Semiconductor Electronics
Get insights from 56 questions on Semiconductor Electronics, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Semiconductor Electronics
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
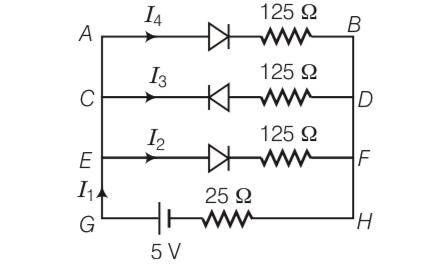
forward biased resistance = 25ohm
Reverse biased resistance = infinity
As CD branch is reverse biased having infinite resistance.
So I3= 0
Resistance in branch AB= 25+125= 150 ohm (R1)
Resistance in branch EF= 25+125= 150 ohm (R2)
They both are in parallel
So
R= 75ohm
So total resistance = 25+75= 100ohm
Current = V/R= 5/100=0.05A
I1=I2+I3+I4
I1=I4+I2
Here the resistance R1 and R2 is same
I4=I2
I1= 2I2
I2= I1/2=0.05/2=0.025A
I4= 0.025A
New question posted
9 months agoNew question posted
9 months agoNew answer posted
10 months agoBeginner-Level 5
As per the NCERT Textbooks
“An integrated Chip consists of many passive and active components fabricated on a single chip of silicon. these ICs are compact, low-cost, and highly reliable. They consume less power and have high speed.”
These ICs are used in majority of our daily use electronics and all advance electronics.
New answer posted
10 months agoBeginner-Level 5
A p-type semiconductor is electrically neutral despite having more holes, because the number of positively charged holes is exactly balanced/equal by the number of negatively charged acceptor ions introduced during doping. so practically untill any volatage is applied the semiconductor remains chargeless in other words doesn't produce any current even after doping.
As per the NCERT Textbooks information"Although the number of holes is more than the number of electrons in a p-type semiconductor, the material as a whole is electrically neutral because the charge of holes is balanced by the negatively charged acceptor ions.”
New answer posted
10 months agoBeginner-Level 5
As per NCERT Textbboks"If forward current is too large, it can produce large heating and damage the junction. So, a resistor is used in series with the diode to limit the current in the circuit.”
It means when a semiconductor diode is connected to a source under high current it causes excess heat due to more electrical energy. This excess heat is responsible to damage the junction in semiconductor diode permanently. Student can check out NCERT Solutions for Semicondutor Electronics of class 12 physics.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 687k Reviews
- 1800k Answers