physics ncert solutions class 11th
Get insights from 951 questions on physics ncert solutions class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about physics ncert solutions class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
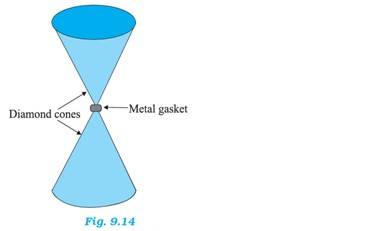
Diameter of the cone at the narrow end, d = 0.5 mm = 0.5 m
Radius, r = d/2 = 0.25 m
Area, A = = 1.96
Compressional force, F = 50000 N
Pressure at the tip of the anvil, p = F/A = 50000/1.96 Pa = 2.54 Pa
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Volume of water, V = 1 liter. If the water is compressed by 10%, then
ΔV = 0.10% of V= (0.1/100) = 1
Bulk modulus of water, k = 2.2 N/
From the relation, k = , we get ΔP = k = 2.2 1 = 2.2 N/
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Length of an edge of the solid copper cube, l = 10 cm = 0.1 m
Volume of the copper cube = 1
Hydraulic pressure, p = 7.0 Pa
Bulk modulus of copper, k = 140 Pa
From the relation k = we get = = = 5
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Hydraulic pressure exerted on glass slab, p = 10 atm = 10 Pa
Bulk modulus of glass, k = 37 N
From the relation k = , we get = = = 2.976
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Let us assume the depth = h, pressure at depth, = 80 atm = 80 Pa
Density of water at the surface, = 1.03 kg/
Let density of water at depth h be
Let be the volume at the surface and be the volume at depth h and ΔV be the change in volume. Let m be the mass of water.
ΔV = From the relation m = we get
ΔV = m ( - ) = ( - )
= 1- ……(i)
Bulk modulus of water, k = =
= …….(ii)
Bulk modulus of water, k = 2.1 Pa
Hence = 3
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Initial volume, = 100 lit = 100
Final volume, = 100.5 lit = 100.5
Increase in volume, ΔV = = 0.5
Increase in pressure, ΔP = 100 atm = 100 1.013
Bulk modulus, k = = Pa = 2.026 Pa
Bulk modulus of air = 1.0
(Bulk modulus of water / Bulk modulus of air) = (2.026 1.0 = 2.026
This higher ratio is attributed to the higher compressibility of air than water.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Mass, m = 14.5 kg
Length of the steel wire, l = 1.0 m
Angular velocity, = 2 rev/s
Cross sectional area of the wire, A = 0.065 = 0.065
Let Δl be the elongation of the wire
When the mass is placed at the position of the vertical circle, the total force on the mass is
F = mg + ml = 14.5 = 200.25 N
Young's modulus for steel, = Stress / Strain = 2 Pa
Stress = F/A = 200.25/0.065
Strain = (Δl/l) = (Δl/1) = Δl
Δl = (200.25/0.065 2 = 1.54 m
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
It is given that the tension, F in each wire is same. Since the wire is of same length, Strain also will be same.
If is the diameter of copper wire and Young's modulus of copper = 110 and strain is s, then = ,
Similarly, if is the diameter of iron wire and is the Young's modulus of iron = 190 , then =
= = = 1.314
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Area of cross-section, A = = 7.07
Maximum stress = Maximum load / cross sectional area
Maximum load = Maximum stress cross sectional area = 108 7.07 = 7.07 N
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Area of cross-section, A = 15.2 mm = 15.2
Force, F = 44500 N
Stress, F/A = (44500/ N/
Modulus of elasticity, = Stress / Strains, Strains = Stress /
For copper, = 42
Strains = (44500/ 42 = 3.65
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers