Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Four
Get insights from 97 questions on Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Four, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Four
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Assertion and Reason Type as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: E
The claim is erroneous, but the reason is right, because the correct assertion is that effective collision leads to the production of a product, and the reason states that the conditions of collision theory must be met for the reaction to be completed.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Assertion and Reason Type as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: A
Both the assertion and the reason are valid, and the reason is a correct of the assertion since the enthalpy of reaction is the difference between the total enthalpy of the reactants and products in the presence of a catalys
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Assertion and Reason Type as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: E
The order and molecularity may or may not be the same, assertion is false, but reason is right. The sum of the power of the reactants is the order of reaction, which may be easily determined. The total of the stoichiometric coefficient of the rate-determining elementary step determines molecularity
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Assertion and Reason Type as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: B
Both assertion and reason are valid, but reason does not explain assertion because the order of reaction can be zero or even fractional because the order of reaction is proportional to the total of the power of the reactants.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Matching Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i)- (b) ; (ii)- (a) ; (iii)- (d); (iv)- (c)
The rate rule was discovered experimentally and can be used to predict the reaction rate and reactant concentrations.
The rate constant is the proportionality constant that describes the relationship between the molar concentration of the reactants and the rate of a chemical reaction.
The rate constant (k) of a reaction is proportional to its temperature, i.e., for a given reaction at a given temperature, the rate constant (k) is constant.
The order of a reaction is a quantity that has been empirically determined. As a result
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Matching Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
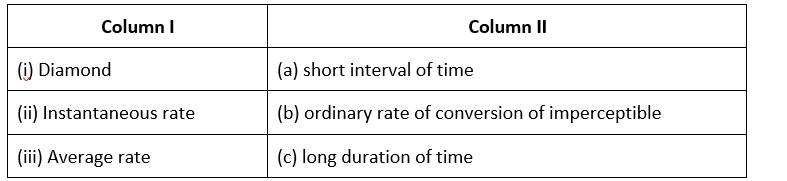
(i)- (b) ; (ii)- (c) ; (iii)- (a)
The rate of conversion in diamond is normally imperceptible.
Long-term rate at a moment's notice
The average rate is only for a short time.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Matching Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i)- (c) ; (ii)- (a) ; (iii)- (d); (iv)- (f); (v)- (b); (vi)- (b)
A catalyst can influence the rate of a process by lowering the activation energy
When it comes to molecularity, there can't be a fraction or a zero.
The second half life of a first order reaction is the same as the first.
Activation energy refers to the percentage of molecules with an energy equal to or greater than activation energy.
Correct orientation is not always present when it comes to energetically favourable activities.
Because the area under the Maxwell Boltzmann curve is constant, the total probability
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Matching Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
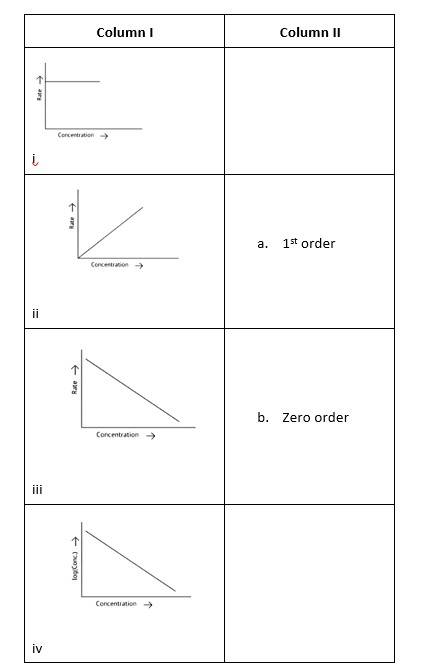
(i)- (a) ; (ii)- (b) ; (iii)- (b); (iv)- (a)
A zero-order reaction is one in which the reactant concentrations do not change over time and the rate of concentration remains constant.
A first-order reaction is one in which the rate of the reaction is linearly proportional to the concentration of only one ingredient. In other terms, a first-order reaction is a chemical reaction whose rate is determined by changes in only one of the reactants' concentration.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct options: A and D
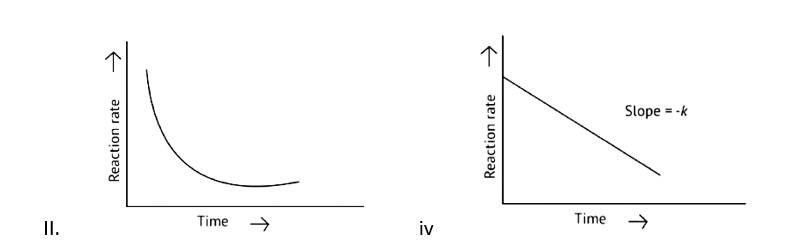
The pace of a reaction that is directly proportional to the concentration of the reacting substance is known as a first order reaction.

Y=mn
k = log
t = log
x= a-
x=
t = log
log2
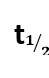
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct options: A and D
A Zero order reaction = [R] = ( - k)t + [R]0
y = (m * ) + c
x = t (time)
y = [R]concentration
Slope (m) = - k
Intercept (c) = [R]0
= - k
= - kto
Rate ∝ t0
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers