Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Four
Get insights from 97 questions on Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Four, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Four
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Given: Order of the reaction = 0
We know that a zero order reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs regardless of the reactant's concentration.
The rate law of 2A + B→C is
r = k [A]0 [B]0
For a zero- order reaction
r = k
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
A bimolecular reaction occurs when two particles collide. The product of the concentrations of both elements determines the rate of reaction. If one of the reactants is taken in substantial excess in such a way that its concentration seldom changes, a bimolecular reaction can be kinetically first order.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Tell us about the pseudo-first-order reaction. It's the reaction with the highest true rate law, yet it behaves like a first order reaction, but it's more specifically a second order reaction.
As an example, consider the hydrolysis of an ester.
CH3COOC2CH5 + H2O→CH3COOH + C2H5OH
rate = k [CH3COOC2H5] [H2O]… (constant)
k1 [CH3COOC2H5]
k = k [H2O]
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Average rate depends upon the change in concentration of reactants or products and the time taken for that change to occur. However, the average rate cannot be used to predict the rate of reaction at a particular instance as it would be constant for the time interval for which it is calculated.
So, to express the rate at a particular moment of time we determine the instantaneous rate. Itis obtained when we consider the average rate at the smallest time interval say dt (i.e. when? t approaches zero).
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Catalyst action is a complicated concept. A catalyst aids in the formation of temporary bonds during a chemical reaction. The objective of a catalyst is to lowers the activation energy. A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change. The action of the catalyst can be explained by intermediate complex theory. According to this theory, a catalyst participates in a chemical reaction by forming temporary bonds with the reactants resulting in an intermediate complex. This has transitory existe
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans:
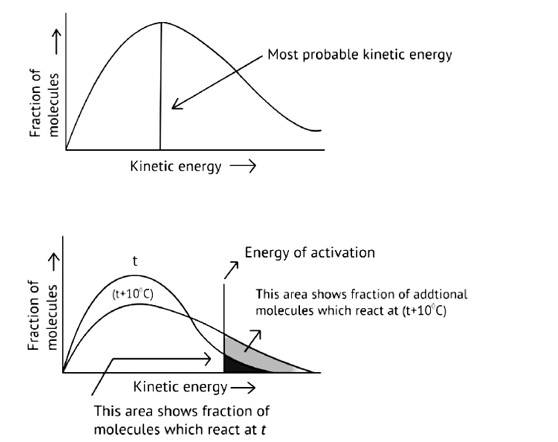
As illustrated in the graph, as the temperature rises, the peak pushes ahead, increasing probable kinetic energy while decreasing the number of molecules utilizing it, resulting in a faster rate of reaction.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The reaction rate in collision theory is determined by two factors: energy and orientation factor. Certain reactions can be highly exothermic and energetically favoured, meaning the reactants have enough activation energy to collide effectively. However, they do not proceed at a fixed temperature, which is why the reactant molecules are not orientated properly during collisions, resulting in atoms of reactant molecules combining to produce products that do not face each other.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
