reflected light is plane polarised represented by arrows.
As the emergent ray is unpolarised, hence intensity cannot be zero when passes through polaroid.
Consider sunlight incident on a slit of width 10 4 Å. The image seen through the slit shall
(a) Be a fine sharp slit white in colour at the centre
(b) A bright slit white at the centre diffusing to zero intensities at the edges
(c) A bright slit white at the centre diffusing to regions of different colours
(d) Only be diffused slit white in colour.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- ( a)
Explanation- given width of slit is 10410-10m= 10-6
Wavelength of sunlight varies from 4000A0 to 8000A0
As the width of slit is comparable to that of wavelength, hence diffraction occurs with maxima at centre. So, at the centre all colours appear i.e., mixing of colours form white patch at the centre.
Consider a ray of light incident from air onto a slab of glass (refractive index n) of width d, at an angle θ. The phase difference between the ray reflected by the top surface of the glass and the bottom surface is
(a) ( )1/2+
(b) ( )1/2
(c) ( )1/2+ /2
(d) ( )1/2+
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- a
Explanation- due to refraction from the glass medium there is a phase change of
= =
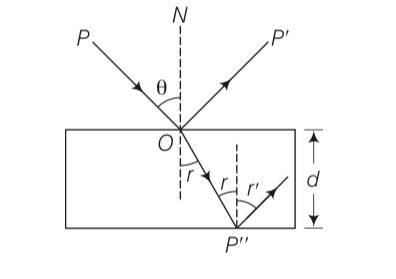
According to snells law n= sin /sinr
Cosr =
= ( )
Phase difference = = = ( )
So net difference = = ( )-1/2+
In a Young’s double-slit experiment, the source is white light. One of the holes is covered by a red filter and another by a blue filter. In this case,
(a) There shall be alternate interference patterns of red and blue
(b) There shall be an interference pattern for red distinct from that for blue
(c) There shall be no interference fringes
(d) There shall be an interference pattern for red mixing with one for blue
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer – (c)
Explanation- For the interference pattern to be formed on the screen, the sources should be coherent and emits lights of same frequency and wavelength. In a Young's double-slit experiment, when one of the holes is covered by a red filter and another by a blue filter. In this case due to filteration only red and blue lights are present. In YDSE monochromatic light is used for the formation of fringes on the screen. Hence, in this case there shall be no interference fringes.
Figure shows a standard two slit arrangement with slits S1, S2, P1, P2 are the two minima points on either side of P (figure).
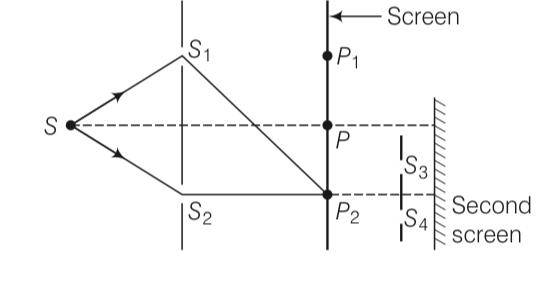
At P2 on the screen, there is a hole and behind P2.is a second 2-slit arrangement with slits S3, S4 and a second screen behind them.
(a) There would be no interference pattern on the second screen but it would be lighted
(b) The second screen would be totally dark
(c) There would be a single bright point on the second screen
(d) There would be a regular two slit pattern on the second screen
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- d
Explanation- According to question, there is a hole at point P2. From Huygen's principle, wave will propagates from the sources S1 and S2. Each point on the screen will acts as secondary sources of wavelets. Now, there is a hole at point P2 (minima). The hole will act as a source of fresh light for the slits S3 and S4.
Therefore, there will be a regular two slit pattern on the second screen
Two sources S1and S2 of intensity I1 and I2 are placed in front of a screen .
(a) The pattern of intensity distribution seen in the central portion is given by Fig. (b).
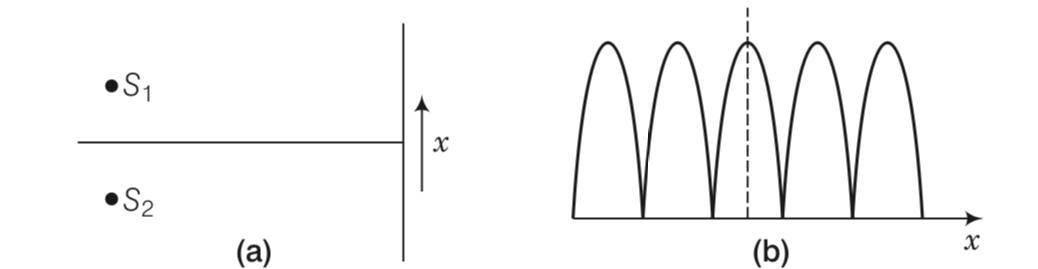
(a) s1 and s2 have same intensities
(b) s1 and s2 have constant phase difference
(c) s1 and s2 have same phase
(d) s1 and s2 have same wavelengthIn this case, which of the following statements are true?
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (a, b, d)
Explanation-Consider the pattern of the intensity shown in the figure
(i) As intensities of all successive minima is zero, hence we can say that two sources S1 and S2 are having same intensities.
(ii) As width of the successive maxima (pulses) increases in continuous manner, we can say that the path difference (x) or phase difference varies in continuous manner.
(iii) We are using monochromatic light in YDSE to avoid overlapping and to have very clear pattern on the screen.
Consider sunlight incident on a pinhole of width 103 Å. The image of the pinhole seen on a screen shall be
(a) A sharp white ring
(b) Different from a geometrical image
(c) A diffused central spot, white in colour
(d) Diffused coloured region around a sharp central white spot
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer – (b, d)
Explanation- We know that wavelength of sunlight ranges from 4000 Å to 8000 Å.
Clearly, wavelength λ < width of the slit.
Hence, light is diffracted from the hole. Due to diffraction from the slight the image formed On the screen will be different from the geometrical image.
Consider the diffraction pattern for a small pinhole. As the size of the hole is increased
(a) The size decreases
(b) The intensity increases
(c) The size increases
(d) The intensity decreases
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (a, b)
Explanation- (a) When a decreases w increases. So, size decreases.
(b) Now, light energy is distributed over a small area and intensity∝1/Area is decreasing so intensity increases
For light diverging from a point source,
(a) The wavefront is spherical
(b) The intensity decreases in proportion to the distance squared
(c) The wavefront is parabolic
(d) The intensity at the wavefront does not depend on the distance
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (a, b)
Explanation- Due to the point source light propagates in all directions symmetrically and hence, wavefront will be spherical as shown in the diagram.
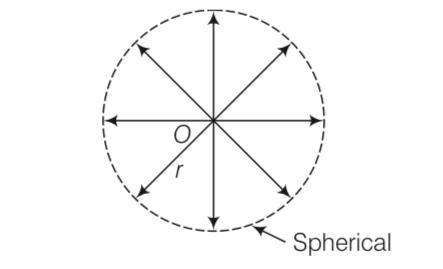
If power of the source is P, then intensity of the source will be I= p/4 2
where, r is radius of the wavefront at anytime.
28th June 2022(First Shift)
28th June 2022(First Shift)
Commonly asked questions
Given below are two statements : One is labeled as Assertion A and the other is labeled as Reason R.
Assertion A : Product of Pressure (P) and time (t) has the same dimension as that of coefficient of viscosity.
Reason R : Coefficient of viscosity =
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Pressure × time
Coefficient of viscosity,
A particle of mass m is moving in a circular path of constant radius r such that its centripetal acceleration (a) is varying with time t as a = k2 rt2, where k is a constant. The power delivered to the particle by the force acting on it is given as
a = k2rt2
⇒ tangential force, Ft = mat = mkr
Note → Power delivered by centripetal force will be zero.
Motion of a particle in x – y plane is described by a set of following equations x = 4sin m and y = 4sin The path of a particle will be
- (i)
- (ii)
From (i) and (ii) cos2
Match List – I with List – II
|
|
List – I |
|
List – II |
|
A. |
Moment of inertia of solid sphere of radius R about and tangent. |
I. |
5/3MR2 |
|
B. |
Moment of inertia of hollow sphere of radius (R) about any tanget |
II. |
7/5MR2 |
|
C. |
Moment of inertia of circular ring of radius (R) about its diameter. |
III. |
1/4MR2 |
|
D. |
Moment of inertial of circular disc of radius (R) about any diameter. |
IV. |
1/2MR2 |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Use formula for M.I.
Two planets A and B of equal mass are having their period of revolutions TA and TB such that TA = 2TB. These planets are revolving in the circular orbits or radii rA and rB respectively. Which out of the following would be the correct relationship of their orbits?
According to kepler’s third law of time period –
A water drop of diameter 2 cm is broken into 64 equal droplets. The surface tension of water is 0.075N/m. In this process the gain in surface energy will be
Gain in surface energy,
from volume centenary,
Initial surface area, Ai = 4pR2
final surface area,
Given below are two statements:
Statement – I : When moment of an ideal gas undergoes adiabatic change from state to state then work done is w = where R = universal gas constant.
Statement – II : In the above case, when work done on the gas, the temperature of the gas would rise.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
In case of adiabatic process
for adiabatic process :-
So, when work is done by the gas, temperature decreases and when work is done on the gas, temperature rises.
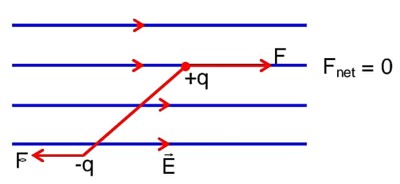
Given below are two statements:
Statement – I : A point change is brought in an electric field. The value of electric field at a point near to the change may increase if the charge is positive.
Statement – I : An electric dipole is placed in a non-uniform electric field. The net electric force on the dipole will not be zero.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
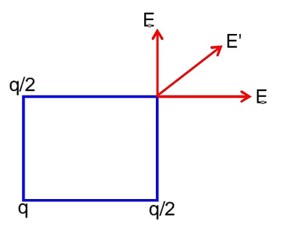
The three charges q/2, q and q/2 are placed at the corners A, B and C of a square of side ‘a’ as shown in figure. The magnitude of electric field (E) at the corner D of the square, is
A radar sends an electromagnetic single of electric (E0) = 2.25 V/m and magnetic field (B0) = 1.5 × 10-8 T which strikes a target on line of sight at a distance of 3km in a medium. After that, a part of signal (echo) reflects back towards the radar with same velocity and by same path. If the signal was transmitted at time t = 0 from radar, then after how much time echo will reach to the radar?
Speed of declromagnetic signal,
Time to reach each to the same
radar,
The refracting angle of a prims is A and refractive index of the material of the prism is cot (A/2). Then the angle of minimum deviation will be
At minimum deviation –
Using snell’s low : -
The aperture of the objective is 24.4 cm. The resolving power of this telescope, if a alight of wavelength 2440 is used to see the object will be
Resolving power, =
THE de Broglie wavelength for an electron and a photon are respectively. For the same kinetic energy of electron and photon, which of the following presents the correct relation between the de Broglie wavelengths of two
- (ii)
Ke = KP
The Q-value of a nuclear reaction and kinetic energy of the projectile particle, Kp are related as
X + p → Y + b
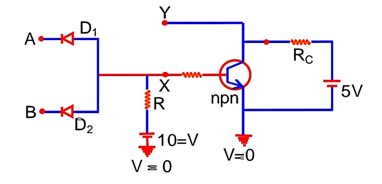
In the following circuit, the correct relation between output (Y) and inputs A and B will be
From Truth table .
For using a multimeter to identify diode from electrical compounds, choose the correct statement out of the following about the diode
Diode conducts current only in one direction.
Given below are two statements : One is labeled as Assertion A and the other is labeled as Reason R.
Assertion A : n-p-n transistor permits more current that a p-n-p transistor.
Reason R : Electrons have greater mobility as a change carrier.
Choose the correct answer form the options given below
Using factual data.
Match List – I with List – II
|
|
List – I |
|
List – II |
|
A. |
Television signal |
I. |
03 KHz |
|
B. |
Radio signal |
II. |
20 KHz |
|
C. |
High Quality Music |
III. |
02 MHz |
|
D. |
Human speech |
IV. |
06 MHz |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Using factual data.
The velocity of sound in a gas, in which two wavelengths 4.08m and 4.16m produce 40 beats in 12s, will be
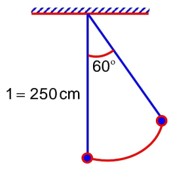
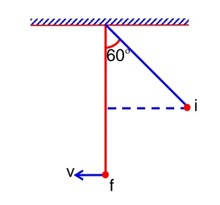
A pendulum is suspended by a string of length 250 cm. The mass of the bob of the pendulum is 200g. The bob is pulled aside until the string is at 60° with vertical as shown in the figure. After releasing the bob, the maximum velocity attained by the bob will be_________ ms-1. (if g = 10m/s2)
From conservation of Energy:
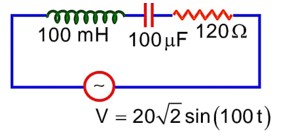
An AC source is connected to an inductance of 100 mH, a capacitance of 100 and a resistance of 120 as shown in figure. The time in which the resistance having a thermal capacity 2 J/°C will get heated by 16°C is________ s.
= 150
The position vector of 1kg object is and its velocity The magnitude of is angular momentum is where x is________.
=
=√=√91
A man of 60kg is running on the road and suddenly jumps into stationary trolly car of mass 120kg. Then, the trolly car starts moving with velocity 2ms-1. The velocity of the running man was _________ ms-1, when he jumps into the car
Using conservation of momentum:
60 × v = (60 + 120) × 2
⇒ v = 6m/s
A hanging mass M is connected to a four times bigger mass by using a string-pulley arrangement, as shown in the figure. The bigger mass is placed on a horizontal ice-slab and being pulled by 2 Mg force. In this situation, tension in the string is for x_________. Neglect mass of the string and fiction of the block (bigger mass) with ice slab.
Using newton’s law:
2mg – T = 4ma - (1)
T – mg = ma - (2)
From (1) & (2) :
The total internal energy of two mole mono atomic ideal gas at temperature T = 300K will be __________J. (Given R = 8.31 J/mol.K)
A singly ionized magnesium atom (A = 24) ion is accelerated to kinetic energy 5 ke V, and is projected perpendicularly into a magnetic field B of the magnitude 0.5 T. The radius of path formed will be ________cm.
=
= 9.975 × 102 cm
= 9.975 cm
A telegraph line of length 100km has a capacity of and it carries an alternating current at 0.5 kilo cycle per second. If minimum impedance is required, then the value of the inductance that need to be introduced in series is _________mH. (if π = )
C = 10-6 f
f = 0.5 × 103 = 500
for minimum impedance :
xL = xC
An infinitely long hollow conducting cylinder with radius R carries a uniform current along its surface. Choose the correct representation of magnetic field (B) as a function of radial distance (r) from the axis of cylinder.
Using Ampere’s law for long hollow cylinder carrying current on its surface
Bin = 0
Important Formulas Related to Physics Chapter 10 NCERT Exemplar
The following are the important formulas of Chapter 10 Wave Optics:
Path Difference for Constructive and Destructive Interference
Constructive Interference
Destructive Interference
Fringe Width in Young's Double-Slit Experiment (YDSE)
Position of Bright and Dark Fringes in YDSE
Bright fringe
Dark fringe
Diffraction by a Single Slit – Angular Width of Central Maximum
Condition for Minima in Single-Slit Diffraction
Brewster’s Law (for Polarization)
Malus’s Law (Intensity after Polarization)
JEE Mains 2022
Commonly asked questions
If the projection of is zero. Then, the value of will be________.
Projection of on is zero = 0
2 + 8 - 2 = 0=> α= 5
A freshly prepared radioactive source of half life 2 hours 30 minutes emits radiation which is 64 times the permissible safe level. The minimum time, after which it would be possible to work safely with source, will be __________hours.
t1/2 = 2hr 30 min
Radiation intensity a disintegrations / sec (Activity)
As,
For safe working,
= 15
In a Young’s double slit experiment, a laser light of 560 nm produces an interference pattern with consecutive bright fringes’ separation of 7.2 mm. Now another light is used to produce an interference pattern with consecutive bright fringes’ separation of 8.1 mm. The wavelength of second light is__________nm.
fringe width, B = 7.2 mm
For
= 630 nm
The frequencies at which the current amplitude in an LCR series circuit becomes times its maximum value, are 212 rad s-1 and 232 rad-1. The value of resistance in the circuit is R = The self inductance in the circuit is_________mH.
at = 212 rad/s
= 232 rad/s
So,
= 250 mH
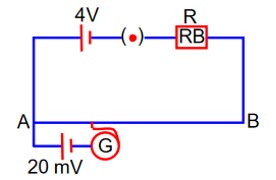
As shown in the figure, a potentiometer wire of resistance and length 300cm is connected with resistance box (R.B) and a standard cell of emf 4 V. For a resistance ‘R’ of resistance box introduced into the circuit, the null point for a cell of 20 mV is found to be 60 cm. The value of ‘R’ is __________
L = 300 cm
Null point is at 60 cm from A, so
Two electric dipoles of dipole moments 1.2 × 10-30 Cm and 2.4 × 10-3 Cm are placed in two different uniform electric fields of strengths 5 × 104 NC-1 and 15 × 104 NC-1 respectively. The ratio of maximum torque experienced by the electric dipoles will be The value of x is_______.
So,
The frequency of echo will be_________Hz if the train bellowing a whistle of frequency 320 Hz is moving with a velocity of 36 km/h towards a hill from which an echo is heard by the train driver. Velocity of sound in air is 330 m/s.
The diameter of an air bubble which was initially 2 mm, rises steadily through a solution of density 1750 kg m-3 at the rate of 0.35 cms-1. The coefficient of viscosity of the solution is_________ poise (in nearest integer). (the density of air is negligible).
d1 = 2mm = 2r
coeff of viscosity H
here,
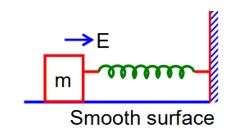
A block of mass ‘m’ (as shown in figure) moving with kinetic energy E compresses a spring through a distance 25 cm when, its speed is halved. The value of spring constant of used spring will be nE Nm-1 for n = _________.
loss in k = Gain in U spring
Four identical discs each of mass ‘M’ and diameter ‘a’ are arranged in a small plane as shown in figure. If the moment of inertia of the system about OO’ is Then, the value of x will be__________.
x=3
Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Ten Exam