Physics
Get insights from 5.6k questions on Physics, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.11 Length of the narrow bore, L = 1 m = 100 cm
Length of the mercury thread, l = 76 cm
Length of the air column between mercury and the closed end, = 15 cm
Since the bore is held vertically in air with the open end at the bottom, the mercury length that occupies the air space is 100 – (76 + 15) = 9 cm
Hence, total length of the air column = 15 + 9 = 24 cm
Let h cm of mercury flow out as a result of atmospheric pressure.
Length of the air column in the bore = 24 + h cm
Length of the mercury column = 76 – h cm
Initial pressure, = 76 cm of mercury
Initial volume, = 15
Final pressure, = 76 – (76 – h) = h cm
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.10 Pressure inside the cylinder containing nitrogen, P = 2.0 atm = 2 Pa
Temperature inside the cylinder, T = 17
Radius of nitrogen molecule, r = 1.0 Å = 1 m
Diameter of nitrogen molecule, d = 2 m
Molecular mass of nitrogen molecule, M = 28 u = 28 g (assume) = 28 kg
The root means square speed of nitrogen is given by the relation
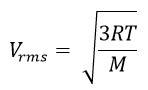
R is the universal gas constant = 8.314 J/mole/K
Hence
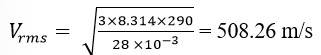
The mean free path is given by
where k = Boltzmann constant = 1.38 kg-
= 1.11 m
Collision frequency = = = 4.57 /s
Collision time, T = =S= 3.93 s
T
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.9 Temperature of the helium atom, = – 20 °C = 253 K and temperature of argon atom be =
Atomic mass of helium, = 4.0 u
Atomic mass of Argon, = 39.9 u
Let be the rms speed of Argon and be the rms speed of Helium
From the relation of we get
rms speed of Argon,
rms speed of Helium,
Since both the speeds are equal, we get
= or = or = = = 2523.675 K = 2.523 K
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Diffraction leads to the formation of patterns of varying intensity. When around obstacles, waves bend and spread through the narrow opening, it is called diffraction. The interference results in a new wave pattern and involves the superposition of two or more coherent waves. Both these phenomena produce patterns of light and dark regions; the interference results from the combination of multiple waves and the diffraction arises from a single wave interacting with an aperture or obstacle. When the size of the aperture or obstacle is comparable to the wavelength of the wave, diffraction patterns are typically observed.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.8 (a) According to Avogadro's law, the three vessels will contain an equal number of the respective molecules. This number is equal to Avogadro's number, N = 6.023
(b) The root mean square speed ( of a gas of mass m and temperature T is given by the relation . Where k is Boltzmann constant. For the given gases, k and T are constants. Hence depends only on the mass of the atoms ![]()
Therefore, the root mean square speed of the molecules in the three cases is not the same. Among Neon, Chlorine and Uranium hexafluoride, the mass of the neon is the smallest, so Neon will have the highest root mean square sp
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
A coherent light source in Young's Double Slit Experiment illuminates two closely spaced slits, and produces two overlapping light waves. The interference of these waves constructively or destructively based on their phase difference lead to a pattern of bright and dark fringes on a screen, When the path difference is an integral multiple of the wavelength, it is constructive interference (bright fringes) and when the path difference is an odd multiple of half the wavelength, it is destructive interference (dark fringes). Through observable interference patterns, Young's Double Slit Experiment, shows the wave nature of light.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.7 (i) At room temperature, T = 27 = 300 K
is Boltzmann constant = 1.38
Average thermal energy = = = 6.21 J
Hence, the average thermal energy of a helium atom at room temperature is 6.21 J
(ii) On the surface of the Sun, T = 6000 K
Hence average thermal energy = = = 1.242 J
Hence, the average thermal energy of a helium atom on the surface of the Sun is 1.242 J
(iii) Inside the core of a star, T = K
Hence average thermal energy = = = 2.07 J
Hence, the average thermal energy of a helium atom
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.21:
(a) Velocity , = 10.0 ? m/s
Acceleration, = (8.0 ? + 2.0 ?) m s-2
We know = = 8.0 ? + 2.0 ?
= (8.0 ? + 2.0 ?)dt
Integrating both sides we get (t) = 8.0t ? + 2.0t ? + ,
Where, velocity vector of the particle at t =0
velocity vector of the particle at time t
But =
= dt
= (8.0t ? + 2.0t ? + )dt
Integrating both sides with the condition at t = 0, r =0 and at t =t, r = r
t + ½ 8.0 t2 ? + ½ 2.0 t2 ? = t + 4.0 t2 ? + t2 ?
Substituting the value of , we g
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.6 Volume of the room, V = 25.0
Temperature of the room, T = 27 = 300 K
Pressure of the room, P = 1 atm = 1 1.013 Pa
The ideal gas equation relating to pressure (P), volume (V) and absolute temperature (T) can be written as
PV = NT, where is Boltzmann constant = 1.38
N is the number of air molecules in the room.
N = = = 6.117
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
According to Chapter 10 Physics Class 12, the Huygens' Principle in wave optics states that every point on a wave front spreads out in all directions at the speed of the wave, and these act as a source of secondary wavelets. According to this principle, all new wave front is the tangent to these secondary wavelets. The principle holds significance when it comes to explaining phenomena like refraction and reflection of light. It is instrumental in understanding the behavior of light in various media and provides a geometric method to determine the propagation of wave fronts. The Huygens' Principle lays the foundation for the wave theory
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 684k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
