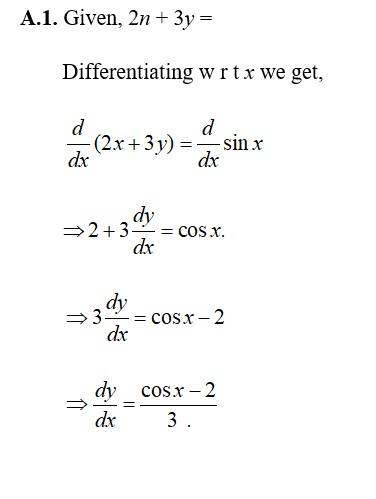Class 12th
Get insights from 11.8k questions on Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
51. Given, sin2x + cos2y = 1.
Differentiating w r t 'x' we get,
(sin2x + cos2y)
= 2sin x cos x + 2 cos y (- sin y)
= sin 2x- sin 2y = 0
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
50. Given, sin2y + cos xy = p
Differentiating w r t 'x' we get,
=
{Qsin 2x = 2sin x cos x}
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
49. Given, x3 + x2y + xy2 + y3 = 81.
Differentiating w r t 'x' we get,
=
= - (3x2 + 2xy + y2)
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
48. Given, x2 + xy + y2 = 100.
Differentiating w r t 'x' we get,
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
47. Given, xy + y2 = tan x + y Differentiating w r t x we get,
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
46. Given, ax + by2 = cos y.
Differentiating w r t 'x' we get,
= a + b 2y = - sin y + sin y = -a
=
= 2by
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
45. Given, 2x + 3y = sin y.
Differentiating w r t x. we get,
=cos y
=
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
43. The given f x n is
f(x) = 0 < < 3
At x = 1
L*H*L* =
Hence lines does not exist
Qf is not differentiable at x = 1
At x = 2
L*H*L =
Hence, limit does not exist.
Qf is not differentiable at x = 2
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
42. The given f x v is
f(x) = |x- 1|, x ε R
For a differentiable f x v f at x = c,
and are finite & equal.
So, at x = 1. f(1) = |1 - 1| = 0.
Now,
L*H*L* =
=
R*H*L = = - 1.
= 1
Hence, L*H*S ¹ R*H*L*
So, f is not differentiable at x = 2.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 685k Reviews
- 1800k Answers