physics ncert solutions class 11th
Get insights from 951 questions on physics ncert solutions class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about physics ncert solutions class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The maximum allowable stress for the structure, P = Pa
Depth of the ocean, d = 3 km = 3 m
Density of water = kg/
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/s
The pressure exerted because of sea water at the depth d = = 3 Pa
= 2.94 Pa
The maximum allowable stress is more than the pressure, hence the structure is suitable.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
11.13 Mass of the copper block, m = 2.5 kg = 2.5 gm
Rise in temperature of the copper block, T = 500°C
Specific heat of the copper, C = 0.39 g–1 K–1
Heat of fusion of water, L = 335 J g–1
The maximum heat the copper block can lose, Q = mc T = 2.5 = 487500 J
Let gm be the mass of the ice, which will melt because of the copper block.
Heat gained by ice block = Q =
= g = 1455.22 gm = 1.45 kg
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Density of mercury, = 13.6 kg/
Density of wine, = 9.84 kg/
Height of the mercury column for atmospheric pressure, = 760 mm = 0.76 m
Height of the mercury column for atmospheric pressure =
From the relation, P = , since the pressure on both the system are equal
= , we get = = = 10.5 m
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
11.12 Power of the drilling machine, P = 10 kW= 10 W
Mass of the Aluminium block, m = 8.0 kg = 8 gm
Time for which the machine is used, t = 2.5 minute = 2.5 s = 150 s
Specific heat of Aluminium, c = 0.91 J/gK
Let the rise of temperature in the block after drilling be T
Total energy consumed by the drilling machine= P = 10 J = 1.5 J
It is given 50% of energy is useful.
So useful energy, = 50% of Pt= 0.5 1.5 7.5 J
We know, = mc T or T = = = 103
Therefore 2.5 minute drilli
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Mass of the girl, m = 50 kg
Diameter of the heel, d = 1.0 cm = 0.01 m, Radius of the heel, r = d/2 = 0.005m
Area of the heel, = 7.85
Force exerted by heel on the floor, F = mg = 50 N = 490 N
Pressure exerted by heel on the ground, p = F/A = 490/ (7.85 N/
= 6.24 N/
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
11.11 Coefficient of volume expansion of glycerin, = 49 /K
Rise in temperature, = 30°C
Fractional change in volume =
We can write, = = 49 = 0.0147 ……(i)
If the final volume is and initial volume is , then
=
and where & are initial and final densities
= = = fractional change in density = 0.0147 = 1.47
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
When air is blown under a paper, the velocity of air is more than the upper portion of the paper. As per Bernoulli's principle, atmospheric pressure reduces under the paper and makes it fall. To keep the paper horizontal, the air needs to be blown on the upper surface of the paper.
For a smaller opening, the flow of fluid is more than when it is bigger. When we try to close the tap with our fingers, water gushes through the small openings. Area and velocity are inversely proportional to each other.
Small opening of a syringe needle controls the velocity of the blood oozing out. At the constriction point of the syringe system, the flow ra
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The surface tension of a liquid is inversely proportional to temperature. Decreases
Most fluids offer resistance to their motion. It is like internal mechanical friction, known as viscosity. Gas viscosity increases with temperature, whereas liquid viscosity decreases with temperature. Because, intermolecular forces weaken with temperature increase, viscosity decreases.
With reference to the elastic modulus of rigidity for solids, the shearing force is proportional to the shear strain. With reference to elastic modulus of rigidity for fluids, the shearing force is proportional to the rate of shear strain.
For a steady-flowing fluid, an inc
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
11.10 Initial temperature, = 40.0°C, Final temperature, = 250°C, T = - = 210°C
Initial length of the brass rod at , = 50 cm, Initial diameter of the brass rod at , = 3 mm
Length of the steel rod
For the expansion of the brass rod, we have:
= , then = 50 = 0.21 cm
For the expansion of the steel rod, we have:
= , then = 50 = 0.126 cm
Total change in length = 0.21 + 0.126 = 0.336 cm
Since the rods are free at the end, no thermal stress developed.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
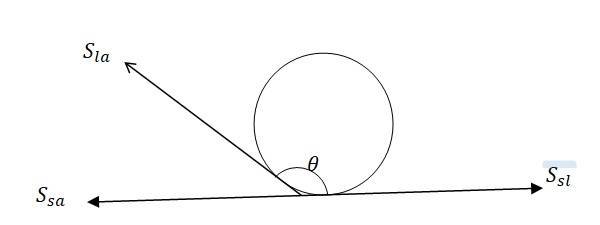
The angle between the tangent to the liquid surface at the point of contact and the surface inside the liquid is called the angle of contact ( , as shown in the diagram
= Interfacial tension between liquid-air interface
= Interfacial tension between solid -liquid interface
= Interfacial tension between solid-air interface
At the line of contact of contact, the surface forces between the three media must be in equilibrium. Hence
=
The angle of contact is obtuse, if , as in the case of mercury on glass
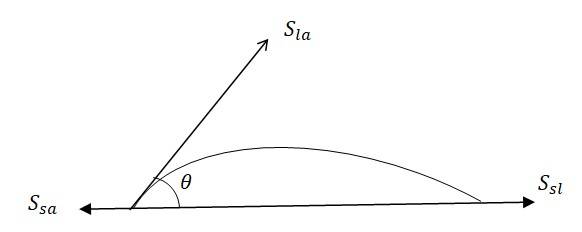
This angle is acute if , as in the case of water on glass
Mercury molecules (which mak
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
