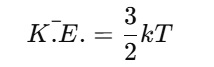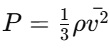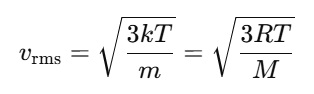Class 11
Get insights from 2.8k questions on Class 11, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 11
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoBeginner-Level 5
Yes, NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Trigonometric Functions are highly useful for JEE and other competitive exams. NCERT Textbook help students develop a clear understanding of fundamental concepts such as trigonometric identities, angle transformations, and general solutions of equations, which form the backbone of many advanced problems in exams like JEE Main and Advanced.
The step-by-step explanations in NCERT Solutions provided by Shiksha helps students in logical problem-solving techniques. Students can build the conceptual strength and formula fluency required to tackle higher-level problems found in books like Cengage or prev
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The main difference between the real and ideal gases is with respect to the kinetic theory. The ideal gas follows assumptions of the kinetic theory but the real gases do not follow it, especially when the temperature is low and there is high pressure.
The following points are applicable in the case of real gases:
- Real gas molecules do have finite volume.
- In such cases, intermolecular forces such as Van there Waals forces become significant.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
According to the kinetic theory of gases class 11, the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution law describes the gas molecules' distribution of speeds (or velocities). All molecules of gas do not move at the same speed, some move fast, some are slow and most move at an average speed. This law provides a mathematical function that helps in finding at a given temperature, how many molecules have a particular speed. The Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution law helps in defining three important types of speeds:
- Average speed: Arithmetic mean of all speeds.
- Most probable speed: Speed at which the maximum number of molecules travel.
- Root mean square (RMS
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The average kinetic energy of the gas molecules is directly related to the temperature of the gas. The average kinetic energy of one gas molecule, according to the kinetic theory, is given by:
Here T is the absolute temperature in Kelvin, and K is the Boltzmann constant. This equation shows that the average kinetic energy of the gas molecules increases with an increase in temperature. It implies that temperature here is the measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles. The equation also reflects that when gas gets heated why it expands - all molecules move faster and exert more pressure on the container walls.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
According to the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory, the pressure is exerted due to gas molecules' collisions with the walls of the container. Each gas molecule has a certain mass and velocity. According to Newton's law, when the molecules collide with a wall, it changes momentum and this change in momentum exerts a force on the container wall. By considering the collisions from all molecules over a period in a unit area, the average force per unit area is called pressure. Mathematically, pressure P is:
p is the gas density.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The kinetic theory talks about the molecular explanation for the classical gas laws:
Boyle's Law (P? 1/V at constant T): Gas molecules will exert more pressure when the volume of the container reduces as it has less space to move and hence it collides with the walls of the container. However, when the temperature is constant, the speed of the molecule will not change.
Charles's Law (V? T at constant P): With the increase in temperature, the speed and average kinetic energy of the molecules increase. The gas expands to maintain constant pressure and increases the volume.
The kinetic theory links the physical behaviour of gases with the mo
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
In a sample, Root mean square (RMS) speed refers to the average of the squares of the speeds of all gas molecules. It helps in measuring the gas particles' speed and takes into account the kinetic energy. Mathematically, it is expressed as:
Here, T is the temperature in Kelvin, k is the Boltzmann constant, and m is the mass of one molecule. M is the molar mass and R is the universal gas constant. The RMS speed is calculated by kinetic theory using the relationship between molecular motion, kinetic energy and pressure. RMS speed shows with which speed the molecules are moving in a gas sample and increases with temperature.
New answer posted
8 months agoBeginner-Level 5
Class 11 Maths Chapter 2 Relations and Functions explores how elements from one set can be connected or related to elements from another. Students get to learn many concepts, can be checked below;
- Concept of the Cartesian product of sets
- Concept of Relations, and how to represent those connections using different methods like arrow diagrams or set notation.
- Idea of a function, and different types of functions such as one-one, onto, bijective, constant, and identity functions.
- Real-valued functions, like linear, quadratic, modulus, and the greatest integer function.
Students can use NCERT Solutions for Chapter 2 Relations and Func
New answer posted
8 months agoBeginner-Level 5
Chapter 2 Relations and Functions of Class 11 Maths holds moderate weight in the annual exams, usually carrying around 6 to 8 marks out of the total 80 in the theory paper.
Class 11 Maths Relations and Functions plays an important role in both in Class 11 and later in Class 12, to understand advance concepts required for competitive exams . Students will get a mix of short answer questions like basic definitions or finding domains and ranges as well as slightly more detailed questions that test your grasp of different types of relations and functions in class 11 annual exams.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The kinetic theory is based on many key assumptions, such as the following:
- The individual gas molecules volume is almost non-existing when compared to the total volume of the gas.
- A gas consists of many small, identical, hard spherical particles.
- The collisions between the gas particles and the container walls are perfectly elastic.
- Except during the collisions, there are no intermolecular forces between the atoms.
- The time spent in collisions is almost nil when compared to the time between collisions.
- The gas molecules are in random and constant motion.
- The average kinetic energy of the molecules is directly proportional to the absolute tem
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers