Amines
Get insights from 72 questions on Amines, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Amines
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) CH3CH2CH2NH2 + HCl → CH3CH2CH2N+H3Cl-
The final product is (N-propyl ammonium chloride.)
(ii) (C2H5)3N + HCl → (C2H5)3N+HCl-
The final product is (Tri ethyl ammonium chloride)
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
1- Alkyl group contribute inductive effect which increases the basic strength of
NH3
Then C6H5NH2 is having –I effect that reduces strength. And C6H5CH2NH2 increases the basic strength but not as much as C2H5 group.
Hence final order will be C6H5NH2<
2- By taking into consideration –R effect and steric hindrance of groups we can arrange them in the order
C6H5NH2< C2H5NH2< (C2H5)3N< (C2H5)2NH.
Because (C2H5)3N has a lot of steric hindrances that reduces the basic strength.
3- In C6H5NH2, N is directly attached to the ring that causes delocalization of electrons of the benzene ring. Whereas in case of C6H5CH2NH2 it is not directly connected to benze
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
Benzene into aniline
When Benzene is treated with HNO3/H2SO4 it forms nitrobenzene. When Nitrobenzene reduced with Sn/HCL it forms Aniline because Sn/HCl is a reducing Mixture.
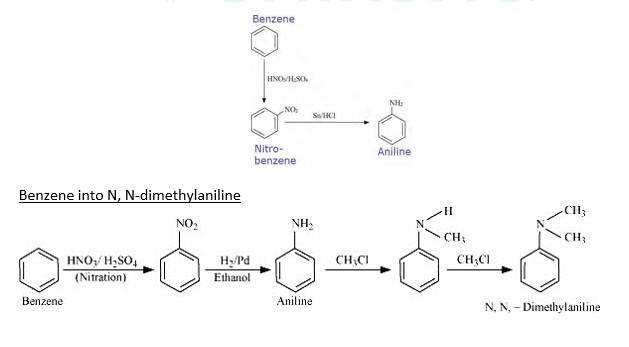
When Benzene is reacted with nitrating mixture it forms nitrobenzene. When it Reduced H2/Pd in ethanol or Sn/HCl, it forms Aniline. When Aniline reacts 2 times with CH3Cl It forms N, N- dimethylaniline.
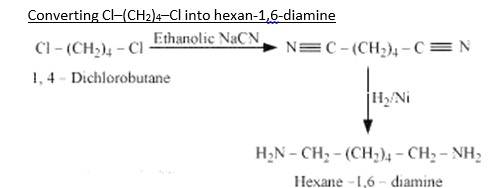
When 1,4-dichlorobutane reacts with NaCN it forms Di cyanide compound, After Hydrogenation it forms the Hexane 1,6-Diamine.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) & (ii) There are total 8 geometrical isomers of the given compound.
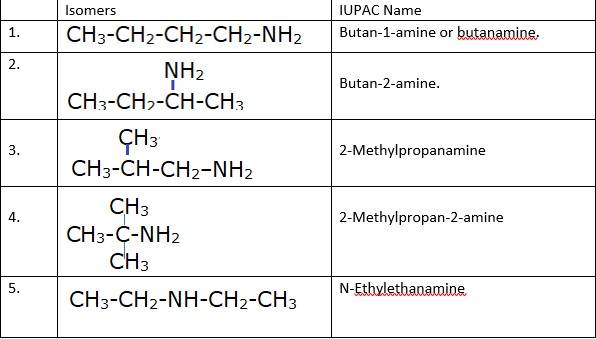
(iii) a) Pairs 1,2,6,7 Exhibit Position isomerism; means the change in position of the substituent.
b) Pairs 1,3 and 1,4 and 2,3 and 2,4 exhibit chain isomerism i.e. in this type of isomerism the different structures can be produced by changing the chain of the
c) Pairs 5,6 and 5,7 exhibit metamerism; e. different group on either side of the central atom.
d) All Primary amines exhibit functional isomers. All secondary amines share functional isomerism and same for The functional isomerism means same functional group.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
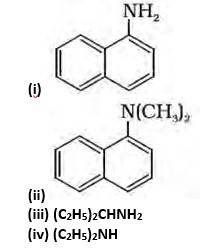
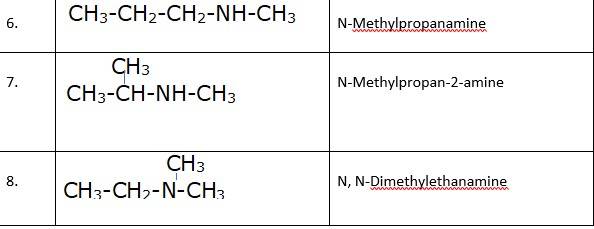
(ii) Tertiary, because the Nitrogen atom is attached to the 3 carbon atoms.
(iii) Primary, because the nitrogen atom is attached to the only 1 carbon atom.
(iv) Secondary, because the nitrogen atom is attached to the only 1 carbon.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 7
NCERT Class 12 Chemistry Amines intext solutions are mentioned in the class textbook.
New answer posted
6 months agoBeginner-Level 1
In the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry board exams, Chapter 9: Amines typically carries a weightage of 6 marks.
New answer posted
6 months agoBeginner-Level 5
Diazonium salts are formed by treating primary aromatic amines (such as aniline) with nitrous acid (generated in situ from NaNO? and HCl) at low temperatures (0–5°C). A common example is benzene diazonium chloride (C? H? N? Cl? ). Diazonium salts contain the functional group –N? X? , where X? is typically a halide like Cl? or Br?
These salts are important because they are highly reactive intermediates used in various chemical processes, Check below;
Azo dye synthesis (via coupling reactions)
Replacement reactions to introduce functional groups like –OH, –CN, –X (halides)
Various organic conversions in synthetic chemistry (vita
New answer posted
6 months agoBeginner-Level 5
Amines are prepared by replacing the hydrogen atom with alkyl or aryl groups from amonia (NH? ). Students can differntiate Aliphatic and aromatic amines differ based on the type of group attached to the nitrogen atom.
- Aliphatic amines have one or more alkyl groups (like methyl or ethyl) bonded to the nitrogen, such as ethylamine (CH? NH? ).
- Aromatic amines have an aryl group (like benzene) directly bonded to nitrogen, for example, aniline (C? H? NH? ).
Aliphatic amines are generally more basic than aromatic amines because, in aromatic amines, the lone pair on nitrogen is delocalized into the aromatic ring through resonanc
New answer posted
6 months agoBeginner-Level 5
Chapter 9 Amines of class 12 chemistry is really important part of organic chemistry. Several questions are asked related to Amine preparation methods in CBSE Boards and other state board exams. Here are several methods to prepare Amine in labs, check below;
Reduction of nitro compounds, nitriles, and amides
Ammonolysis of alkyl halides
Gabriel Phthalimide synthesis
Hoffmann bromamide degradation
Students can check the ncert solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Amines, to better understand the question types and concepts asked in the exams.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 65k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers