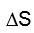Chemistry Thermodynamics
Get insights from 21 questions on Chemistry Thermodynamics, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Chemistry Thermodynamics
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
Work depends on the path followed by the system so work is path function.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
q = 0 as adiabatic process is given
W = 0 as paxt = 0
q + W = DU
q = 0
W = 0
Þ DU = 0
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
We consider the enthalpy change (delta H) more important than the internal energy (delta U) for practical reasons. When we go by the definitions alone, internal energy is the heat absorbed or released at a constant volume. This only happens in a sealed container. But in real life experiments held at laboratories, we have open vessels like test tubes, and there, only atmospheric pressure as a state variable remains constant, and not volume per se. This condition of constant pressure becomes more useful to calculate enthalpy in the chemical reaction.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
We cannot universally say that negative enthalpy is the cause for spontaneity in chemical reactions. Though it is commonly seen in spontaneous reactions that heat releases or follows the exothermic definition, some spontaneous reactions can also absorb heat. They can be endothermic in nature. With that, we get a positive value for enthalpy change. So the better approach is to look into entropy and Gibbs Energy. These two quantities can define or tell us that a chemical process is spontaneous when the total entropy change is positive and when the Gibbs energy change is negative.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
This can be a little confusing when we already know the equation from the First Law of Thermodynamics (delta U = q + W) has internal energy as a state function. Work (W) and heat (q) are dependent on the path entirely, but internal energy is only concerned with initial and final states. We can consider the example of work done for an extremely slow or quick process of a gas expanding. The work done for slow work will be different from that of a faster one, but their initial and final states won't have any effect.
New question posted
4 months agoTaking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers