physics ncert solutions class 11th
Get insights from 951 questions on physics ncert solutions class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about physics ncert solutions class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Mass of the big structure, M = 50000 kg = 50000 = 4.9 N
Inner radius of the column, r = 30 cm = 0.3 m
Outer radius of the column, R = 60 cm = 0.6 m
Young's modulus of steel, Y = 2 Pa
Total force exerted on 4 columns, F = 4.9 N
Force exerted on single column, f = F/4 = 1.225 N
Cross sectional area of each column, A = = = 0.848
Stress in each column = f/A
Young's modulus, Y = Stress / Strain, Strain = Stress / Y = f/ (A = m
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Edge of the aluminium cube, L = 10 cm = 0.1 m, Area A = 0.01
Mass attached, m = 100 kg = 100 9.8 = 980 N = Applied force F
Shear modulus = 25 GPa = 25
Shear modulus = Shear stress / Shear strain = , = = 3.92
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
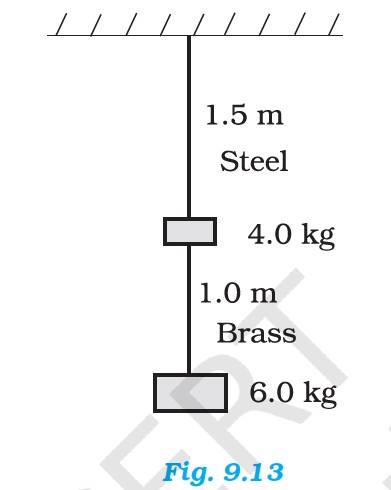
Diameter of wires, d = 0.25 cm, radius, r = 0.125 cm
Cross-sectional area, = = = 4.908
Length of the steel wire, , length of the brass wire,
Change in length of the steel wire Change in length of the copper wire
Total force exerted on the steel wire, = ( 4+6) kg = 10 kg = 98 N
Young's modulus of steel , = = 2.0 Pa
= = 1.497 m
Similarly for brass wire, = 6 kg = 58.8 N, =
= = 1.316 m
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
For a given stress, the strain in rubber is more than it is in steel, hence the Young's modulus of rubber is lesser than in steel. So the statement is False.
Shear modulus is the ratio of the applied stress to the change in the shape of a body. The stretching of a coil changes its shape. Hence, shear modulus of elasticity is involved in this process.
= 2.2
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
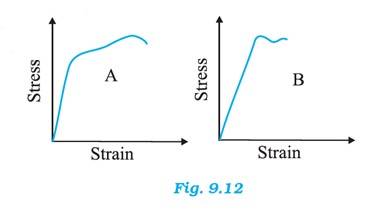
Material A has greater Young's modulus.
Material A is the strongest as it can withstand more strain than material B without fracture.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
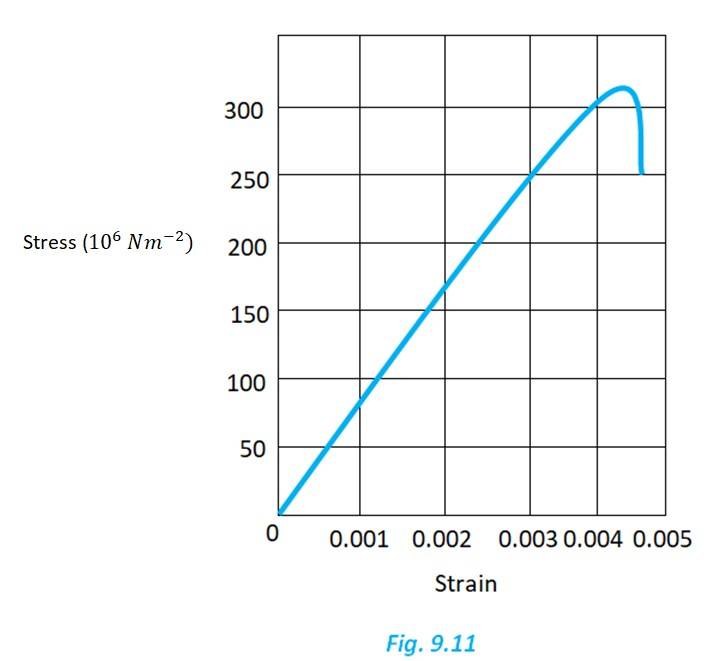
From the given graph, for the value stress 150 N/ , the strain is 0.002
Young's modulus = = 7.5 N/
Yield strength is the maxium strength the material can withstand in elastic limit. From the graph, the yield strength is 300 or 3
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Length of the steel wire, = 4.7 m
Area of cross-section of the steel wire, = 3.0 m2
Length of the copper wire, = 3.5 m
Area of cross-section of the copper wire, = 4.0 m2
Change in length,
Let the force applied = F
Young's modulus in steel wire,
= ….(1)
Young's modulus in copper wire,
= …….(2)
The ratio of Young's modulus
= = = =
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Volume of the balloon, V = 1425
Mass of the payload, m = 400 kg
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/
= 8000 m
= 0.18 kg m–3
= 1.25 kg m–3
Density of the balloon =
Height to which the balloon will rise = y
Density of air decreases with height and the relationship is given by:
= ……(i)
Differentiating equation (i), we get
, where k is the constant of proportionality
, height changes from 0 to y, while density changes from to . Integrating both sides between the limits, we get:
= -ky
= ….(ii)
From equation (i) and (ii), we get
=&nbs
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Diameter of the 1st bore, = 3 mm = 3 m
Radius of the first bore, = 1.5 mm = 1.5 m
Diameter of the 2nd bore, = 6 mm = 6 m
Radius of the 2nd bore, = 3.0 mm = 3 m
Surface tension of water, s= 7.3 N/m
Angle of contact between the bore surface and water,
Density of water, kg/
Acceleration due to gravity. g = 9.8 m/
Let and be the heights to which water rises in 1st and 2nd tubes respectively. These heights are given by the relations:
…(i)
…(ii)
The difference in level of water in the 2 li
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Radius of the narrow tube, r = 1 mm= 1 m
Surface tension of mercury at the given temperature, s= 0.465 N/m
Density of mercury kg/
Dipping depth = h
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/
Surface tension related with angle of contact and dipping depth is given by:
s = or h = = = -5.345 m= -5.345 mm
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers