physics ncert solutions class 11th
Get insights from 951 questions on physics ncert solutions class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about physics ncert solutions class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
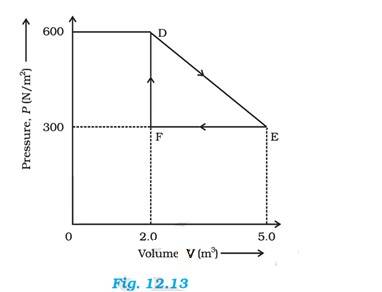
Total work done by the gas from D to E to F = Area of = EF
Where DF = Change in pressure = 600 – 300 = 300 N/
FE = change in volume = 5-2 = 3
Area of 3 = 450 J
Therefore work done by the gas from D to E to F is 450 J.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Heat is supplied to the system at a rate of 100W
Hence, heat supplied, Q = 100 J/s
The system performs at the rate of 75 J/s
Hence, work done, W = 75 J/s
From the 1st law of Thermodynamics, we have Q = U + W, where U is the internal energy
U = Q – W = 100 – 75 = 25 J/s = 25 W
Therefore the internal energy of the given electric heater increases at a rate of 25 W.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Work done by the steam engine per minute, W = 5.4 J
Heat supplied by the boiler, H = 3.6 J
Efficiency of the engine, = = = 0.15
Amount of heat wasted = Input energy – Output energy
= 3.6 5.4 J
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a) When the stopcock is opened, the volume became double between cylinders A and B. Since volume is inversely proportional to pressure, the pressure will become half. So the initial pressure of 1 atm in cylinder A will become ½ atm in cylinder A and B.
(b) The internal energy will change when there is work done by the gas. In absence of any work done, there will be no change in internal energy.
(c) In absence of any work done, there will be no change in the temperature.
(d) The given process is a case of free expansion. It is rapid and cannot be controlled. The intermediate states do not satisfy the gas equation an
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The work done, W = 22.3 J
Being an adiabatic process, Q = 0
W = -22.3 J : since the work is done on the system
From the 1st law of thermodynamics, we know Q = W, where is the change of internal energy of the gas
U = 22.3 J
When the gas goes from state A to state B via a process, the net heat absorbed by the system is:
Q = 9.35 cal = 9.35 J = 39.1765 J
Heat absorbed Q = W
W = Q - = 39.1765 – 22.3 = 16.8765 J
Therefore, work done by the system is 16.8765 J
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The cylinder is completely insulated from its surroundings. As a result, no heat is exchanged between the system (cylinder) and its surroundings. Thus the process is 'Adiabatic'.
Let the initial and final pressure inside the cylinder be & and volume be & .
Ratio of specific heat, = 1.4
For an adiabatic process, we know =
It is given
Hence = or = ( ( = = = 2.639
Hence the pressure increases by a factor of 2.639
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a) When the two bodies at different temperatures brought in contact, heat flows from the body of higher temperature to the body with lower temperature till the thermal equilibrium is achieved and both the body attains the temperature of (T1 + T2 )/2. But only when the thermal capacities of both the bodies are equal.
(b) The coolant used in Chemical or in Nuclear plant should have high specific heat. Higher specific heat allows coolant to absorb more heat.
(c) In motion, the air temperature inside the tyre increases due to the motion of the air molecules. According to Charles's law, temperature is directly proportional to
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Mass of Nitrogen, m = 2.0 * kg = 20 g
Rise in temperature, = 45 °C
Molecular mass of . M = 28
Universal gas constant, R = 8.3 J mol–1 K–1
Number of moles, n = = = 0.714
Molar specific heat at constant pressure for nitrogen, = R = 29.05 J/mol/K
The total amount of heat to be supplied is given by the relation
Q = n = 0.714 = 933.38 J
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Initial temperature, = 27 °C
Final temperature, = 77 °C
Rise in temperature,
Heat of combustion = 4.0 * J/g
Specific heat of water, c = 4.21 J/g/
Mass of flowing water, m = 3 lit/min = 3000 g/min
Total heat used, = 3000 = 6.315 J/min
Rate of consumption = g/min = 15.79 g/min
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The displacement equation for an oscillating mass is given by : x = Acos ( , where
A = the amplitude
x = the displacement
Velocity, V = = -A t +
At t = 0, x = , = ….(i)
And = = A …….(ii)
Squaring and adding, we get
, A =
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers