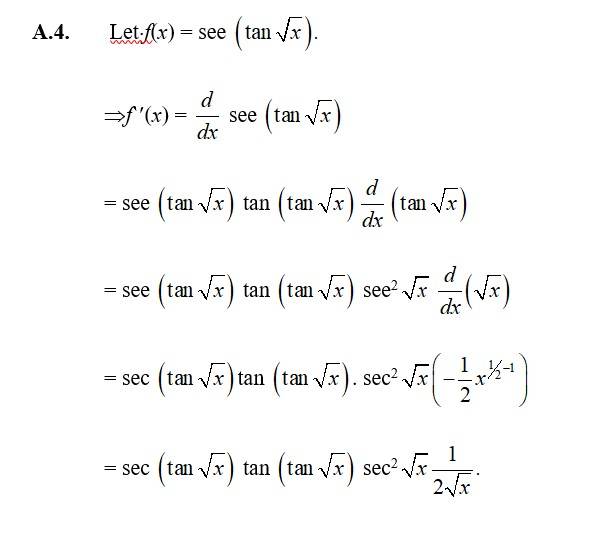Class 12th
Get insights from 11.8k questions on Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
We know that through three collinear points i.e., through a straight line, we can pass an infinite number of planes.
(a) The given points are
Since are collinear points, there will be infinite number of planes passing through the given points.
(b) The given points are
Therefore, a plane will pass through the points A, B, and C.
It is known that the equation of the plane through the points, , is
This is the Cartesian equation of the required plane.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a) The position vector of point is
The normal vector N perpendicular to the plane is
The vector equation of the plane is given by,
is the position vector of any point in the plane.
Therefore, equation (1) becomes
This is the Cartesian equation of the required plane.
(b) The position vector of the point is
The normal vector perpendicular to the plane is
The vector equation of the plane is given by,
is the position vector of any point in the plane.
Therefore, equation (1) becomes
This is the Car
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
39. Let f (x) = cos (x3) sin2 (x5).
f' (x) = cos (x3) sin2 (x5) + sin2 (x5) cos (x3)
= cos (x3) 2sin (x5) sin (x5) + sin2 (x5) [sin (x3)] x3.
= 2 cos (x3) sin (x5). cos (x5) (x5) - sin2 (x5) sin (x3). 3x2
= 2. cos (x3) sin (x5) cos (x5). 5 - 3x2sin2 (x5) sin (x3)
= x2 sin (x5). [2x2 cos (x3) cos (x5) - 3 sin (x5) sin x3].
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a) Let the coordinates of the foot of perpendicular P from the origin to the plane be


New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a) It is given that equation of the plane is
For any arbitrary point on the plane, position vector I s given by,
Substituting the value of in equation (1), we obtain
This is the Cartesian equation of the plane.
(b)
For any arbitrary point on the plane, position vector is given by,
Substituting the value of in equation (1), we obtain
This is the Cartesian equation of the plane.
(c)
For any arbitrary point on the plane, position vector is given by,
Substituting the value
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a) It is given that equation of the plane is
For any arbitrary point on the plane, position vector I s given by,
Substituting the value of in equation (1), we obtain
This is the Cartesian equation of the plane.
(b)
For any arbitrary point on the plane, position vector is given by,
Substituting the value of in equation (1), we obtain
This is the Cartesian equation of the plane.
(c)
For any arbitrary point on the plane, position vector is given by,
Substituting the value
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 685k Reviews
- 1800k Answers