Class 11th
Get insights from 8k questions on Class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
SSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSS
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 6
Here are some of the best NCERT Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 11 exercise solutions you can download and study .
1. LearnCBSE
Provides detailed, step by step solutions covering every question—from Intext to Exercise problems.
Available in English, per the latest NCERT syllabus for 2023–24 & 2025- 2026
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
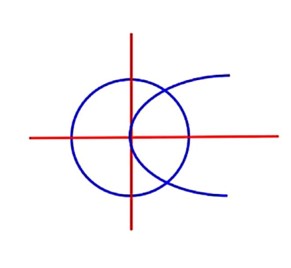
Equation of tangent to parabola y = mx + passes
though (a, b)
25(a2 + a) = 1 …………(iii)
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
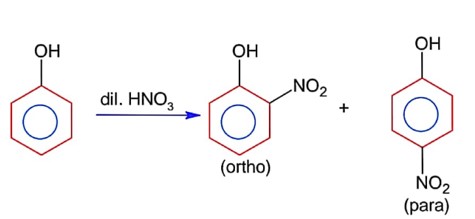
Ortho product has intramolecular H- bonding & para product has intermolecular H- bonding. Thus it can be separated by steam distillation due to difference in B.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers