- Chemical Kinetics Question and Answers
- Chemical Kinetics
- JEE Mains 2022
- NEET 2022
Chemical Kinetics Question and Answers
| 1. All energetically effective collisions do not result in a chemical change. Explain with the help of an example. |
| Ans: The reaction rate in collision theory is determined by two factors: energy and orientation factor. Certain reactions can be highly exothermic and energetically favoured, meaning the reactants have enough activation energy to collide effectively. However, they do not proceed at a fixed temperature, which is why the reactant molecules are not orientated properly during collisions, resulting in atoms of reactant molecules combining to produce products that do not face each other. |
| 2. What happens to most probable kinetic energy and the energy of activation with increase in temperature? |
| Ans:
|
| 3. Describe how the enthalpy of reaction remains unchanged when a catalyst is used in the reaction. |
| Ans: Catalyst action is a complicated concept. A catalyst aids in the formation of temporary bonds during a chemical reaction. The objective of a catalyst is to lowers the activation energy. A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change. The action of the catalyst can be explained by intermediate complex theory. According to this theory, a catalyst participates in a chemical reaction by forming temporary bonds with the reactants resulting in an intermediate complex. This has transitory existence and decomposes to yield products and the catalyst. A small amount of the catalyst can catalyst a large number of reactants. A catalyst does not alter Gibbs energy, ΔG of a reaction. The difference in energy between reactants and products is constant. It is also found that a catalyst does not change the equilibrium constant of a reaction rather, it helps in attaining the equilibrium faster, that is, it catalyses the forward as well as the backward reactions to the same extent so that the equilibrium state remains the same enthalpy of reaction means the difference in energy between reactant and product it will also remain unchanged. |
| 4. Explain the difference between instantaneous rate of a reaction and average rate of a reaction. |
| Ans: Average rate depends upon the change in concentration of reactants or products and the time taken for that change to occur. However, the average rate cannot be used to predict the rate of reaction at a particular instance as it would be constant for the time interval for which it is calculated. So, to express the rate at a particular moment of time we determine the instantaneous rate. Itis obtained when we consider the average rate at the smallest time interval say dt (i.e. when △t approaches zero).
|
| 5. With the help of an example explain what is meant by pseudo first order reaction. |
| Ans: Tell us about the pseudo-first-order reaction. It's the reaction with the highest true rate law, yet it behaves like a first order reaction, but it's more specifically a second order reaction. As an example, consider the hydrolysis of an ester. CH3COOC2CH5 + H2O→CH3COOH + C2H5OH rate = k[CH3COOC2H5][H2O]…(constant) k1[CH3COOC2H5] k = k[H2O] |
Commonly asked questions
Assertion: All collision of reactant molecules leads to product formation.
Reason: Only those collisions in which molecules have correct orientation and sufficient kinetic energy lead to compound formation.
Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
A. Both assertion and reason are correct, and the reason is correct of assertion.
B. Both assertion and reason are correct, but reason does not explain assertion.
C. Assertion is correct, but reason is incorrect
D. Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
E. Assertion is incorrect, but reason is correct.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: E
The claim is erroneous, but the reason is right, because the correct assertion is that effective collision leads to the production of a product, and the reason states that the conditions of collision theory must be met for the reaction to be completed.
Assertion: Rate constants determined from Arrhenius equation are accurate for simple as well as complex molecules.
Reason: Reactant molecules undergo chemical change irrespective of their orientation during collision.
Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
A. Both assertion and reason are correct, and the reason is correct of assertion.
B. Both assertion and reason are correct, but reason does not explain assertion.
C. Assertion is correct, but reason is incorrect
D. Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
E. Assertion is incorrect, but reason is correct.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: C
The assertion is valid, but the reasoning is erroneous because Arrhenius equation rate constants are accurate for both simple and complex molecules with suitable orientation during effective collision and sufficient kinetic energy to cause chemical change.
At high pressure the following reaction is zero order
2NH3(g) ![]() KN2(g) + 3H2(g)
KN2(g) + 3H2(g)
Which of the following options are correct for this reaction?
A. Rate of reaction = Rate constant
B. Rate of the reaction depends on concentration of ammonia.
C. Rate of decomposition of ammonia will remain constant until ammonia disappears completely.
D. Further increase in pressure will change the rate of reaction.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct options: A, C and D
The pressure in this reaction is extremely high, and it becomes independent of the ammonia concentration. The metal surface becomes saturated with gas molecules when the rate of reaction=Rate constant. The rate of a zero-order reaction is independent of the concentration of reactants in the reaction.
During decomposition of an activated complex
A. Energy is always released
B. Energy is always absorbed
C. Energy does not change
D. Reactants may be formed
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct options: A and D
Activation Energy is the amount of energy released when reactant molecules collide and form an activated complex. When energy is released, the complex decomposes into a product.
In the graph showing Maxwell Boltzmann distribution of energy, ___________.
A. Area under the curve must not change with increase in temperature.
B. Area under the curve increases with increase in temperature.
C. Area under the curve decreases with increase in temperature.
D. With increase in temperature curve broadens and shifts to the right-hand side.
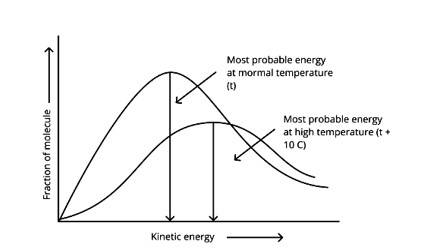
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct options: A and D
According to the graph, the area under the cure must not vary as the temperature rises.T2 > T1
The energy level of T2 is higher than T1.
Assertion: Order and molecularity are same.
Reason: Order is determined experimentally, and molecularity is the sum of the stoichiometric coefficient of rate determining elementary step.
Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
A. Both assertion and reason are correct, and the reason is correct of assertion.
B. Both assertion and reason are correct, but reason does not explain assertion.
C. Assertion is correct, but reason is incorrect
D. Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
E. Assertion is incorrect, but reason is correct.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: E
The order and molecularity may or may not be the same, assertion is false, but reason is right. The sum of the power of the reactants is the order of reaction, which may be easily determined. The total of the stoichiometric coefficient of the rate-determining elementary step determines molecularity
Assertion: The enthalpy of reaction remains constant in the presence of a catalyst.
Reason: A catalyst participating in the reaction, forms different activated complex and lowers down the activation energy but the difference in energy of reactant and product remains the same.
Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
A. Both assertion and reason are correct, and the reason is correct of assertion.
B. Both assertion and reason are correct, but reason does not explain assertion.
C. Assertion is correct, but reason is incorrect
D. Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
E. Assertion is incorrect, but reason is correct.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: A
Both the assertion and the reason are valid, and the reason is a correct of the assertion since the enthalpy of reaction is the difference between the total enthalpy of the reactants and products in the presence of a catalys
The role of a catalyst is to change ______.
A. Gibbs energy of reaction
B. Enthalpy of reaction
C. Activation energy of reaction
D. Equilibrium constant
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option C
Gibbs energy of reaction - Gibbs free energy is a single-valued combination of entropy and enthalpy. The direction of a chemical reaction at constant temperature and pressure is predicted by Gibbs free energy.
Enthalpy of reaction – When one mole of matter is converted by a chemical reaction under specified conditions, the enthalpy of reaction is the change that occurs in the system.
Activation energy of reaction – The lowest amount of energy necessary to activate molecules to a state where they can perform physical and chemical transformations is known as the activation energy of a process. The catalyst creates a lower-activation-energy pathway.
Equilibrium constant – The equilibrium constant is denoted by the letter "K." It is the equilibrium relationship between the products and reactants of a reaction in terms of a specified unit.
All energetically effective collisions do not result in a chemical change. Explain with the help of an example.
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The reaction rate in collision theory is determined by two factors: energy and orientation factor. Certain reactions can be highly exothermic and energetically favoured, meaning the reactants have enough activation energy to collide effectively. However, they do not proceed at a fixed temperature, which is why the reactant molecules are not orientated properly during collisions, resulting in atoms of reactant molecules combining to produce products that do not face each other.
What happens to most probable kinetic energy and the energy of activation with increase in temperature?
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans:
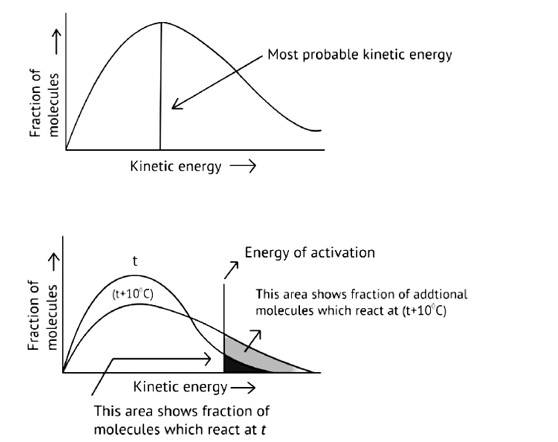
As illustrated in the graph, as the temperature rises, the peak pushes ahead, increasing probable kinetic energy while decreasing the number of molecules utilizing it, resulting in a faster rate of reaction.
Describe how the enthalpy of reaction remains unchanged when a catalyst is used in the reaction.
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Catalyst action is a complicated concept. A catalyst aids in the formation of temporary bonds during a chemical reaction. The objective of a catalyst is to lowers the activation energy. A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change. The action of the catalyst can be explained by intermediate complex theory. According to this theory, a catalyst participates in a chemical reaction by forming temporary bonds with the reactants resulting in an intermediate complex. This has transitory existence and decomposes to yield products and the catalyst.
A small amount of the catalyst can catalyst a large number of reactants. A catalyst does not alter Gibbs energy? G of a reaction. The difference in energy between reactants and products is constant.
It is also found that a catalyst does not change the equilibrium constant of a reaction rather, it helps in attaining the equilibrium faster, that is, it catalyses the forward as well as the backward reactions to the same extent so that the equilibrium state remains the same enthalpy of reaction means the difference in energy between reactant and product it will also remain unchanged.
Explain the difference between instantaneous rate of a reaction and average rate of a reaction.
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Average rate depends upon the change in concentration of reactants or products and the time taken for that change to occur. However, the average rate cannot be used to predict the rate of reaction at a particular instance as it would be constant for the time interval for which it is calculated.
So, to express the rate at a particular moment of time we determine the instantaneous rate. Itis obtained when we consider the average rate at the smallest time interval say dt (i.e. when? t approaches zero).
With the help of an example explain what is meant by pseudo first order reaction.
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Tell us about the pseudo-first-order reaction. It's the reaction with the highest true rate law, yet it behaves like a first order reaction, but it's more specifically a second order reaction.
As an example, consider the hydrolysis of an ester.
CH3COOC2CH5 + H2O→CH3COOH + C2H5OH
rate = k [CH3COOC2H5] [H2O]… (constant)
k1 [CH3COOC2H5]
k = k [H2O]
State a condition under which a bimolecular reaction is kinetically first order reaction.
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
A bimolecular reaction occurs when two particles collide. The product of the concentrations of both elements determines the rate of reaction. If one of the reactants is taken in substantial excess in such a way that its concentration seldom changes, a bimolecular reaction can be kinetically first order.
Write the rate equation for the 2A + B→C if the order of the reaction is zero
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Given: Order of the reaction = 0
We know that a zero order reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs regardless of the reactant's concentration.
The rate law of 2A + B→C is
r = k [A]0 [B]0
For a zero- order reaction
r = k
How can you determine the rate law of the following reaction?
2NO(g) + O2(g)→2NO2(g)
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Experimentally, the reaction's rate law can be calculated.
Step 1
2NO (g) + O2 (g)→2NO2 (g)
O2 (g) is taken in excess
x molecules of NO number reacting with excess of O2
r = k [NO]x
Step 2
2NO (g) + O2 (g)→2NO2 (g)
When 2No (g)is taken in excess
Y molecules of O2 reacting with excess of [NO]
rate = k [O2]y
rate = k [NO]x [NO]y
For which type of reactions, order and molecularity have the same value?
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The order and molecularity of elementary reactions are the same. As a result of a single collision between two molecules or ions, a complicated process occurs. A reaction mechanism is a set of elementary reactions.
In a reaction if the concentration of reactant A is tripled, the rate of reaction becomes twenty-seven times. What is the order of the reaction?
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Let order of reaction be = n
rate = k [A]n- (i)
27r = k [3A]n- (ii)
Divide (ii) by (i)
= k [3A]nn
3n = 27
n = 3
Derive an expression to calculate time required for completion of zero order reaction.
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The concentration of the reactants does not change with time in a zero- order reaction, and the rate of concentration remains constant.
For aA + B→Products, the rate law isRate = k[A][B]3/2.Can the reaction be an elementary reaction? Explain
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The number of ions or atoms that collide to react is known as molecularity in an elementary reaction. The order of reaction about B should be 1 if this is an elementary reaction, however the rate law given is
For a certain reaction a large fraction of molecules has energy more than the threshold energy, yet the rate of reaction is very slow. Why?
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
When the Threshold energy is less than the energy of the molecules and the orientation of the molecules is proper for the effective collision, the reaction happens. As a result, the reaction is slow, and the number of effective collisions is reduced
For a zero-order reaction will the molecularity be equal to zero? Explain
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The concentration of the reactants does not change with time in a zero -order reaction, and the rate of concentration remains constant. The molecularity of a reaction cannot be 0 because it indicates the number of reactants involved.
For a general reaction A + B→C, plot of concentration of A vs time is given in Fig. 4.3. Answer the following based on this graph.
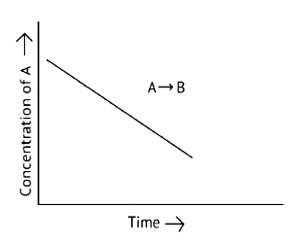
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
A. The reaction has a zero order. The concentration of the reactants does not change with time in a zero order reaction, and the rate of concentration remains constant
B. Slope of the curve is - k
C. The rate constant's units are molL 1s - 1
The reaction between H2(g) and O2(g) is highly feasible yet allowing the gases to stand at room temperature in the same vessel does not lead to the formation of water. Explain.
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The reaction's activation energy is relatively high at room temperature and not readily available, the reaction is highly viable. H2 (g) and O2 (g)bond break and clash, allowing particles to pass across the energy barrier.
2H2 + O2→2H2O
Because of the large activation energy, the water molecule does not form in this equation.
Why does the rate of a reaction increase with rise in temperature?
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The energy possessed by the reacting species increases as the temperature rises, the pace of a reaction increases. This raises the temperature and raises the average kinetic energy of the reactant molecules
Oxygen is available in plenty in the air, yet fuels do not burn by themselves at room temperature. Explain
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The activation energy for fuel combustion reactions is very large, and because every substance or element requires an ignition temperature to function and excite to a higher temperature, oxygen in air does not combust to fire.
Why is the probability of reaction with molecularity higher than three very rare?
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The chance of more than three molecules meeting at the same time is extremely minimal, reactions with molecularity more than three are extremely rare. Simultaneous collisions decrease as the number grows, the probability is very low, and more than three reactions with molecularity are uncommon.
Why does the rate of any reaction generally decrease during the reaction?
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The pace of any reaction is determined by the concentration of the reactants, the rate of any reaction generally declines during the reaction. As the reaction progresses, the reactant concentration declines, and the product concentration rises.
Thermodynamic feasibility of the reaction alone cannot decide the rate of the reaction. Explain with the help of one example
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Thermodynamic feasibility is determined by ΔG factors. So, while the conversion of diamond to graphite is thermodynamically viable, the reaction is sluggish and has a high activation energy.
Gibb's free energy is ΔG
ΔG =Rtlnk
ΔGP, T o
at constant pressure and temperature should be negative or less than 0.
For example, Diamond to be converted to Graphite
ΔG=−ve
It is theoretically conceivable, but the rate is extremely slow, and the activation energy is extremely high. The energy required to transform diamond to graphite is insufficient.
Why in the redox titration of KMnO4 vs oxalic acid, we heat oxalic acid solution before starting the titration?
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
At room temperature, the redox titration of KMnO4vs oxalic acid is exceedingly slow; nevertheless, as the temperature rises, so does the rate of reaction. At a temperature of 500c., KMnO4 is acidified with dil H2SO4 and interacts with oxalic acid.
Why can’t molecularity of any reaction be equal to zero
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The number of molecules of the reactants involved in an elementary reaction is referred to as the molecularity of the reaction. For this, a single molecule with a minimum molecularity of one is required, and it cannot be zero
Why molecularity is applicable only for elementary reactions and order is applicable for elementary as well as complex reactions?
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Simple reactions occur in a single stage, whereas complicated reactions occur in multiple steps. Each phase in a multi-step process has its own molecularity, which is not added together. There is no molecularity in complex reactions. The sequence of a complex reaction is decided by the slowest step. As a result, it can be used for both simple and complex processes
Why can we not determine the order of a reaction by taking into consideration the balanced chemical equation?
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Incorrect order results from a balanced chemical equation. KClO3 + 6FeSO4 + 3H2SO4→KCl + 3H2O + 3Fe2 (SO4)3
This reaction is complex and occurs in several steps. The order is determined by the slowest in the reactions
Rate law cannot be determined from balanced chemical equation if _______.
A. Reverse reaction is involved.
B. It is an elementary reaction.
C. It is a sequence of elementary reactions.
D. Any of the reactants is in excess
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct options : A, C and D.
Rate law = Experimental rate of the reaction
Suppose aA + bB→cC + dD
Then rate = k [A] α [B] β
Here instead of using complex reaction we use elementary reaction which gets solved in one step
Which of the following statements are applicable to a balanced chemical equation of an elementary reaction?
A. Order is the same as molecularity.
B. Order is less than molecularity.
C. Order is greater than molecularity.
D. Molecularity can never be zero.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct options: A and D
Elementary reaction: It is a reaction that occurs in a single step.
Here we must understand about the Order and Molecularity.
Molecularity of a reaction = number of reacting species (collide to bring a chemical reaction).
Discussing about the Order, Rate law is used in Order and how do we equate shall be seen in the next step
rate = k [A] α [B] β
For a balanced chemical equation of an elementary reaction Order and Molecularity is same and can never be 0.
In any unimolecular reaction ______________.
A. Only one reacting species is involved in the rate determining step.
B. The order and the molecularity of the slowest step are equal to one.
C. The molecularity of the reaction is one and order is zero.
D. Both molecularity and order of the reaction are one.
Correct options: A and B
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Unimolecular reaction: Unimolecular means relating to a single molecular reaction that describes decomposition of a single reactant.
If product A→ (B)
rate = k [A]
Example Na2O4 (g)→2No2 (g)
Order = 1
Molecularity = 1
The slowest step is the rate determining which determines the Order and Molecularity.
For a complex reaction ______________.
A. Order of overall reaction is same as molecularity of the slowest step.
B. Order of overall reaction is less than the molecularity of the slowest step.
C. Order of overall reaction is greater than molecularity of the slowest step.
D. Molecularity of the slowest step is never zero or non-integer
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct options: A and D
A complex reaction is one that does not happen in a single step.
The total number of molecules involved in the slowest step of the reaction determines the overall reaction rate.
According to Maxwell Boltzmann distribution of energy, __________.
A. The fraction of molecules with most probable kinetic energy decreases at higher temperatures.
B. The fraction of molecules with most probable kinetic energy increases at higher temperatures.
C. Most probable kinetic energy increases at higher temperatures.
D. Most probable kinetic energy decreases at higher temperatures.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct options: A and C
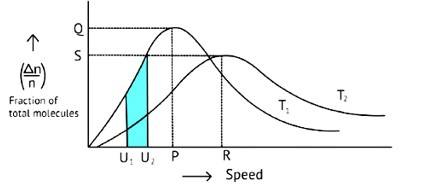
The Maxwell Boltzmann distribution, often known as the Gibbs distribution, is a measure that expresses the likelihood of a system being in each state as a function of the energy of that state.
Look at the graph.
T2 > T1
The fraction of molecules falls as the temperature rises because the area under the curve shrinks.
Which of the following statements are in accordance with the Arrhenius equation?
A. Rate of a reaction increases with increase in temperature.
B. Rate of a reaction increases with decrease in activation energy.
C. Rate constant decreases exponentially with increase in temperature.
D. Rate of reaction decreases with decrease in activation energy.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct options: A and B
Arrhenius equation k = Ae –
When the temperature rises, value falls and –
As a result, e- increases, and it is certain that k and T increases as well. As a result, Option A is proven.
Catalyst increases the rate of reaction by lowering the activation energy. Thus option B is also correct.
Mark the incorrect statements.
A. Catalyst provides an alternative pathway to reaction mechanism.
B. Catalyst raises the activation energy.
C. Catalyst lowers the activation energy.
D. Catalyst alters enthalpy change of the reaction
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct options: B, C and D
Catalysts reduce the activation energy of a process and give an alternate path by reducing or raising the activation energy between reactants and products, altering the reaction's enthalpy change. As a result, B, C, and D statements are the proper responses
Match the graph given in Column I with the order of reaction given in Column II. More than one item in Column I may link to the same item of Column II.
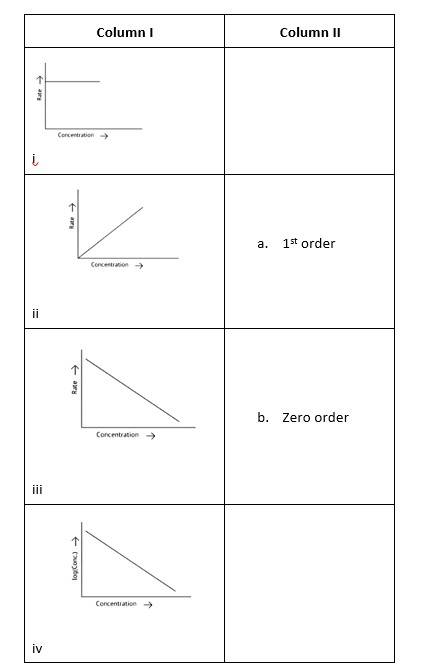
This is a Matching Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i)- (a) ; (ii)- (b) ; (iii)- (b); (iv)- (a)
A zero-order reaction is one in which the reactant concentrations do not change over time and the rate of concentration remains constant.
A first-order reaction is one in which the rate of the reaction is linearly proportional to the concentration of only one ingredient. In other terms, a first-order reaction is a chemical reaction whose rate is determined by changes in only one of the reactants' concentration.
Match the items of Column I and Column II.
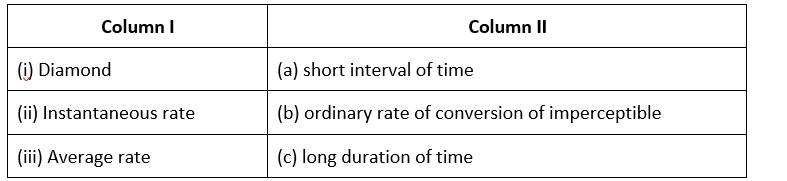
This is a Matching Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i)- (b) ; (ii)- (c) ; (iii)- (a)
The rate of conversion in diamond is normally imperceptible.
Long-term rate at a moment's notice
The average rate is only for a short time.
Match the items of Column I and Column II.

This is a Matching Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i)- (b) ; (ii)- (a) ; (iii)- (d); (iv)- (c)
The rate rule was discovered experimentally and can be used to predict the reaction rate and reactant concentrations.
The rate constant is the proportionality constant that describes the relationship between the molar concentration of the reactants and the rate of a chemical reaction.
The rate constant (k) of a reaction is proportional to its temperature, i.e., for a given reaction at a given temperature, the rate constant (k) is constant.
The order of a reaction is a quantity that has been empirically determined. As a result, the reaction rate is mostly determined by the slowest phase of the reaction. In the event of a complicated reaction, the stoichiometric coefficients of this rate-determining step match to the reaction order.
Assertion: Order of the reaction can be zero or fractional.
Reason: We cannot determine order from balanced chemical equation.
Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
A. Both assertion and reason are correct, and the reason is correct of assertion.
B. Both assertion and reason are correct, but reason does not explain assertion.
C. Assertion is correct, but reason is incorrect
D. Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
E. Assertion is incorrect, but reason is correct.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: B
Both assertion and reason are valid, but reason does not explain assertion because the order of reaction can be zero or even fractional because the order of reaction is proportional to the total of the power of the reactants.
Derive an expression to calculate time required for completion of zero order reaction.
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The concentration of the reactants does not change with time in a zero- order reaction, and the rate of concentration remains constant.
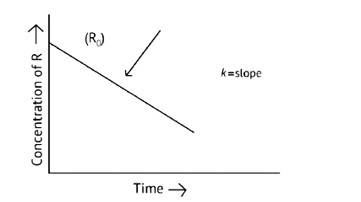
R= [R]0 – Kt
Kt = [R]0
t =
Which of the following graphs is correct for a zero-order reaction?
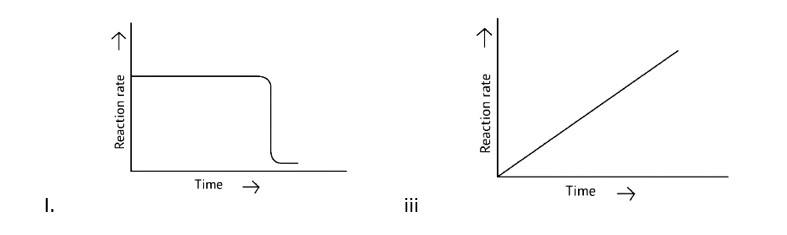
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct options: A and D
A Zero order reaction = [R] = ( - k)t + [R]0
y = (m × ) + c
x = t (time)
y = [R]concentration
Slope (m) = - k
Intercept (c) = [R]0
= - k
= - kto
Rate ∝ t0
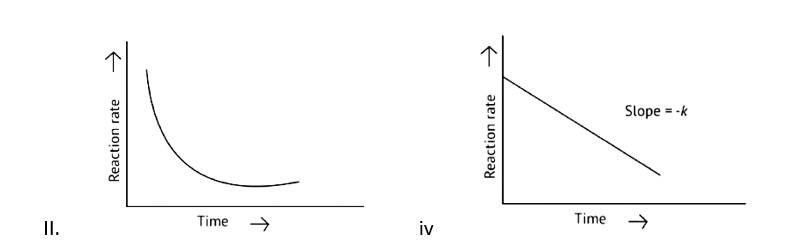
Which of the following graphs is correct for a first order reaction?
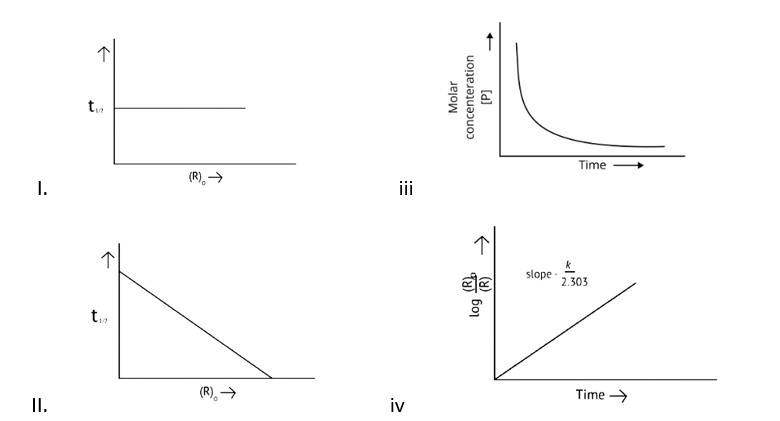
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct options: A and D
The pace of a reaction that is directly proportional to the concentration of the reacting substance is known as a first order reaction.

Y=mn
k = log
t = log
x= a-
x=
t = log
log2
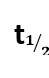
Match the statements given in Column I and Column II


This is a Matching Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i)- (c) ; (ii)- (a) ; (iii)- (d); (iv)- (f); (v)- (b); (vi)- (b)
A catalyst can influence the rate of a process by lowering the activation energy
When it comes to molecularity, there can't be a fraction or a zero.
The second half life of a first order reaction is the same as the first.
Activation energy refers to the percentage of molecules with an energy equal to or greater than activation energy.
Correct orientation is not always present when it comes to energetically favourable activities.
Because the area under the Maxwell Boltzmann curve is constant, the total probability is one.
In the presence of a catalyst, the heat evolved or absorbed during the reaction _____.
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Remains unchanged
D. May increase or decrease
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: C
A catalyst allows a chemical reaction to occur at a faster rate or under different conditions than it would otherwise. As a result, a catalyst affects the reaction's enthalpy change, or heat. As a result, in the presence of the reaction, the enthalpy does not vary, i.e., it remains constant, and no heat is produced or absorbed.
Activation energy of a chemical reaction can be determined by ________.
A. Determining the rate constant at standard temperature
B. Determining the rate constants at two temperatures
C. Determining probability of collision
D. Using catalyst
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: B
The Arrhenius equation can be used to calculate the activation energy of a chemical process. At two temperatures, this determines the rate constants.
2.303log = =
Consider Fig. 4.1 and mark the correct option.
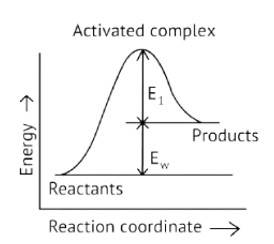
C. Activation energy of both forward and backward reaction isE1 + E2 and reactant is more stable than product.
D. Activation energy of backward reaction is E1and product is more stable than reactant.
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option A
Activation Energy → The amount of energy required to overcome the obstacle and generate a product
The activation energy of a forward reaction can be seen in the [Eaf = E1 + E2] (This is an endothermic reaction.
Therefore, [Eaf > Eab]
The energy of the product is high, while the energy of the reactant is low.
The lower the energy, the more stable and positive the situation becomes.
Δ? = posistive
Consider a first order gas phase decomposition reaction given below:
A(g) → B(g) + C(g)
The initial pressure of the system before decomposition of A waspt . After lapse of time ‘t’, total pressure of the system increased by x units and became ‘t’ the rate constant k for the reaction is given as _________.
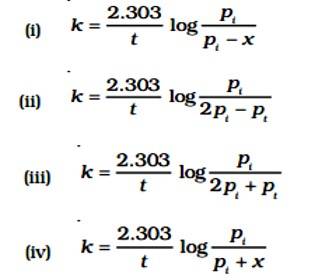
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option B
Given:
A (g) → B (g) + C (g)
pi= Initial pressure
(Time) t = 0
A (g) → B (g) + C (g)
pi →0atm + 0atm
t, (pi - x)atm
pt = (pi - x)atm + x + x = pi + x
pA = (pi - x)
The value of x changes when it is substituted.
pA = pi - (pt - pi) = 2pi - pt
K = log
According to Arrhenius equation rate constant k is equal to Ae - . Which of the following options represents the graph of in k vs .
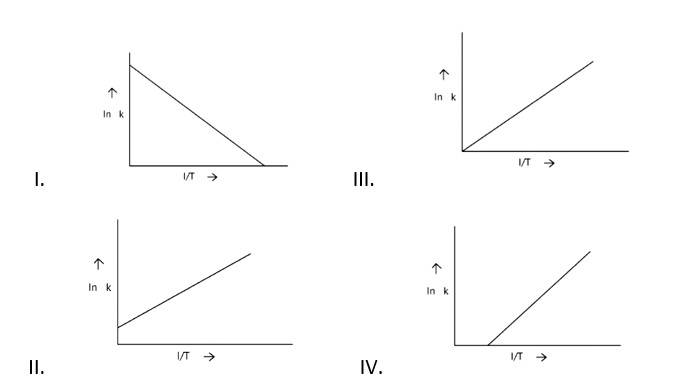
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option A
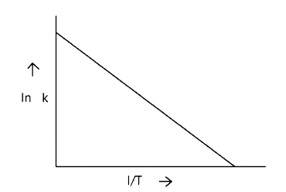
Arrhenius equation Ae -
K = rate constant
A= frequency factor
Ea= Activation Energy
R= gas constant
T= temperature
ln k = lnA -
When the temperature rises, ln falls.
∴ ln kv/s , is a negative slope.
ln A is intercepted by k, and its magnitude decreases with time.
∴ Negative slope is obtained.
When compared to the other possibilities, T is increasing over time, which is incorrect.
ln k = + lnA
Consider the Arrhenius equation given below and mark the correct option.
k = Ae
A. Rate constant increases exponentially with increasing activation energy and decreasing temperature.
B. Rate constant decreases exponentially with increasing activation energy and decreasing temperature.
C. Rate constant increases exponentially with decreasing activation energy and decreasing temperature.
D. Rate constant increases exponentially with decreasing activation energy and increasing temperature.
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option D
k = Ae -
From this equation
Kα
When Activation energy Ea decreases, rate constant k
increases.
Hence, Rate constant increases exponentially with decreasing activation energy and increasing temperature.
A graph of volume of hydrogen released vs time for the reaction between zinc and dil. HCl is given in Fig. 4.2. Based on this mark the correct option
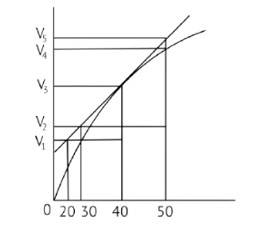
(I) Average rate upto 40s is
(II) Average rate upto 40 seconds is
(III) Average rate upto 40 seconds is
(IV) Average rate upto 40 seconds is
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option C
In the given graph V is the volume in the Y axis and time is in X axis
Zn + dil.HCl→ZnCl2 + H2↑
Average rate = 40s
Average rate of reaction =
Analyzing the graph line where time and volume intersect.
Which of the following statements is not correct about order of a reaction
A. The order of a reaction can be a fractional number.
B. Order of a reaction is experimentally determined quantity.
C. The order of a reaction is always equal to the sum of the stoichiometric coefficients of reactants in the balanced chemical equation for a reaction.
D. The order of a reaction is the sum of the powers of molar concentration of the reactants in the rate law expression.
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option C
Option (c) is the only one of the four assertions that is incorrect. In rate law expression, the order of reaction is equal to the sum of the power of concentration of the reactants.
xA + yB→zC
r = k (A)x (B)y
Order x + y
The order of the reactions can also be a fraction. In a balanced chemical equation, the order of reaction may or may not be equal to the total of the stoichiometric coefficients of the reactants.
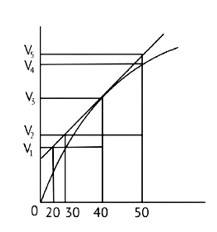
Consider the graph given in Fig. 4.2. Which of the following options does not show instantaneous rate of reaction at 40th second?
I.
II.
III.
IV.
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option B
Reaction occurring at the smallest time interval is known as instantaneous rate of reaction. For e.g the instantaneous rate of reaction at 40s is the rate of reaction during a small interval of time close to 40s. Volume changes during a small-time interval close to the 40s.
Instantaneous rate can be determined graphically by drawing a tangent on the curve
Instantaneous reaction=
Option B is incorrect since the line travels through the graph but does not link to any of the Y axis lines. As a result, option B is incorrect.
Which of the following statements is correct?
A. The rate of a reaction decreases with passage of time as the concentration of reactants decreases.
B. The rate of a reaction is same at any time during the reaction.
C. The rate of a reaction is independent of temperature change.
D. The rate of a reaction decreases with increase in concentration of reactants.
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option A
Because reactant concentrations fall as reactants are transformed to products, reaction rates decrease over time. When reactant concentrations are raised, reaction rates generally increase
Which of the following expressions is correct for the rate of reaction given below?
5Br - (aq) + BrO3 - (aq) + 6H + (aq)→3Br2(aq) + 3H2O(l)
A. = 5
B. =
C. =
D. = 6
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option C
Rate of Disappearance = = - =
=
Which of the following graphs represents exothermic reaction?
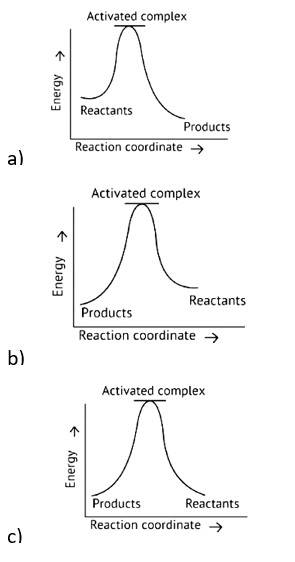
D. (a) and (b) only
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option A
Exothermic Reaction: Exothermic reaction is a chemical reaction in which the enthalpy change is negative, and energy is released in the form of light and heat.
As we all know, ΔH is negative.
Activation energy (forward reaction) – (backward reaction)
(Forward reaction) - Ea (backward reaction)
The product's exothermic energy exceeds the activation energy of the reactants, therefore the correct answer is A, or graph 1, which depicts an exothermic reaction.
Rate law for the reaction A + 2B→C is found to be
Rate = k[A][B]
Concentration of reactant ‘B’ is doubled, keeping the concentration of ‘A’ constant, the value of rate constant will be______.
A. The same
B. Doubled
C. Quadrupled
D. Halved
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option A
The rate concentration of a reaction does not depend upon concentrations of the reactions. Hence, it will remain the same. Even if the equation shows the double concentration level even the rate concentration doubles so it’s the same throughout.
Following with the equation
A + 2B→C
If rate considered as (1)
Rate1 = k [A] [B]
If rate considered as 2
Then, Rate1 = k [A] [2B]
Rate2 = 2Rate1
Option A is correct answer
Which of the following statements is incorrect about the collision theory of chemical reaction?
A. It considers reacting molecules or atoms to be hard spheres and ignores their structural features.
B. Number of effective collisions determines the rate of reaction.
C. Collision of atoms or molecules possessing sufficient threshold energy results into the product formation.
D. Molecules should collide with sufficient threshold energy and proper orientation for the collision to be effective.
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option C
In the case of gases, collision theory is used to predict the speeds of chemical processes. According to this idea, the reacting chemicals must collide with enough energy and in the right direction. The molecules travel quicker and the frequency increases as the temperature rises.
This proves that all three other possibilities, A, B, and D, are correct. Option C does not correspond to the correct answer.
A first order reaction is 50% completed in 1.26 ×1014s. How much time would it take for 100% completion?
A. 1.26 ×1015s
B. 2.52 ×1014s
C. 2.52 ×1028s
D. Infinite
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option D
Note. It is not possible to perform 100% of the reaction because is half-life
Basically, it is called half-line period of the reaction. So, the time taken for 100% completion of the reaction is infinite.
Compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ react according to the following chemical equation.
A[g] + 2B[g]→2C
Concentration of either ‘A’ or ‘B’ were changed keeping the concentrations of one of the reactants constant and rates were measured as a function of initial concentration. Following results were obtained. Choose the correct option for the rate equations for this reaction.

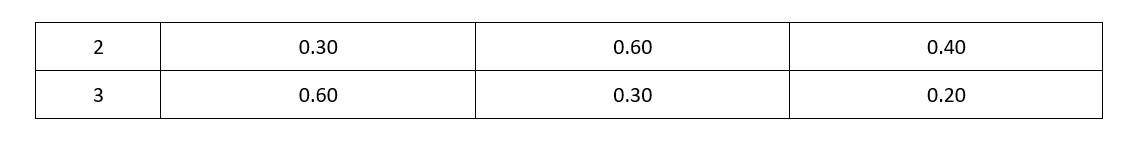
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option B
Let order of A and B be x and y.
r = k [A]x [B]y
0.1 = k (0.3)x (0.3)y_______1
0.4 = 0.1 = k (0.3)x (0.6)y_______2
0.2 = 0.1 = k (0.6)x (0.3)y______3
Divide 2 by 1
=
Divide 3 by 1
=
Hence Rate law is
r = k [A]1 [B]2
Which of the following statements is not correct for the catalyst?\
A. It catalyses the forward and backward reaction to the same extent.
B. It alters ∆G of the reaction.
C. It is a substance that does not change the equilibrium constant of a reaction.
D. It provides an alternate mechanism by reducing activation energy between reactants and products
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option C
In the presence of a catalyst, the value of ΔG cannot be changed for any reaction.
ΔG=−RtlnQ
Where Q is the Reaction Quotient, which is determined by the product and reactant concentrations. As a result, ΔG has no connection to the catalyst. Only when the reaction is spontaneous, which must be negative, is it checked. As a result, ΔG cannot be changed.
Which of the following statements is not correct for the catalyst?
A. It catalyses the forward and backward reaction to the same extent.
B. It alters ∆G of the reaction.
C. It is a substance that does not change the equilibrium constant of a reaction.
D. It provides an alternate mechanism by reducing activation energy between reactants and products
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option C
In the presence of a catalyst, the value of ΔG cannot be changed for any reaction.
ΔG=−RtlnQ
Where Q is the Reaction Quotient, which is determined by the product and reactant concentrations. As a result, ΔG has no connection to the catalyst. Only when the reaction is spontaneous, which must be negative, is it checked. As a result, ΔG cannot be changed.
The value of rate constant of a pseudo first order reaction ____________.
A. Depends on the concentration of reactants present in small amount
B. Depends on the concentration of reactants present in excess.
C. Is independent of the concentration of reactants.
D. Depends only on temperature.
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option C
Let's start with what a pseudo-first-order response is.
Although the pseudo-first-order reaction looks to be an order, it belongs to another order. It's a second-order reaction because it involves two reactants.
Let's have a look at a reaction.
CH3Br + OH→CH3OH + Br-
So, the rate law for the reaction is
Rate = k [OH] [CH3Br]
Rate = k [OH- ] [CH3Br] = k (constant) [CH3Br] = K' [CH3Br]
Only the concentration of CH3Br will change during the reaction, and the rate will be determined by the reaction's modifications.
Consider the reaction A⇌B. The concentration of both the reactants and the products varies exponentially with time. Which of the following figures correctly describes the change in concentration of reactants and products with time?
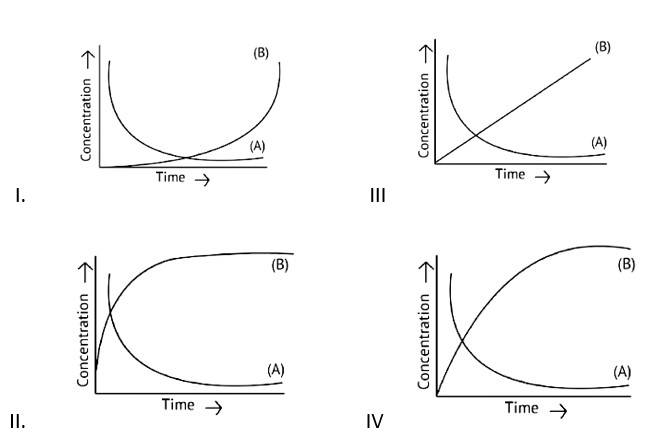
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option B
If A→B then the concentration of both reactants and the products vary exponentially with time. But, in option B graph the reactant concentration decreases exponentially and the product concentration increases.
Chemical Kinetics
| The role of a catalyst is to change ______. A. Gibbs energy of reaction B. enthalpy of reaction C. activation energy of reaction D. equilibrium constant |
| Ans: Option C Gibbs energy of reaction - Gibbs free energy is a single-valued combination of entropy and enthalpy. The direction of a chemical reaction at constant temperature and pressure is predicted by Gibbs free energy. Enthalpy of reaction – When one mole of matter is converted by a chemical reaction under specified conditions, the enthalpy of reaction is the change that occurs in the system. Activation energy of reaction – The lowest amount of energy necessary to activate molecules to a state where they can perform physical and chemical transformations is known as the activation energy of a process. The catalyst creates a lower-activation-energy pathway. Equilibrium constant – The equilibrium constant is denoted by the letter "K." It is the equilibrium relationship between the products and reactants of a reaction in terms of a specified unit.
|
| 2. In the presence of a catalyst, the heat evolved or absorbed during the reaction _____. A. increases B. decreases C. remains unchanged D. may increase or decrease |
| Ans: Correct option: C A catalyst allows a chemical reaction to occur at a faster rate or under different conditions than it would otherwise. As a result, a catalyst affects the reaction's enthalpy change, or heat. As a result, in the presence of the reaction, the enthalpy does not vary, i.e., it remains constant, and no heat is produced or absorbed. |
| 3. Activation energy of a chemical reaction can be determined by ________. A. determining the rate constant at standard temperature B. determining the rate constants at two temperatures C. determining probability of collision D. using catalyst |
| Ans: Correct option: B The Arrhenius equation can be used to calculate the activation energy of a chemical process. At two temperatures, this determines the rate constants. 2.303log = =
|
| 4. Consider Fig. 4.1 and mark the correct option.
|
| Ans: Correct option A Activation Energy → The amount of energy required to overcome the obstacle and generate a product The activation energy of a forward reaction can be seen in the [Eaf = E1 + E2] (This is an endothermic reaction. Therefore, [Eaf > Eab] The energy of the product is high, while the energy of the reactant is low. The lower the energy, the more stable and positive the situation becomes. Δℎ= posistive |
| 5. Consider a first order gas phase decomposition reaction given below: A(g) → B(g) + C(g) The initial pressure of the system before decomposition of A waspt . After lapse of time ‘t’, total pressure of the system increased by x units and became ‘t’ the rate constant k for the reaction is given as _________.
|
| Ans: Correct option B Given: A(g) → B(g) + C(g) pi= Initial pressure (Time) t = 0
A(g) → B(g) + C(g) pi →0atm + 0atm t,(pi - x)atm pt = (pi - x)atm + x + x = pi + x pA = (pi - x)
The value of x changes when it is substituted. pA = pi - (pt - pi) = 2pi - pt K = log
|
| 6. According to Arrhenius equation rate constant k is equal to Ae - . Which of the following options represents the graph of in k vs .
|
| Ans: Correct option A
|
| 7. Consider the Arrhenius equation given below and mark the correct option. k = Ae A. Rate constant increases exponentially with increasing activation energy and decreasing temperature. B. Rate constant decreases exponentially with increasing activation energy and decreasing temperature. C. Rate constant increases exponentially with decreasing activation energy and decreasing temperature. D. Rate constant increases exponentially with decreasing activation energy and increasing temperature. |
| Ans: Correct option D k = Ae - From this equation Kα When Activation energy Ea decreases, rate constant k increases. Hence, Rate constant increases exponentially with decreasing activation energy and increasing temperature.
|
| 8. A graph of volume of hydrogen released vs time for the reaction between zinc and dil. HCl is given in Fig. 4.2. Based on this mark the correct option
|
| Ans: Correct option C In the given graph V is the volume in the Y axis and time is in X axis Zn + dil.HCl→ZnCl2 + H2↑ Average rate = 40s Average rate of reaction =
Analyzing the graph line where time and volume intersect.
|
| 9. Which of the following statements is not correct about order of a reaction A. The order of a reaction can be a fractional number. B. Order of a reaction is experimentally determined quantity. C. The order of a reaction is always equal to the sum of the stoichiometric coefficients of reactants in the balanced chemical equation for a reaction. D. The order of a reaction is the sum of the powers of molar concentration of the reactants in the rate law expression. |
| Ans: Correct option C Option (c) is the only one of the four assertions that is incorrect. In rate law expression, the order of reaction is equal to the sum of the power of concentration of the reactants. xA + yB→zC r = k(A)x(B)y Order x + y The order of the reactions can also be a fraction. In a balanced chemical equation, the order of reaction may or may not be equal to the total of the stoichiometric coefficients of the reactants. |
| 10. Consider the graph given in Fig. 4.2. Which of the following options does not show instantaneous rate of reaction at 40th second? I. II. III. IV. |
| Ans: Correct option B Reaction occurring at the smallest time interval is known as instantaneous rate of reaction. For e.g the instantaneous rate of reaction at 40s is the rate of reaction during a small interval of time close to 40s. Volume changes during a small-time interval close to the 40s.
Instantaneous rate can be determined graphically by drawing a tangent on the curve Instantaneous reaction= Option B is incorrect since the line travels through the graph but does not link to any of the Y axis lines. As a result, option B is incorrect. |
| 11. Which of the following statements is correct? A. The rate of a reaction decreases with passage of time as the concentration of reactants decreases. B. The rate of a reaction is same at any time during the reaction. C. The rate of a reaction is independent of temperature change. D. The rate of a reaction decreases with increase in concentration of reactants. |
| Ans: Correct option A Because reactant concentrations fall as reactants are transformed to products, reaction rates decrease over time. When reactant concentrations are raised, reaction rates generally increase. |
| 12. Which of the following expressions is correct for the rate of reaction given below? 5Br - (aq) + BrO3 - (aq) + 6H + (aq)→3Br2(aq) + 3H2O(l) A. = 5 B. = C. = D. = 6 |
| Ans: Correct option C
Rate of Disappearance = = - = =
|
| 13. Which of the following graphs represents exothermic reaction?
|
| Ans: Correct option A Exothermic Reaction: Exothermic reaction is a chemical reaction in which the enthalpy change is negative, and energy is released in the form of light and heat. As we all know, ΔH is negative. Activation energy (forward reaction) – (backward reaction) (Forward reaction) - Ea(backward reaction) The product's exothermic energy exceeds the activation energy of the reactants, therefore the correct answer is A, or graph 1, which depicts an exothermic reaction. |
| 14. Rate law for the reaction A + 2B→C is found to be Rate = k[A][B] Concentration of reactant ‘B’ is doubled, keeping the concentration of ‘A’ constant, the value of rate constant will be______. A. the same B. doubled C. quadrupled D. halved |
| Ans: Correct option A The rate concentration of a reaction does not depend upon concentrations of the reactions. Hence, it will remain the same. Even if the equation shows the double concentration level even the rate concentration doubles so it’s the same throughout. Following with the equation A + 2B→C If rate considered as (1) Rate1 = k[A][B]
If rate considered as 2 Then, Rate1 = k[A][2B] Rate2 = 2Rate1 Option A is correct answer |
| 15. Which of the following statements is incorrect about the collision theory of chemical reaction? A. It considers reacting molecules or atoms to be hard spheres and ignores their structural features. B. Number of effective collisions determines the rate of reaction. C. Collision of atoms or molecules possessing sufficient threshold energy results into the product formation. D. Molecules should collide with sufficient threshold energy and proper orientation for the collision to be effective. |
| Ans: Correct option C In the case of gases, collision theory is used to predict the speeds of chemical processes. According to this idea, the reacting chemicals must collide with enough energy and in the right direction. The molecules travel quicker and the frequency increases as the temperature rises. This proves that all three other possibilities, A, B, and D, are correct. Option C does not correspond to the correct answer. |
| 16. A first order reaction is 50% completed in 1.26 ×1014s. How much time would it take for 100% completion? A. 1.26 ×1015s B. 2.52 ×1014s C. 2.52 ×1028s D. infinite |
| Ans: Correct option D Note. It is not possible to perform 100% of the reaction because is half-life Basically, it is called half-line period of the reaction. So, the time taken for 100% completion of the reaction is infinite. |
| 17. Compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ react according to the following chemical equation. A[g] + 2B[g]→2C Concentration of either ‘A’ or ‘B’ were changed keeping the concentrations of one of the reactants constant and rates were measured as a function of initial concentration. Following results were obtained. Choose the correct option for the rate equations for this reaction. |
| Ans: Correct option B Let order of A and B be x and y. r = k[A]x[B]y 0.1 = k(0.3)x(0.3)y_______1 0.4 = 0.1 = k(0.3)x(0.6)y_______2 0.2 = 0.1 = k(0.6)x(0.3)y______3 Divide 2 by 1 = Divide 3 by 1 = Hence Rate law is r = k[A]1[B]2 |
| 18. Which of the following statements is not correct for the catalyst?\ A. It catalyses the forward and backward reaction to the same extent. B. It alters ∆G of the reaction. C. It is a substance that does not change the equilibrium constant of a reaction. D. It provides an alternate mechanism by reducing activation energy between reactants and products |
| Ans: Correct option C In the presence of a catalyst, the value of ΔG cannot be changed for any reaction. ΔG=−RtlnQ Where Q is the Reaction Quotient, which is determined by the product and reactant concentrations. As a result, ΔG has no connection to the catalyst. Only when the reaction is spontaneous, which must be negative, is it checked. As a result, ΔG cannot be changed. |
| 19. The value of rate constant of a pseudo first order reaction ____________. A. depends on the concentration of reactants present in small amount B. depends on the concentration of reactants present in excess. C. is independent of the concentration of reactants. D. depends only on temperature. |
| Ans: Correct option C Let's start with what a pseudo-first-order response is. Although the pseudo-first-order reaction looks to be an order, it belongs to another order. It's a second-order reaction because it involves two reactants. Let's have a look at a reaction. CH3Br + OH→CH3OH + Br- So, the rate law for the reaction is Rate = k[OH][CH3Br] Rate = k[OH- ][CH3Br] = k(constant)[CH3Br] = K'[CH3Br] Only the concentration of CH3Br will change during the reaction, and the rate will be determined by the reaction's modifications.
|
| 20. Consider the reaction A⇌B. The concentration of both the reactants and the products varies exponentially with time. Which of the following figures correctly describes the change in concentration of reactants and products with time?
|
| Ans: Correct option B If A→B then the concentration of both reactants and the products vary exponentially with time. But, in option B graph the reactant concentration decreases exponentially and the product concentration increases. |
JEE Mains 2022
JEE Mains 2022
Commonly asked questions
Using the rules for significant figures, the correct answer for the expression will be
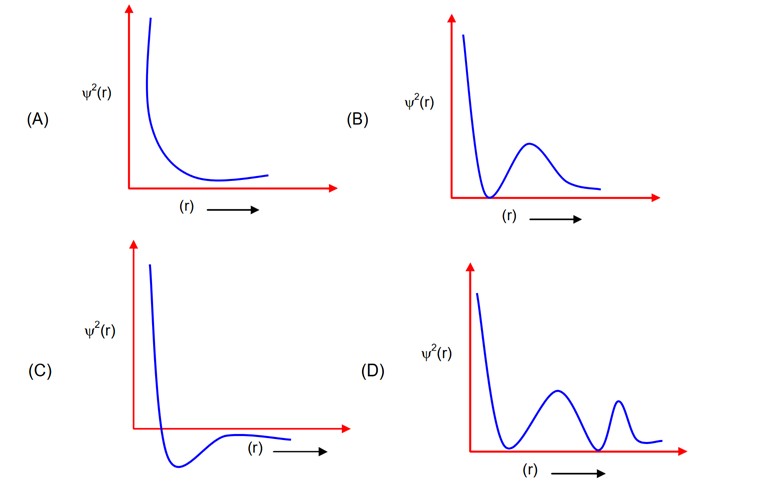
Which of the following is the correct plot for the probability density as a function of distance ‘r’ of the electron from the nucleus for 2s orbital?
For 2S, number of radial moles = and will always be positive
it has one radial node and it is positive.
Consider the species CH4, Choose the correct option with respect to the there species
Species =CH4
Electrons =101010
4.0 moles of argon and 5.0 moles of PCl5 are introduced into an evacuated flask of 100 litre capacity at 610 K. The system is allowed to equilibrate. At equilibrium, the total pressure of mixture was found to be 6.0 atm. The KP for the reaction is
[Given R = 0.082 L atm K-1 mol-1]
Moles of PCl5 = 5 mol
Moles of Ar = 4 mol
Total no of moles = 9 moles
2.5 00
2.5 PPP
P = 1.5 atm
A 42.12% (w/v) solution of NaCl causes precipitation of a certain sol in 10 hours. The coagulating value of NaCl for the sol is
[Given molar mass : Na = 23.0g mol-1; Cl = 35.5g mol-1]
Data is not sufficient but official answer is (D)
Given below are two statements. One is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R.
Assertion (A) : The first ionization enthalpy for oxygen is lower than that of nitrogen
Reason (R) : The four electrons in 2p orbitals of oxygen experience more electron electorn repulsion.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1st ionization energy of N>O in oxygen atom, 2 electrons out of 4 electron of 2p orbital resulting in an increased electron repulsion.
Match List – I with List – II:
List – I (Ore) List – II (Composition)
(A) Siderite (I) FeCO3
(B) Malachite (II) CuCO3 . Cu(OH)2
(C) Sphalerite (III) ZnS
(D) Calamine (IV) ZnCO3
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Ore Formula
Siderite FeCO3
Malachite CuCO3 Cu (OH)2
Calamine ZnCO3
Sphalarite ZnS
Given below are two statements:
Statement I : In CuSO4.5H2O, Cu-O bonds are present
Statement II : In CuSO4.5H2O, ligands coordinating with Cu(II) ion are O- and S- based ligands
In the light of the above statements, choose Correct answer from the options given below:
From the given structure of CuSO4 . 5H2O Cu (II) ion and oxygen bonds are present but ligands coordinating with Cu (II) ion are not O and S both.
Amongst baking soda, caustic soda and washing soda, carbonate anion is present
Baking soda = NaHCO3
Washing soda = Na2CO3. 10H2O
Caustic soda = NaOH
Number of lone pair(s) of electrons on central atom and the shape of BrF3 molecule respectively.
Kindly consider the following figure
Aqueous solution of which of the following boron compounds will be strongly basic in nature?
Borax forms basic buffer solution in aqueous medium.
Sulphur dioxide is one of the components of polluted air. SO2 is also a major contributor to acid rain. The correct and complete reaction to represent acid rain caused by SO2 is
Complete reaction of acid rain is
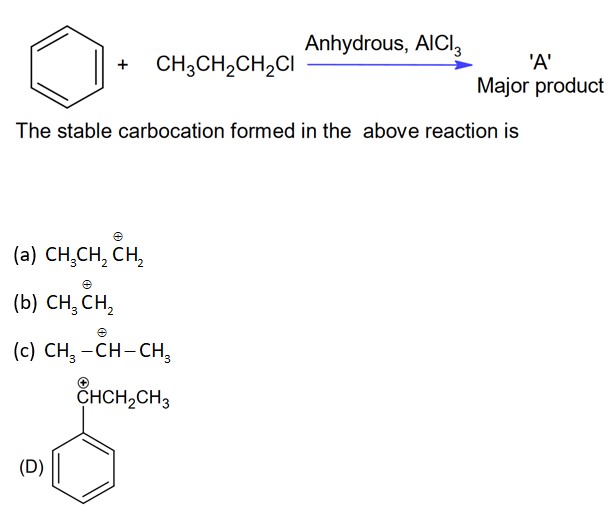
Which of the following carbocations is most stable?
In this carbocation +M effect of -OCH3 group stabilizes the carbocation.
While in option (A) and (B), +M of -OCH3 will not work but in option (C), +M of -OCH3 works so due to more delocalization in option (D), it is more stable.
Kindly consider the following figure
With AlCl3, alkyl halide will form cabocation which will show rearrangement.
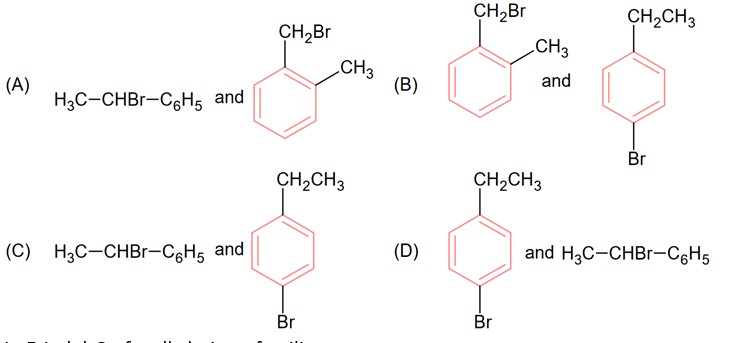
Two isomers (A) and (B) with molar mass 184 g/mol and elemental composition C, 52.2%; H. 4.9% and Br 42.9% gave benzoic acid and p-bromobenzoic acid respectively on oxidation with KMnO4. Isomer ‘A’ is optically active and gives a pale yellow precipitate when warmed with alcoholic AgNO3. Isomer ‘A’ and ‘B’ are respectively
Kindly consider the following figure
In Friedel-Crafts alkylation of aniline, one gets
Aniline show acid-base reaction with AlCl3
aniline is a Lewis base while AlCl3 acts as lewis acid.
Given below are two statements : one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R.
Assertion A : Dacron is an example of polyester polymer.
Reason R : Dacron is made up of ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid monomers.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
Kindly consider the following figure
The structure of protein that is unaffected by heating is
Primary structure of protein in unaffected by physical or chemical changes.
The mixture of chloroxylenol and terpineol is an example of
Antiseptic Dettol is mixture of chloroxylenol and terpineol
A white precipitate was formed when BaCl2 was added to water extract of an inorganic salt. Further, a gas ‘X’ with characteristic odour was released when the formed white precipitate was dissolved in dilute HCl. The anion present in the inorganic salt is
A box contains 0.90g of liquid water in equilibrium with water vapour at 27°C. The equilibrium vapour pressure of water at 27°C is 32.0 Torr. When the volume of the box is increased, some of the liquid water evaporates to maintain the equilibrium pressure. If all the liquid water evaporates, then the volume of the box must be________ litre. [Nearest Integer]
(Given : R = 0.082 L atm K-1 mole-1)
(Ignore the volume of the liquid water and assume water vapours behave as an ideal gas.)
V =
2.2g of nitrous oxide (N2O) gas is cooled at a constant pressure of 1 atm from 310 K to 270 K causing the compression of the gas from 217.1mL to 167.75mL. The change in thermal energy of the process, is ‘-x’ J. The value of ‘x’ is________. [Nearest Integer]
(Given : atomic mass of N = 14 g mol-1 and of O = 16 g mol-1.
Molar heat capacity of N2O is 100 J K-1 mol-1)
Moles of N2O
Elevation in boiling point for 1.5 molal solution of glucose in water is 4 K. The depression in freezing point for 4.5 molal solution of glucose in water is 4K. The ratio of molal elevation constant to molal depression constant (Kb/Kf) is________.
The cell potential for the given cell at 298 K
The pH of the acidic solution is found to be 3, whereas the concentration of Cu2+ is 10x M. The value of x is________.
(Given :
H2 (g) + Cu2+ (aq)
0.31 = 0.34 -
x = 7
The equation
k =
Is followed for the decomposition of compound A. The activation energy for the reaction is________ kJ mol-1 [nearest integer] (Given : R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1)
Ea = 216.164kJ/mol
Spin only magnetic moment of is________ B.M (round off to the closest integer)
(Number of unpaired electron = 5)
For the reaction given below
CoCl3 . xNH3 + AgNO3(aq) ->
If the equivalents of AgCl precipitate but, then the value of x will be__________.
CoCl3.NH3 + AgNO3
x = 5
The number of chiral alcohol(s) with molecular formula C4H10O is__________.
Kindly consider the following figure
In the given reaction
The number of sp2 hybridised carbon(s) in compound ‘X’ is____________.
Number of sp2 carbon = 8
In the given reaction,
The number of π- electron present in the product ‘p’ in__________.
It is aldol condensation.
NEET 2022
NEET 2022
Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Four Exam