Class 12th
Get insights from 11.8k questions on Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.37 From Arrhenius equation, we obtain
Also, k1 = 4.5 * 103 s -1
T1 = 273 + 10 = 283 K
k2 = 1.5 * 104 s -1
Ea = 60 kJ mol -1 = 6.0 * 104 J mol -1
Then,
→ 0.5229 = 3133.627 * (T2-283)/ (283 * T2)
→ 0.0472T2 = T2-283 T2 = 297K or T2 = 240 C
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.36 We know, The Arrhenius equation is given by k = Ae-Ea/RT Taking natural log on both sides,
Ln k = ln A- (Ea/RT)
Thus, log k = log A - (Ea/2.303RT). eqn 1
The given equation is log k = 14.34 – 1.25 * 104K/T. eqn 2
Comparing 2 equations, Ea/2.303R = 1.25 * 104K
Ea = 1.25 * 104K * 2.303 * 8.314
Ea = 239339.3 J mol-1 (approximately) Ea = 239.34 kJ mol-1
Also, when t1/2 = 256 minutes,
k = 0.693 / t1/2
= 0.693 / 256
= 2.707 * 10-3 min-1 k = 4.51 * 10-5s–1
Substitute k = 4.51 * 10-5s–1 in eqn 2,
log 4.51 * 10-5 s–1 = 14.34 – 1.25 * 104K/T
log (0.654-5) = 14.34– 1.25 * 104K/T = 1.25 * 104/ [ 14.34- log (0.654-5)] T = 668.9K or T =
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.35 The given equation is
k = (4.5 x 1011 s-1) e-28000K/T (i)
Comparing, Arrhenius equation
k = Ae -E/RT (ii)
We get, Ea / RT = 28000K / T
⇒Ea = R x 28000K
= 8.314 J K-1mol-1 * 28000 K
= 232792 J mol–1 or 232.792 kJ mol–1
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.34 t1/2 = 3.00 hours
We know, t1/2 = 0.693/k
? k = 0.693/3 k = 0.231 hrs-1
We know, time
Where, k- rate constant
[R]° -Initial concentration
[R]-Concentration at time 't'
Thus, substituting the values,
log ( [R]0/ [R]) = 0.8
log ( [R]/ [R]0) = -0.8
[R]/ [R]0 = 0.158
Hence, 0.158 fraction of sucrose remains.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.33 Given,
k = 2.0 * 10–2s-1
time t = 100s
Concentration [A0] = 1.0 mol L-1
We know,
On substituting the values, Log (1/ [A]) = 2.303/2
Log [A] = -2.303/2 [A] = 0.135 mol L–1
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.32 Given,
k = 2.418 * 10-5 s-1
T = 546 K
Ea = 179.9 kJ mol-1 = 179.9 * 103J mol-1
The Arrhenius equation is given by k = Ae-Ea/RT Taking natural log on both sides,
Ln k = ln A- (Ea/RT) Substituting the values,
ln (2.418 * 10-5 ) = ln A-179.9/ (8.314 * 546)
ln A = 12.5917
A = 3.9 * 1012 s-1 (approximately)
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
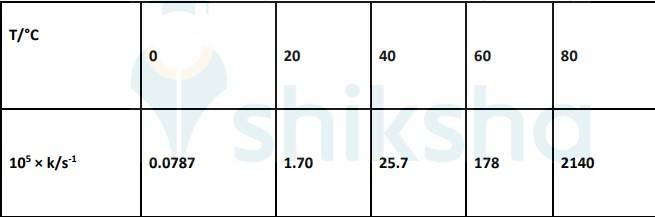
4.31 To convert the temperature in °C to °K we add 273 K.
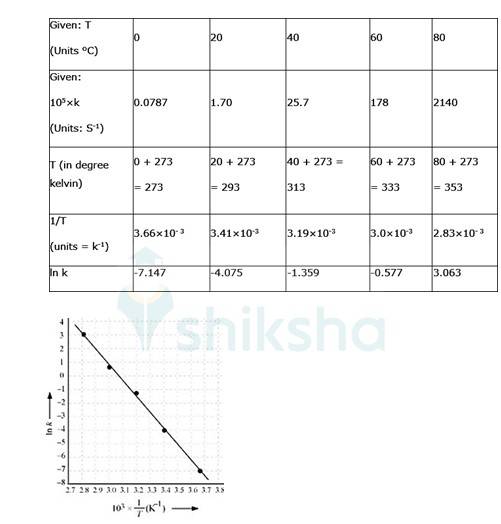
The graph is given as:
The Arrhenius equation is given by k = Ae-Ea/RT
Where, k- Rate constant
A- Constant
Ea-Activation Energy
R- Gas constant
T-Temperature
Taking natural log on both sides,
ln k = ln A- (Ea/RT). equation 1
By plotting a graph, ln K Vs 1/T, we get y-intercept as ln A and Slope is –Ea/R.
Slope = (y2-y1)/ (x2-x1)
By substituting the values, slope = -12.301
? –Ea/R = -12.301
But, R = 8.314 JK-1mol-1
? aE= 8.314 JK-1mol-1 * 12.301 K
? aE= 102.27 kJ mol-1
Substituting the values in equation 1 for data at T = 273K
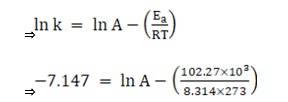
(? At T = 273K, ln k =-7.147)
On solving, we get ln A = 37.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.30 When t = 0, the total partial pressure is P0 = 0.5 atm
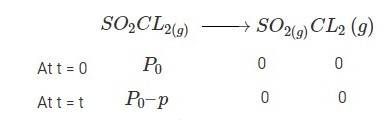
When time t = t, the total partial pressure is Pt = P0 + p
P0-p = Pt-2p, but by the above equation, we know p = Pt-P0
Hence, P0-p = Pt-2 (Pt-P0)
Thus, P0-p = 2P0 – Pt
We know that time
t= 2.303/K log R0 / R
Where, k- rate constant
[R]° -Initial concentration of reactant [R]-Concentration of reactant at time 't'
Here concentration can be replaced by the corresponding partial pressures.
Hence, the equation becomes,
t= 2.303/K log P0 / P0 - P
t= 2.303/K log P0 / 2P0 - Pt
? equation 1
At time t = 100 s, Pt = 0.6 atm and P0 = 0.5 atm,
Substituting in equation 1,
100 = 2.303/k log 0.5 /
New question posted
8 months agoNew answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
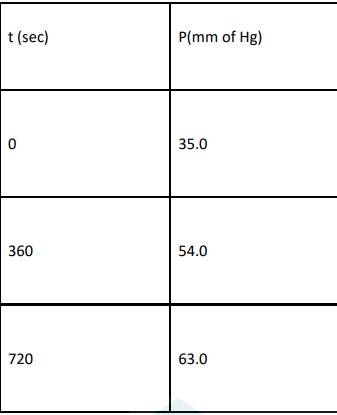
4.29 When t = 0, the total partial pressure is P0 = 35.0 mm of Hg
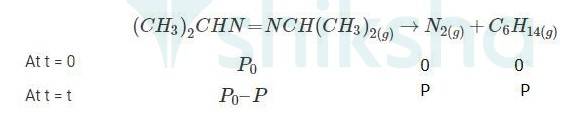
When time t = t, the total partial pressure is Pt = P0 + p
P0-p = Pt-2p, but by the above equation, we know p = Pt-P0 Hence, P0-p = Pt-2 ( Pt-P0)
Thus, P0-p = 2P0 – Pt
We know that time
t= 2.303/K log R0 / R
Where, k- rate constant
[R]° -Initial concentration of reactant
[R]-Concentration of reactant at time 't'
Here concentration can be replaced by the corresponding partial pressures.
Hence, the equation becomes,
t= 2.303/K log P0 / P0 - P
t= 2.303/K log P0 / 2P0 - Pt
? equation 1
At time t = 360 s, Pt = 54 mm of Hg and P0 = 30 mm of Hg, Substituting in equation 1,
360 = 2
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 685k Reviews
- 1800k Answers