Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Four
Get insights from 97 questions on Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Four, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Four
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
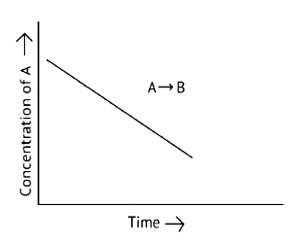
A. The reaction has a zero order. The concentration of the reactants does not change with time in a zero order reaction, and the rate of concentration remains constant
B. Slope of the curve is - k
C. The rate constant's units are molL 1s - 1
New question posted
6 months agoNew answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The concentration of the reactants does not change with time in a zero -order reaction, and the rate of concentration remains constant. The molecularity of a reaction cannot be 0 because it indicates the number of reactants involved.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
When the Threshold energy is less than the energy of the molecules and the orientation of the molecules is proper for the effective collision, the reaction happens. As a result, the reaction is slow, and the number of effective collisions is reduced
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The number of ions or atoms that collide to react is known as molecularity in an elementary reaction. The order of reaction about B should be 1 if this is an elementary reaction, however the rate law given is
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The concentration of the reactants does not change with time in a zero- order reaction, and the rate of concentration remains constant.
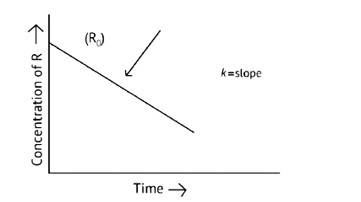
R= [R]0 – Kt
Kt = [R]0
t =
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The concentration of the reactants does not change with time in a zero- order reaction, and the rate of concentration remains constant.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Let order of reaction be = n
rate = k [A]n- (i)
27r = k [3A]n- (ii)
Divide (ii) by (i)
= k [3A]nn
3n = 27
n = 3
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The order and molecularity of elementary reactions are the same. As a result of a single collision between two molecules or ions, a complicated process occurs. A reaction mechanism is a set of elementary reactions.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Experimentally, the reaction's rate law can be calculated.
Step 1
2NO (g) + O2 (g)→2NO2 (g)
O2 (g) is taken in excess
x molecules of NO number reacting with excess of O2
r = k [NO]x
Step 2
2NO (g) + O2 (g)→2NO2 (g)
When 2No (g)is taken in excess
Y molecules of O2 reacting with excess of [NO]
rate = k [O2]y
rate = k [NO]x [NO]y
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers