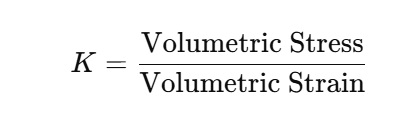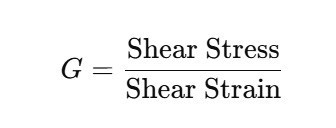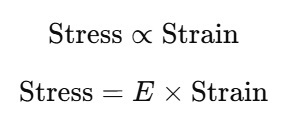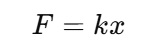Physics Spl
Get insights from 6.8k questions on Physics Spl, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics Spl
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
Mock Exam Resources available on the websites mentioned below:
- MSOMI BORA: Free mock exams for Form Four students
- Free KCSE Past Papers: KCSE past papers and mock exams
- AQA, Revision World, Skolatis: Past papers and resources for GCSE, iGCSE, and A-Level exams
These resources can help with exam preparation.
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
Poisson's Ratio (? ) is used when a material is subjected to axial stress. It is the ratio of lateral strain to longitudinal strain. Mathematically, it is:
Derivation of the Poisson Ratio includes when a material is stretched, its width decreases (called lateral strain) and its length increases which is called longitudinal strain.
Poisson's Ratio (? ) is a dimensionless quantity and it is normally between a range of 0 to 0.5 for most materials. It is used in engineering applications including for bridge and building design. It is used in analyzing the structural deformations. Materials like rubber which has a high Poisson's ratio when s
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
According to the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids, when an external force is applied to a solid, the solid undergoes changes in shape or size which is called deformation. The solid deformation can be classified into:
Elastic Deformation: It is when the body returns to its original size and shape after the force is removed. It occurs within the elastic limit and follows Hooke's law. The most common examples include stretching a helical spring or a rubber band.
Plastic Deformation: It occurs beyond the elastic limit and here after the removal of the force, the body does not return to its origin
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
The modulus of elasticity refers to the material's capacity to withstand or resist deformation when stress is applied. There are three types of the modulus of elasticity including:
Young's Modulus (E): It is used to measure a solid's elasticity when longitudinal stress (tensile or compressive) is applied to it. Mathematically, it is represented by the following formula;
SI Unit is N/m² (Pascal, Pa).
Bulk Modulus (K): It is used to measure the ability of the material to resist volume change when uniform pressure is applied to it. Mathematically, it is:
Shear Modulus (G) or Modulus of Rigidity: It is used when a shear
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 6
Candidates must check their target university's subject mapping criteria to decide which subject to map with CUET Physics. However, the common CUET subject combinations for CUET Physics include:
- Mathematics
- Chemistry
- Biology
- Computer Science
- Environmental Science
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 6
The difficulty level for CUET Physics exam is uaully considered moderate to high. The question paper my include questions that require candidates to use their analytical thinking skills. Additionally, calculation-based questions might be time consuming making it hard for candidates to complete their exam on time.
New answer posted
10 months agoBeginner-Level 5
The CUET Physics Paper consists of 50 questions and the candidates are required to attempt all questions within 60 minute time frame. Each correct answer carries 5 marks, and 1 mark is deducted for incorrect responses. Candidates taking the exam must ensure to manage their time effectively.
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
The chapter consists of fundamental topics that are important for board exams preparation as well as for competitive tests:
Composition and Size of the Nucleus: Understanding protons, neutrons, and nuclear density.
Nuclear Force: The forces that hold the nucleus together.
Mass-Energy Equivalence (E = mc²): Einstein's equation and its significance in nuclear reactions.
Nuclear Binding Energy: Understanding nuclear stability and energy release.
Radioactivity: Concepts of alpha, beta, and gamma decay.
Laws of Radioactive Decay: Half-life, mean life, and decay constant derivations.
Nuclear Fission and Fusion: Their
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
Hooke's Law states that within the elastic limit, the stress applied to a material is directly proportional to the strain produced. Mathematically,
E stands for the modulus of elasticity also called Young's modulus in case of linear deformation.
The Hooke's Law defines the elastic behaviour of materials, determines its elastic limit and helps in material selection for construction and manufacturing. It is used to design springs and elastic components in machines. Hook's law is applicable for the solids within their elastic limit.
Hooke's law for a spring and other elastic material is shown as:
F is the force applied on the mat
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
Students can download the Class 12 Physics Chapter 13 Nuclei NCERT Solutions PDF from various online platforms or they can visit the Shiksha homepage.
These PDFs are useful for students who want to study anywhere even if there is no internet access, which makes it easier to practice important numerical problems related to decay laws, nuclear binding energy, and nuclear reactions. To get access to NCERT Solutions PDF Class 12 Physics Chapter 13 Nuclei students mucst click on the following link.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers