physics ncert solutions class 11th
Get insights from 951 questions on physics ncert solutions class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about physics ncert solutions class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
No total mechanical energy of the body falling freely under gravity is not conserved because a small part of its energy is utilised against resistive force of air, which is non conservative force. Gain in KE< loss in PE.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Force of gravity acts on the car vertically downward while car is moving along horizontal direction. So angle between them is 90. So work done is zero.
W= fscos90=0
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) Force is applied on the body to lift it in the upward direction and displacement of the body is also in upward direction. So angle is zero.
Work done = fscos = fs
W= positive
(b) But the gravitational force in downward direction and displacement in upward direction so angle is 180. So work done will be negative. W= fscos 180= -fs
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
When the elevator is descending then electric power is required to prevent it from falling freely under gravity.
Also as the weight inside the elevator increases, its speed of descending increases, therefore there should be a limit on the number of passengers in the elevator to prevent the elevator from descending with a large velocity.
So when we increase the weight it fall with more speed . that is why there is limit in elevator.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
As the block M is at rest and frictional force =Mgsin
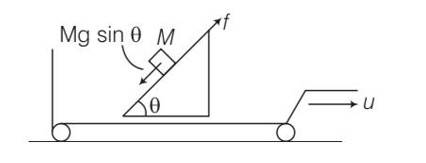
The force of friction acting between the blocks and incline opposes the tendency of sliding of the block . since block not in motion therefore no work is done. Hence no dissipation of energy.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
V= volume of ballon
density of air
density of helium
V( )g= ma= mdv/dt= upthrust
Integrating with respect to t
V( )gt=mv
½ mv2= ½ m v2/m2 ( )2g2t2
= ½v2/m ( )2g2t2
= if the ballon rises to height h then s= ut +1/2at2
h=1/2at2= ½
so from above equation
1/2mv2= [V( )g][ ]
= V( )gh
So ½ mv2+V gh= hg
KEballon+PEballon= change in PE of air
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
m =50g = 50
Side = 1cm = 0.01m
Speed v = 0.1m/s
Young's modulus= 2 2
According to the formula
F/A= Y
And F= K where K is the compression in the spring.
K= YA/L = YL
Initial KE= 2 (1/2mv2)= 5
Final PE= 2 (1/2)K ( )2
=
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Let M be the mass of the rocket at any time t and v1 the velocity of the rocket at the same time t
Let? m = mass of gas ejected in? t time
Relative speed of the gas ejected =u
KE +? t = KE of rocket +KE of gas
= ½ (M-? m) (v+? v)2 + ½? m (v-u)2
KEt= KE of rocket at time t= ½ Mv2
So? K = KEt+? t -KEt
= (M? v=? mu)v+1/2? mu2
Since action and reaction forces are equal
M? v/? t=? m/? t|u|
M? v=? m u
So? K= ½? mu2
? K=? W
? W=1/2? mu2
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) As ball 1 is rolling down without slipping there is no dissipation of energy hence, total mechanical energy is conserved. Ball 3 is having negligible friction hence, there is no loss of energy.
(b) Ball 1 acquires rotational energy, ball 2 loses energy by friction. They cannot cross at C. Ball 3 can cross over.
(c) Ball 1, 2 turn back before reaching C. Because of loss of energy, ball 2 cannot reach back to A. Ball 1 has a rotational motion in “wrong” sense when it reaches B. It cannot roll back to A, because of kinetic friction.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
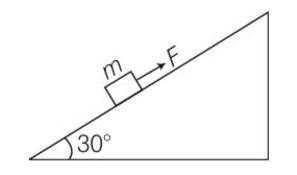
(a) work done= increase in PE
= mg (vertical distance travelled)
= mg (s)sin = 50J
(b) work done against friction = fs
=
= 0.1
(c) increase in PE =mgh
=1
(d) according to work energy theorem W= change in KE
= -mgh-fs+FS
= -50-8.66+10 (10)
= 41.34J
(e) force f = FS
= 10 (10)= 100J
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers