Class 11th
Get insights from 8k questions on Class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
Density of metal a very specific and depends upon many factors.
Li -> 0.53 gm/cm3
Na -> 0.97 gm/cm3
K -> 0.86 gm/cm3
Rb ->1.53 gm/cm3
Cs -> 1.90 gm/cm3
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
The principle of circular motion follows Newtonian mechanics. It can be stated that an object will move in a circle only when there is a centripetal force that continuously acts perpendicular to its tangential velocity. That changes the direction but not its speed. The inward acceleration a_c = v squared/r obeys Newton's laws and ensures circular path motion.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
Circular motion has the following characteristics.
- Fixed radius with the same and constant distance from the centre
- Constant speed, when the motion is uniform
- A changing velocity vector with continuous direction of change
- Centripetal acceleration that is directed radially inwards, while the force that causes it is the centripetal force that maintains the curved path
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
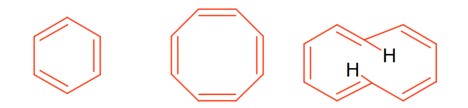
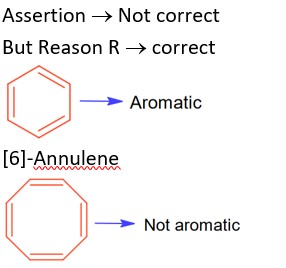
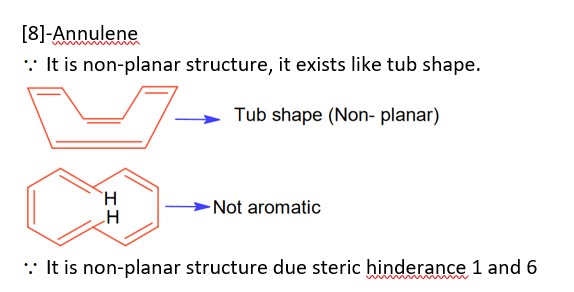
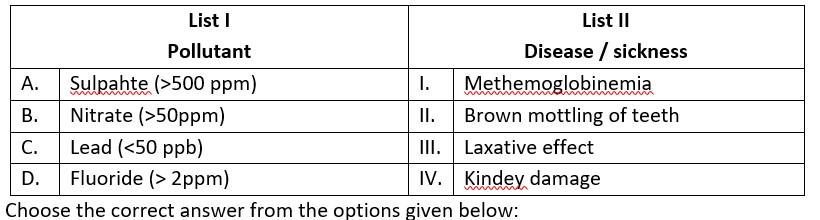
(A) Sulphate (>500 ppm) ® causes laxative effect that leads to dehydration.
(B) Nitrate (> 50 ppm) ® causes methemoglobinemia, skin appears blue.
(C) Lead (>50 ppb) ® It damage kidney and RBC.
(D) Fluoride (>2ppm) ® It causes brown mottling of teeth.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers