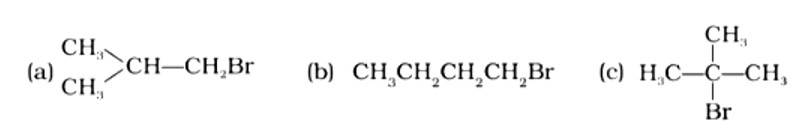Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Get insights from 279 questions on Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The correct answer is option ii.
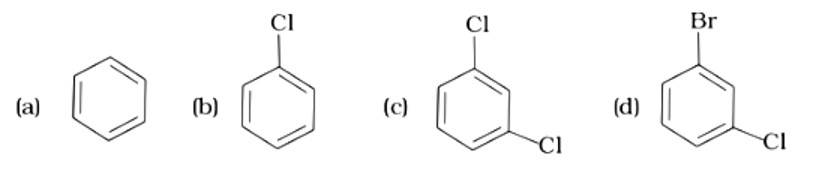
Aluminum chloride is a Lewis acid catalyst that functions similarly to FeCl3. By chlorinating benzene in the presence of AlCl3, benzene is transformed to chlorobenzene. Electrophilic substitution is used to carry out the reaction. Cl2 forms a coordination complex with AlCl3 called Cl + AlCl4- , which has a small positive charge on Cl and is negatively charged on AlCl4- . This Cl+ then interacts with the benzene ring's aromatic double bond to generate an addition product, followed by deprotonation to produce chlorobe
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The correct answer is Option (i).
When the halogen atom is linked to an sp3-hybridised carbon atom next to an allylic carbon, a carbon-carbon double bond is formed.
Aryl halides are produced when a halogen atom is directly linked to an aromatic ring's sp2-hybridised carbon atom.
When a halogen atom is linked to a sp2-hybridised carbon atom in a carbon-carbon double bond, vinylic bonds are produced. Simply defined, it's an ethylene molecule with one hydrogen atom substituted by another -R group.
When the halogen is attached to a secondary carbon atom in the molecule, secondary
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (iv).
Geminal halides or gem-dihalides and vicinal halides or vic-dihalides are dihaloalkanes with the same halogen. Vic-dihalides are dihaloalkanes with halogen atoms on two adjacent carbon atoms, whereas Gem-dihalides are molecules with halogen atoms on two adjacent carbon atoms. Gem-dihalides are called alkylidene halides in the conventional naming system, whereas vic-dihalides are called alkylene dihalides. Because dichloromethane has just one carbon, it cannot contain neighbouring halogen atoms. Two carbon atoms are sandwiched between two h
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (i).
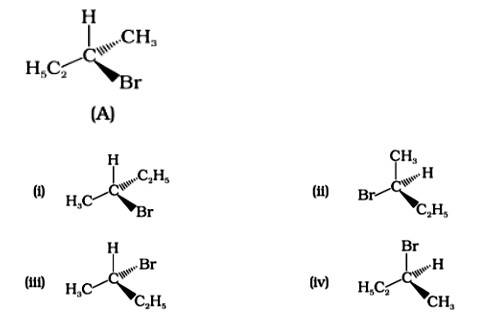
Enantiomers are stereoisomers of a substance that are not superimposable on each other. The carbon atom in the molecule (A) is asymmetric. The molecule's mirror image (i) and 180? rotation cannot be superimposed on each other (A). The molecules (ii), (iii), and (iv) can all be superimposed on one other (A). The molecules (iii) and (iv) have 180? rotations that are superimposable on one another (A).
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
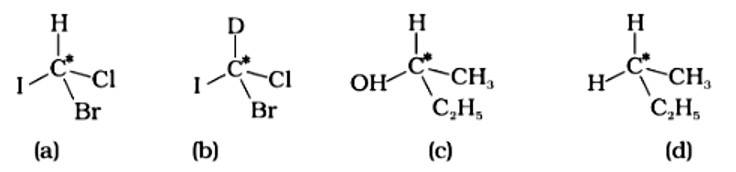
The correct answer is (ii).The mirror copies of the molecules (a), (b), and (c) are non-superimposable. Because all four species linked to the carbon atom are identical, molecule (d) cannot have an asymmetric carbon atom, thus the mirror image of (d) when rotated 180? is superimposable on the original picture.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (iii).
Isomeric alkyl halides' boiling points are related to their branching, with a reduction in B.P. as branching increases. As a result, the boiling point of the tertiary isomer is the lowest, while that of the primary isomer is the highest. Thus, the order of lowering boiling points is (b) > (a) > (c).
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (i).
Alkyl halides have a higher density than water. Their densities are determined by the masses of the halogen atoms, the number of halogen atoms, and the number of carbon atoms. Simply expressed, Br has an atomic mass of 79 while Cl has an atomic mass of 35. (d) will be the heaviest of the molecules, followed by (c), (b), and (a). Because density is exactly proportional to mass, the order of decreasing densities will be the same. The right answer is (i).
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The correct Answer is Option (i).
Chlorination in the presence of UV light can be used to produce alkyl chlorides from alkanes. Under the action of UV radiation, the chlorine molecule generates free radicals, which react with alkanes to create a mixture of isomeric mono- and poly haloalkanes.
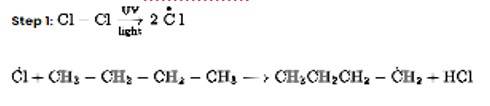
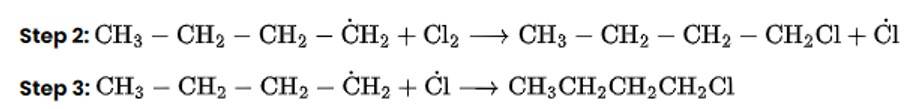
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
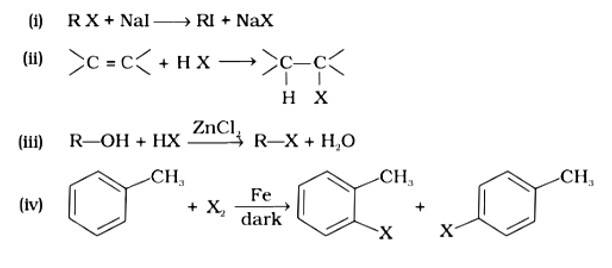
Option (i)
The correct answer is option (i). Option (i) is an example of a Finklestein reaction, which is a halogen exchange reaction that produces alkyl iodide by treating alkyl halides with NaI in dry acetone. Option (ii) is an addition reaction in which an alkene is transformed to the equivalent alkyl halide. Option (iii) is a substitution reaction, whereas option (iv) is an electrophilic substitution reaction.
New question posted
7 months agoTaking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers