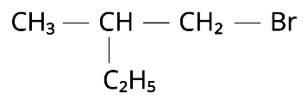Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Get insights from 279 questions on Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (i).
When benzyl chloride is treated with aqueous sodium hydroxide, where -OH is the nucleophile, a nucleophilic substitution reaction occurs, resulting in the formation of benzyl alcohol. The benzene ring is resonance stabilised here, and this stability is extended to the connected methylene group, giving a positive charge to -CH2, making the whole carbocation stable when the link between benzyl and bromide is broken. This is an SN1 reaction with two stages that is followed due to the stability of the carbocation. This is a coordinated reaction
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (i).
The structure of 2-Bromobutane is depicted in the diagram below. Because all of the groups connected to the central carbon atom differ, the mirror image of the molecule cannot be superimposed on the original molecule.
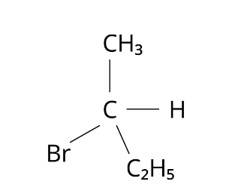
The structure of 1-Bromobutane is shown in the diagram below. Because there are just three groups that vary from one another, the molecule is not chiral in nature.
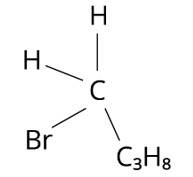
The structure of 2-Bromopropan-2-ol, shown below, has two identical species and hence cannot be chiral.

New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (iii).
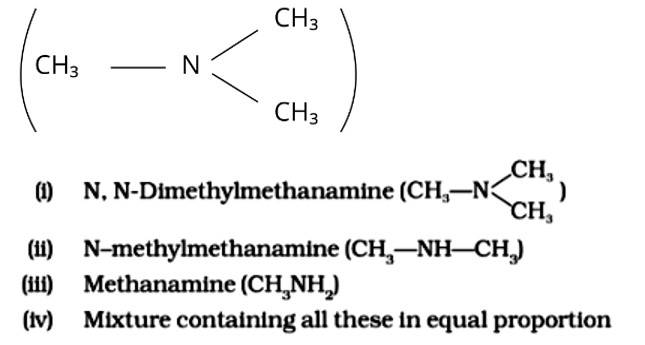
Because it possesses unpaired electrons, the ammonia molecule is a nucleophile in nature. By nucleophilic substitution, this nucleophile attacks the chloromethane molecule and forms methyl amine or methanamine. The carbon atom in the molecule is partially positive due to the electronegativity of the linked halide, which is partially negative. The positive ion is attacked by the electron-rich nucleophile, causing the halide ion to be detached from the molecule. The proper response is (iii).
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (iv).
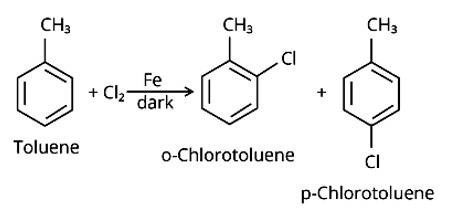
By electrophilic substitution, aromatic arenes react with chlorine in the presence of Lewis acid catalysts such as iron (III) chloride, yielding ortho and para isomers of haloarenes. (ii) and (iii) are both products of the reaction. Cl2 forms a coordination complex with FeCl3, creating the Cl + FeCl4 - complex, which has a small positive charge on Cl and a negative charge on FeCl4 - . This Cl+ then interacts with the aromatic double bonds of the toluene molecule to create an addition product, which is su
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (ii).
We may conclude from the given compound's common name that there are two -C2H5 groups and one -Br group linked to a CH4 molecule. Bromomethane would be represented by the symbol CH3-Br. Two ethyl groups can be replaced for the hydrogens in the methyl molecule to make diethylbromomethane (C2H5)CH (C2H5)Br. The longest parent chain must be identified in order to offer an IUPAC name. The parent chain is CH3-CH2-CH (Br)-CH2-CH3, with the -Br group from either side connected to the third carbon atom. Because the parent chain has five carbons,
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (iii)
The correct answer is option iii.
First, we must determine which carbon chain is the longest. After that, we should have CH3-CH2-CH (CH3)-CH2-Br as the real structure. -Br, because the functional halide group is linked to the first carbon atom, we begin numbering there. The methyl group branch is joined to the chain's second carbon atom. Butane is named from the number of carbons in the unbranched parent chain, which is four. 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane is the name of the molecule. Option (iii) is the right answer.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (iv).
SN1 reactions occur mostly in polar protic solvents such as H2O and follow first-order kinetics. This indicates that the reaction rate is solely determined by one reactant. Because of the great stability of the generated carbocation, this reaction favours tertiary alkyl halides. When a molecule is polarised in water, it generates a carbocation as well as a halide ion. The halides' reactivity is R-I > R-Br > R-Cl > > R-F. As a result, (CH3)3C-I will be the most likely to undergo the reaction.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (ii).
When an alkyl halide with -hydrogen atoms reacts with a base or a nucleophile, depending on the nature of the alkyl halide, the strength of the base or nucleophile, the size of the molecules, and the reaction circumstances, it can undergo a specific kind of reaction. A substitution or elimination process can be followed by an alkyl halide, as well as the two kinds of substitution, SN1 and SN2. Because the entering nucleophile cannot engage with the bulky substituents on or near the carbon atom, the main alkyl halide prefers the SN2reaction
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
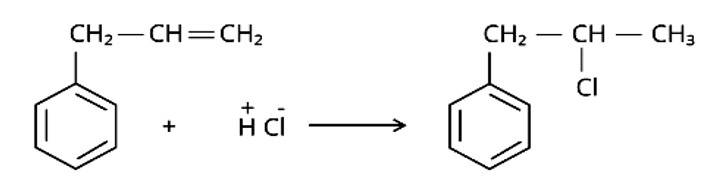
The correct answer is Option (iii).
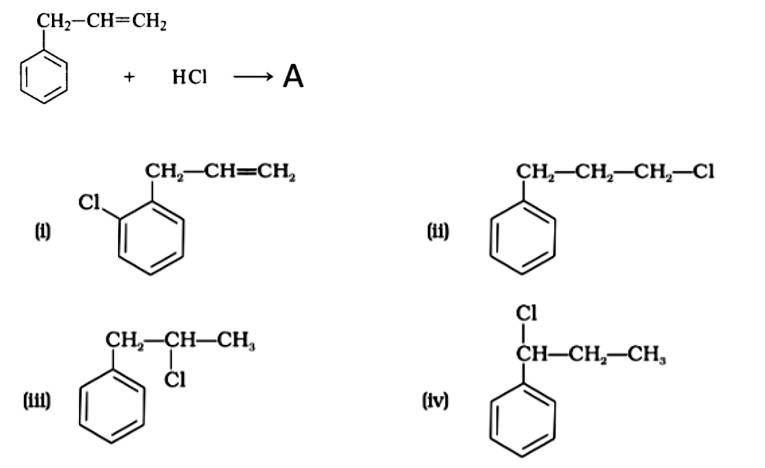
Markonikov's rule can be used to explain the results. The hydrogen from HCl is added to the carbon immediately bonded to the most hydrogen atoms, whereas the -Cl is attached to the carbon directly bonded to the least hydrogens, according to the rule. As a result, the right response is (iii).
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (ii).
Dihaloalkanes with two halogen atoms of the same kind bonded to the same carbon atom are known as gem-dihalides. Alkylidene dihalides is the most frequent naming scheme for gem-dihalides. As a result, ethylidene dichloride is a gem-dihalide. The best choice is (ii).
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers