physics ncert solutions class 11th
Get insights from 951 questions on physics ncert solutions class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about physics ncert solutions class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Radius of the uncharged drop, r = 2.0 m
Density of the uncharged drop, = 1.2 kg/
Viscosity of air, = 1.8 Pas
Density of air , can be taken as zero in order to neglect the buoyancy of air
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/
Terminal velocity, v can be written as
v = = = 0.05807 m/s = 5.8 cm/s
The viscous force on the drop is given by
F = 6 = 6 1.8 2.0 0.05807
= 3.9 N
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The area of the wing of the plane, A = 2 = 50
Speed of air over the lower wing, = 180 km/h = 50 m/s
Speed of air over the upper wing, = 234 km/h = 65 m/s
Density of air, = 1 kg/
Let us assume, pressure over the lower wing = and pressure over the upper wing =
The upward force on the plane can be obtained using Bernoulli's equation:
On lower wing= + , On upper wing = +
From equilibrium of momentum
+ = +
( - )
The net upward force = ( - = )
=&nbs
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Radius of the artery, r = 2 m
Diameter of the artery, d = 4 m
Viscosity of blood, = 2.084 Pa-s
Density of the blood, = 1.06 kg/
Reynolds's number for laminar flow, = 2000
The largest velocity is given by the relation: =
= = 0.983 m/s
Flow rate is given by the relation:
R = = 3.1416 = 1.235 /s
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Diameter of the artery, d = 2 m
Viscosity of the blood, = 2.084 Pa-s
Density of the blood, = 1.06 kg/
Reynolds's number for laminar flow, = 2000
= = = 1.966 m/s
As the fluid velocity increases, the dissipative forces become more important. This is because of the rise of turbulence. Turbulent flow causes dissipative loss in a fluid.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Gauge pressure, P = 2000 Pa
Density of whole blood, = 1.06 kg/
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/s
Let the height of the blood container = h
Pressure on the blood container P =
By equating, we get h = (2000)/ ( 1.06 = 0.1925m
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Two vessels, having the same base area, will have identical force and equal pressure acting on their common base area. Since the shapes of the two vessels are different, the force exerted on the sides of the vessels has non-zero vertical components.
When these vertical components are added, the total force on one vessel comes out to be more than on the other vessel. Hence, when these vessels are filled with water to the same height, they give different readings on the weighing scale.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
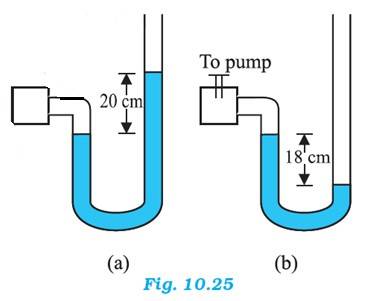
Atmospheric pressure, = 76 cm of Hg
For figure (a)
Difference between the levels of mercury in the two limbs gives gauge pressure
Hence, gauge pressure = 20 cm of Hg
Absolute pressure = Atmospheric pressure + Gauge pressure = 76 + 20 = 96 cm of Hg
For figure (b),
Difference between the levels of mercury in the two limbs gives gauge pressure
Hence, gauge pressure = - 18 cm of Hg
Absolute pressure = Atmospheric pressure + Gauge pressure = 76 - 18 = 58 cm of Hg
When 13.6 cm of water is poured into the right limb of figure (b)
Relative density of mercury = 13.6
Hence, a column of 13.6 cm of water is equivalent to 1 cm of Mercury.
Let h be
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
11.22
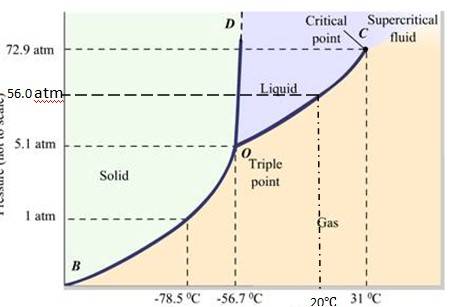
The fusion and boiling points are given by the intersection point where this parallel line cuts the fusion and vaporization curves. It departs from ideal gas behavior as pressure increases.
(a) At 1 atm pressure and at – 60 °C, it lies left of -56.6 (triple point O). Hence, it lies in the region of vapour and solid phases. Thus, CO2 condenses into solid state directly, without going through liquid phases.
(b) At 4 atm pressure, CO2 lies below 5.11 atm (triple point O). Hence it lies in the region of vaporous and solid phases. Thus, CO2 condenses into solid state directly, without going through liquid state.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Base area of the given tank, A = 1.0
Area of the hinged door, a = 20 = 20
Density of water, = kg/
Density of acid, = 1.7 kg/
Height of the water column, = 4 m
Height of the acid column, = 4 m
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/
The pressure due to Water column, = = = 3.92 Pa
The pressure due to Acid column, = = 1.7 = 6.64 Pa
Pressure difference between two columns ΔP = - = 2.774 Pa
Force exerted on the small hi
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Soap bubble radius, r = 5.0 mm = 5 m
Surface tension of the soap bubble, S = 2.50 N/m
Relative density of soap solution = 1.20, hence density of soap solution, = 1.2 Kg/
Air bubble formed at a depth, h = 40 cm = 0.4 m
1 atmospheric pressure = 1.01 Pa
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/
We know, the excess pressure inside the soap bubble is given by the relation:
P = = Pa = 20 Pa
Hence, the excess pressure inside the air bubble is given by the relation, P' = = 10 Pa
At a depth of h, the total pressure inside the air bubble = Atmospheric press
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers