Physics
Get insights from 5.6k questions on Physics, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New question posted
8 months agoNew answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
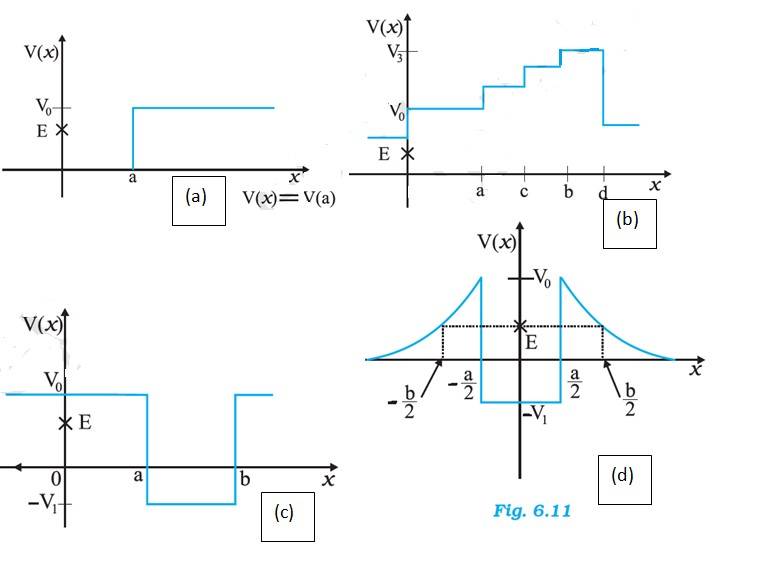
6.3 We know the total energy E is given by E = Kinetic energy (KE) + Potential energy (PE)
(a) In figure (a), we have at x=0, the potential energy is zero. So KE is positive. At x>a, the potential energy has a value greater than E, so the KE becomes 0. Thus the particle will not exist in the region x>a. Minimum total energy is zero.
(b) For the entire x-axis, PE >E, the KE of the object would be negative. Thus the particle will not exist in this region.
(c) In x=0 to x=a and x>b, PE is greater than E, so he KE has to be negative. The object cannot exist in this region.
(d) For x=-b/2 to x =-a/2 and x=a/2 to x=b/2, KE
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
6.2 Given, mass of the body, m = 2 kg
Horizontal force applied, F = 7 N
Coefficient of friction, = 0.1
Acceleration, a = F/m = 7/2 = 3.5 m/s2
Frictional force, f = 0.1 1.96 N
Retardation produced by the frictional force, = -f/m = -1.96 /2 = 0.98 m/s2
The net acceleration by which the body moves forward
= a - = 3.5 – 0.98 = 2.52 m/s2
Distance moved by the body in 10 s is given by
s = ut + (1/2) = 0 = 126 m
(a) Work done in 10 s is given by
W = Force
(b) Work done by friction in 10 s is given by
W = -f - 247J
(c) Work done by the net force
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
6.1 (a) While the person lifts a bucket out of a well by means of a rope tied to the bucket, the direction of both the force and the displacement are same, hence the work done is positive.
(b) While lifting the bucket, he works against gravity, but the work done by the gravitational force is downward, hence the work done is negative.
(c) The direction of motion of the object is in the opposite direction of the frictional force; hence the work done is negative.
(d) While a body moves on a rough horizontal plane, the frictional forces try to oppose the motion. But since the applied force maintains uniform velocity
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.25
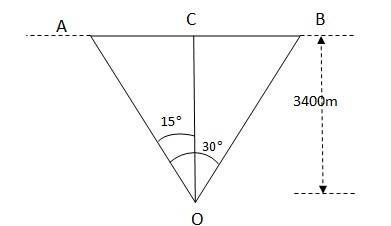
Height of the aircraft from the ground = 3400m
Let A and B be the positions of the aircraft, making an angle of AOB = 30 . The perpendicular OC and OC is the height of the aircraft. Angles AOC = angle BOC = 15
In AOC, AC = OC
= 3400 = 911.03m
AB = AC + CB = 2AC = 1822m
The distance of AB is covered in 10s, so the speed of the aircraft = 1822/10 m/s = 182.2 m/s
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.24
(a) Despite being a scalar quantity, energy is not conserved in elastic collisions. False
(b) Despite being a scalar quantity, the temperature can take negative values. False
(c) The total path length is a scalar quantity. Yet it has the dimension of length. False
(d) A scalar quantity such as gravitational potential can vary from one point to another point in space. False
(e) The value of a scalar does not vary for observers with different orientation of axis. True
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.23
(a) For any arbitrary motion of a particle average velocity cannot be expressed by this equation. False
(b) The arbitrary motion of the particle can be represented by this equation, True
(c) For arbitrary motion of the particle, the acceleration may also be non uniform. False
(d) The motion of the particle is arbitrary, acceleration of the particle may also be non-uniform, so can not represent the motion of the particle in space. False
(e) The arbitrary motion of the particle can be represented by the given equation. True
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.14 Let the atomic mass of a substance be = M and the density of the substance be =
Avogadro's number, N = 6.023
Volume of N number of molecules = ……. (i)
Volume of one mole of a substance = …… (ii)
Equating (i) and (ii), we get

New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.13 According to law of atmospheres, we have
n2 = n1 exp [ -mg (h2 – h1)/ kBT] ….(i)
where is the number of density at height and is the number of density at height
mg is the weight of the particle suspended in the gas column
Density of the medium =
Density of the suspended particle =
Mass of one suspended particle = m'
Mass of medium displaced = m
Volume of the suspended particle = V
According to Archimedes's principle for a particle suspended in a liquid column, the effective weight of the suspended particle is given as:
Weight of the medium displaced – weight of the suspended particle = mg – m'g
= mg- V = mg –
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.12 Rate of diffusion of hydrogen, = 28.7 cm3 s–1
Rate of diffusion of another gas, = 7.2 cm3 s–1
According to Graham's law of diffusion, we have:
= , where = molecular mass of hydrogen = 2.02 g and is the molecular mass of the unknown gas
= 2.02= 32.09 = Molecular mass of Oxygen
Hence, the unknown gas is Oxygen.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 684k Reviews
- 1800k Answers