Class 11th
Get insights from 8k questions on Class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
5 months agoBeginner-Level 5
The difference in boiling or melting point, even after nearly the same molecular geometry, is because opf the presence of hydrogen bond. HF forms intermolecular hydrogen bonds due to fluorine's high electronegativity. This intermolecular hydrogen bonding requires more energy due to break the hydrogen bonds and melt or boil. So, stronger intermolecular forces of HF result in a higher boiling point.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
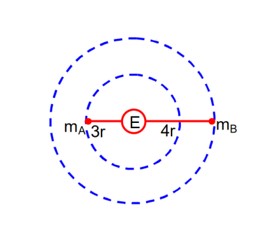
g = 10 m/s2
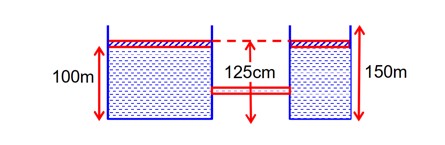
Final height in both vessels
So, less in U =
= 625 * 16 * 104
= 1J.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
As we know that
The percentage decrease in the weight of the object =
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
As we know that
Speed of sound in a gas, and
Rms speed of gas molecules, so
According formula of specific heat ratio of mixture, we can write
5n = 14 n = 2.8
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers