Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Four
Get insights from 97 questions on Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Four, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Four
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option C
In the presence of a catalyst, the value of ΔG cannot be changed for any reaction.
ΔG=−RtlnQ
Where Q is the Reaction Quotient, which is determined by the product and reactant concentrations. As a result, ΔG has no connection to the catalyst. Only when the reaction is spontaneous, which must be negative, is it checked. As a result, ΔG cannot be changed.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option B
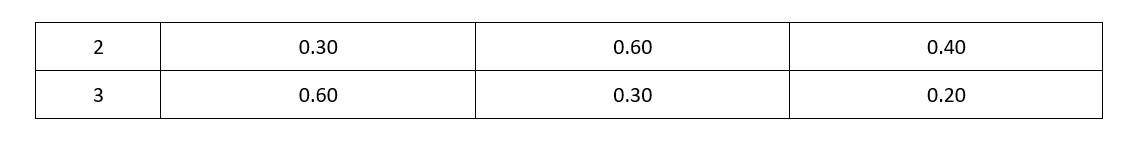
Let order of A and B be x and y.
r = k [A]x [B]y
0.1 = k (0.3)x (0.3)y_______1
0.4 = 0.1 = k (0.3)x (0.6)y_______2
0.2 = 0.1 = k (0.6)x (0.3)y______3
Divide 2 by 1
=
Divide 3 by 1
=
Hence Rate law is
r = k [A]1 [B]2
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option D
Note. It is not possible to perform 100% of the reaction because is half-life
Basically, it is called half-line period of the reaction. So, the time taken for 100% completion of the reaction is infinite.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option C
In the case of gases, collision theory is used to predict the speeds of chemical processes. According to this idea, the reacting chemicals must collide with enough energy and in the right direction. The molecules travel quicker and the frequency increases as the temperature rises.
This proves that all three other possibilities, A, B, and D, are correct. Option C does not correspond to the correct answer.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option A
The rate concentration of a reaction does not depend upon concentrations of the reactions. Hence, it will remain the same. Even if the equation shows the double concentration level even the rate concentration doubles so it's the same throughout.
Following with the equation
A + 2B→C
If rate considered as (1)
Rate1 = k [A] [B]
If rate considered as 2
Then, Rate1 = k [A] [2B]
Rate2 = 2Rate1
Option A is correct answer
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option A
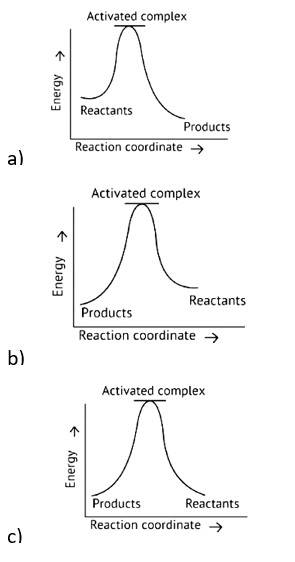
Exothermic Reaction: Exothermic reaction is a chemical reaction in which the enthalpy change is negative, and energy is released in the form of light and heat.
As we all know, ΔH is negative.
Activation energy (forward reaction) – (backward reaction)
(Forward reaction) - Ea (backward reaction)
The product's exothermic energy exceeds the activation energy of the reactants, therefore the correct answer is A, or graph 1, which depicts an exothermic reaction.
New question posted
6 months agoNew answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option C
Rate of Disappearance = = - =
=
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option A
Because reactant concentrations fall as reactants are transformed to products, reaction rates decrease over time. When reactant concentrations are raised, reaction rates generally increase
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option B
Reaction occurring at the smallest time interval is known as instantaneous rate of reaction. For e.g the instantaneous rate of reaction at 40s is the rate of reaction during a small interval of time close to 40s. Volume changes during a small-time interval close to the 40s.
Instantaneous rate can be determined graphically by drawing a tangent on the curve
Instantaneous reaction=
Option B is incorrect since the line travels through the graph but does not link to any of the Y axis lines. As a result, option B is incorrect.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers