Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Get insights from 279 questions on Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Heat an alkyl chloride/bromide in the presence of a metallic fluoride such as AgF, Hg2F2, CoF2, or SbF3 to produce alkyl fluorides. Swarts reaction is the name given to this reaction. CoF2 and Hg2F2 are the only choices that work as reagents. NaF is not suitable because the end products of NaF + RCl→ RF + NaCl are soluble in the solvent, i.e. water, making separation difficult. As a result, the right alternatives are (ii) and (iii).
Correct Answer: Option (ii) and (iii)
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
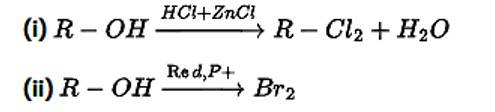
Correct Answer: Option (i) and (ii)
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Aryl halides are halides in which the halogen atom is directly linked to the aromatic ring's sp2 hybridised carbon atom. Only (i) and (iv) contain halogen atoms directly linked to aryl rings among the choices. As a result, they are known as aryl halides. (i) and (ii) are the right answers (iv).
Correct Answer: Option (i) and (iv)
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Checking with the carbon atom it is connected to is one way to see if a compound has a secondary bromide. In a molecule, a secondary carbon group is linked to one hydrogen atom and three non-hydrogen groups. As a result of the foregoing possibilities, secondary bromides are formed when the -Br group is linked to the -CH group. (i) and (iii) are the right answers.
Correct Answer: Option (i) and (iii)
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Dihaloalkanes with two halogen atoms linked to the same carbon atom are known as gem-dihalides. Alkylidene halides are another name for them. The chemical ethylene dichloride is a vicinal dihalide, meaning that chlorine atoms are linked to neighbouring carbon atoms. There is only one chlorine atom in benzoyl chloride. According to the molecule's nomenclature, ethylidene chloride is a gem-dihalide. The IUPAC terminology for methylene chloride is dichloromethane. Two chlorine atoms are joined to a single carbon atom in this compound.
Correct Answer: Option (i) and (iii)
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Isomers are ethylene chloride ClCH2-CH2Cl and ethylidene dichloride CH3-CHCl2. Because the carbon atoms are not surrounded by distinct groups, neither molecule is optically active. When haloalkanes are treated with alcoholic KOH, they undergo an elimination process in which a hydrogen atom from the -carbon atom and a halogen atom from the -carbon atom are eliminated. To form the ethyne molecule, each of these chemicals lose hydrogen and chlorine atoms. When exposed to aqueous NaOH, the molecules undergo nucleophilic substitution, with the –Cl groups being replaced by -OH
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (i) and (iv) have a halogen atom linked to an sp3 hybridised carbon that is single-bonded to other groups. The other possibilities are sp2 hybridised because they are linked to carbon atoms, which are coupled to other groups in double bonds. Option I and (iv) are both correct.
Correct Answer: Option (i) and (iv)
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
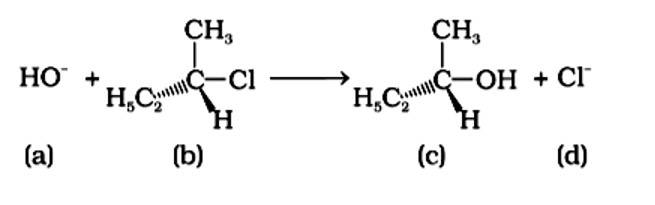
The reaction is of the type SN1 nucleophilic substitution. This sort of reaction is governed by second order kinetics, in which the rate of reaction is determined only by the concentration of the reactant. A reaction's molecularity is defined as the number of molecules involved in the rate-determining phase. Because of second order kinetics, the moleculeity of this reaction is one. (i) and (iii) are the right answers .
Correct Answer: Option (A) and (C)
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Because it is a tertiary alkyl halide, the described reaction is a nucleophilic substitution that follows the SN1 mechanism. It's a two-step process. The first step is the gradual breaking of a polarised C-Br bond, which results in the formation of a carbocation and a bromide ion. To complete the substitution, the stable intermediate carbocation is attacked by the nucleophile OH−. (i) and (iv) are the right statements.
Correct Answer: option (A) and (iv)
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Because the carbon atom is transiently linked to five atoms, the intermediate (iii) is less stable than reactant (ii), which is coupled to four groups.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers