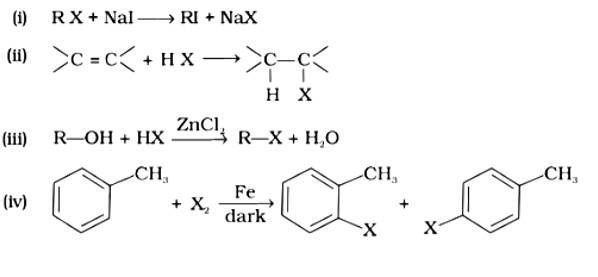
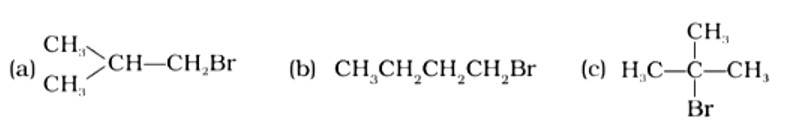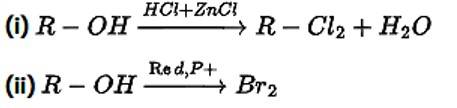- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Questions and Answers
- 28th June 2022(First Shift)
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Multiple Choice Type Questions
- JEE Mains 2022
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Questions and Answers
| 1. Some alkylhalides undergo substitution whereas some undergo elimination reaction on treatment with bases. Discuss the structural features of alkyl halides with the help of examples which are responsible for this difference. |
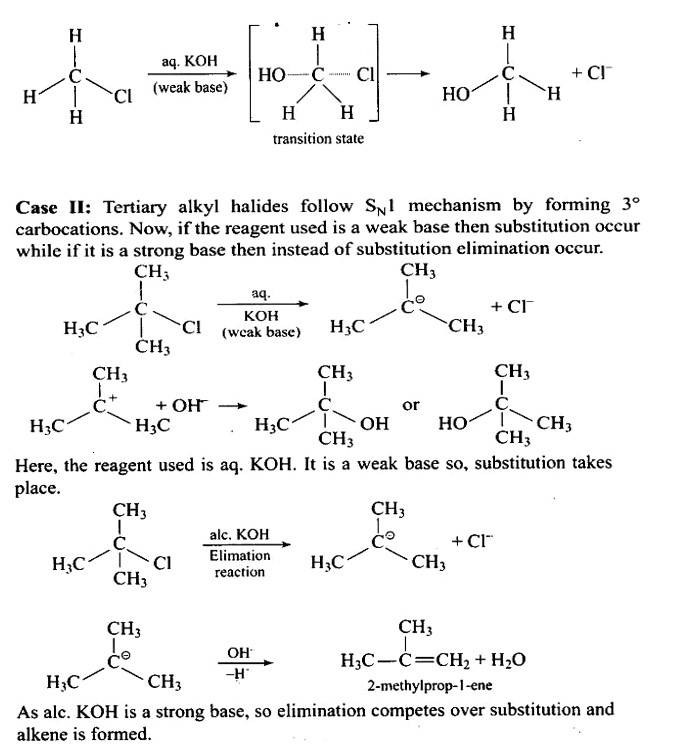
| Ans: The structure of the alkyl halide as well as the chemicals used in the reaction dictate whether it undergoes substitution or elimination. The reactivity of alkyl halides to substitution processes can be examined to better understand their structural characteristics. The SN2 mechanism, which involves cleavage of the halide from the carbon atom and simultaneous attachment of the attacking nucleophile, is preferred by primary alkyl halides for substitution reactions. Tertiary halides, on the other hand, go through an elimination process due to the production of stable carbocation. Tertiary halides also prefer to go through the SN1 reaction, which is a two-step reaction including the creation of a stable carbocation once the halide atom is cleaved. Depending on the solvent and temperature circumstances, secondary halides exhibit intermediate reactivity in both elimination and substitution processes. The given reaction is for a primary alkyl halide undergoing SN2 substitution. The provided reaction is for an SN2 substitution of a tertiary alkyl |
| 2. Some halogen containing compounds are useful in daily life. Some compounds of this class are responsible for exposure of flora and fauna to more and more of UV light which causes destruction to a great extent. Name the class of these halocompounds. In your opinion, what should be done to minimise harmful effects of these compounds. |
| Ans: Multiple halogen groups are present in these carbon compounds, which have a wide range of applications in industry. Polyhalogen compounds are what they're called. The following are the different chemicals and their impact on life: 1. Dichloromethane, commonly known as methylene chloride, is a solvent that is used as a paint remover, an aerosol propellant, a process solvent in drug manufacturing, and a metal cleaning and finishing solvent. The central nervous system has been documented to be harmed by dichloromethane. Low amounts of this chemical might cause mild hearing and visual impairment, while larger levels in the air can induce dizziness, nausea, tingling, and numbness in the fingers and toes. Methylene chloride produces severe burning and moderate skin redness in humans when it comes into close contact with the skin. The cornea can be burned by direct contact with the eyes. 2. Trichloromethane or Chloroform: This is mostly utilised as a solvent for lipids, alkaloids, iodides, and other compounds, and it is also used to make Freon R-22. It used to be used as an anaesthetic in medicine, but now it's replaced with less harmful alternatives like ether. Chronic exposure to chloroform, which is transformed to phosgene and causes liver and kidney damage as well as skin ulcers, is deadly. 3. Tetrachloromethane, also known as carbon tetrachloride, was commonly utilised to make cleaning solutions, chlorofluorocarbons, and aerosol propellants. The use of CCl4 has resulted in the loss of the ozone layer, which shields the planet from UV radiation, leading to an increase in skin cancer and other diseases. 4. DDT, or p,p'-dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, was a commonly used pesticide. They're chlorinated organic pesticides that became popular after WWII due to their excellent effectiveness against malaria-causing mosquitoes and typhus-carrying lice. The major consequences began with insects developing resistance to DDT and a high toxicity to fish. The issue was exacerbated by DDT's chemical persistence and fat solubility. In terms of chemistry, DDT is not metabolised or solubilized well by mammals. The fatty tissues are where it is deposited and kept. DDT builds up within the animal over time if it is consumed at a constant pace, harming the ecosystem. |
| 3. Why are aryl halides less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions than alkyl halides? How can we enhance the reactivity of aryl halides? |
| Ans: Because of the following reasons, aryl halides are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution processes than alkyl halides: (i) The halogen atom's electrons are conjugated to the aryl ring's -electrons, giving the C---X bond a partial double bond character. The whole molecule is then resonance stabilised, allowing for the formation of the following configurations. C---X bond cleavage in haloarenes is more difficult than in haloalkanes due to this bond creation. ii) The carbon linked to the halogen in haloalkanes is sp3 hybridised, whereas the carbon coupled to the halogen in haloarene is sp2 In haloalkanes, the sp2 hybridised carbon atom binds the halogen atom more firmly than a connection between sp3 carbon atom and halogen atom. Haloarenes have a shorter C---X bond than haloalkanes, making them more difficult to break. (iii) Because the phenyl cation is not resonance stabilised, the SN1 mechanism of substitution cannot be used. (iv) Because of the potential for repulsion between electron-rich arenes and approaching electron-rich nucleophiles, aryl halides are less reactive than alkyl halides. The inclusion of an electron withdrawing group at the ortho- and para-positions can enhance the reactivity of aryl halides. At the meta-position, there is no impact. The presence of an electron withdrawing group, such as the nitro group, at ortho- and para- locations pulls electrons away from the benzene ring, making it easier for the nucleophile to attack haloarene. The carbanion is stabilised as a result of resonance. The --NO2 group stabilises the negative charge at ortho- and para-positions with regard to the halogen substituent, but none of the resonant structures in meta-nitrobenzene contain the negative charge on the carbon atom bearing the --NO2 group. As a result, the inclusion of a meta-position electron withdrawing group has no influence on the aryl halide's reactivity.
|
Commonly asked questions
Which of the following compounds (a) and (b) will not react with a mixture of NaBr and H2SO4.Explain why?

This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) Br2 gas is produced when NaBr and H2SO4 are combined. Because of the stable molecule created as a result of resonance stabilisation, molecule
(b) Will not react with Br2 gas.
Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution. Predict and explain the order of reactivity of the following compounds towards nucleophilic substitution:
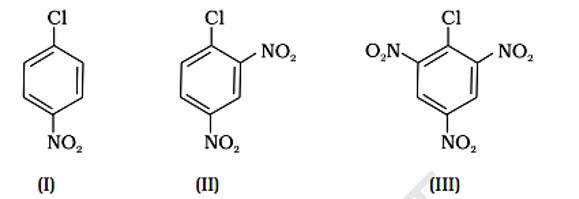
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Because of resonance stabilisation, aryl halides are less reactive to nucleophilic substitution. The inclusion of a -NO2, an electron-withdrawing group in the ortho or para position, enhances the aryl halide's sensitivity to substitution. The more electron withdrawing groups there are in the aryl halide, the more reactive it is. The decreasing sequence of reactivity, according to this theory, is III > II > I.
Identify the compound Y in the following reaction.
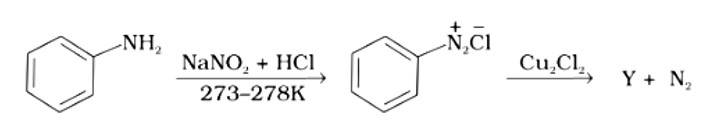
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
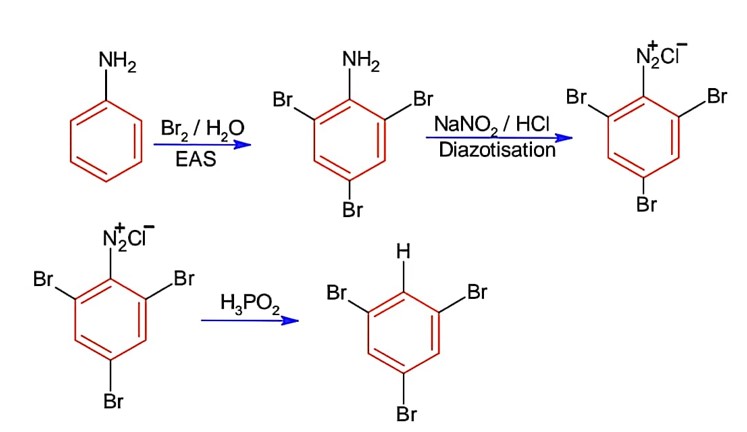
The correct answer is (i). Sandmeyer's reaction can be used to synthesise haloarenes from amines. A primary aromatic amine that has been dissolved or suspended in cold aqueous mineral acid is treated with sodium nitrite to create a diazonium salt in this procedure. When this freshly produced salt is combined with cuprous chloride, the diazonium group is replaced with - Cl, resulting in aryl chloride. Option I is the chemical Y, which is an aryl chloride.
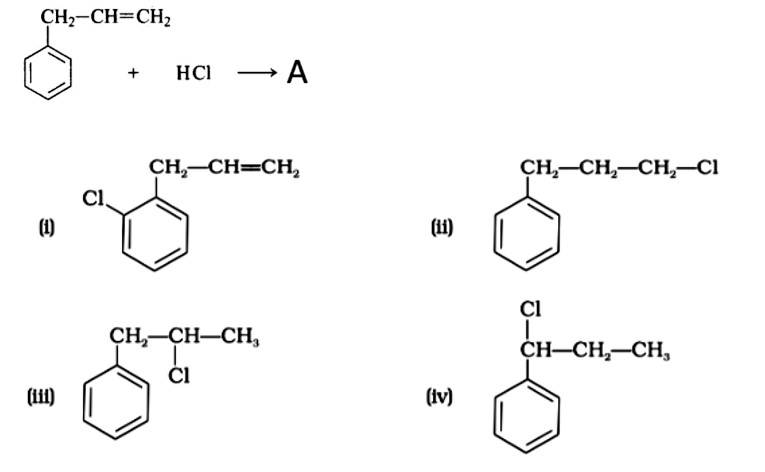
What is 'A' in the following reaction?
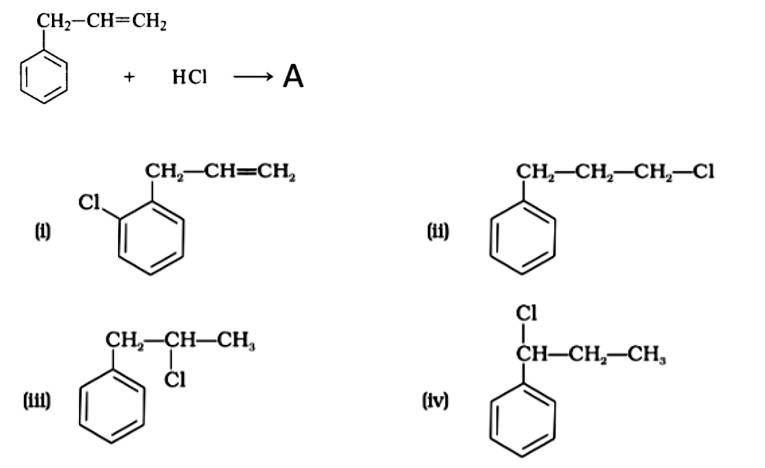
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The correct answer is Option (iii).
Markonikov's rule can be used to explain the results. The hydrogen from HCl is added to the carbon immediately bonded to the most hydrogen atoms, whereas the -Cl is attached to the carbon directly bonded to the least hydrogens, according to the rule. As a result, the right response is (iii).
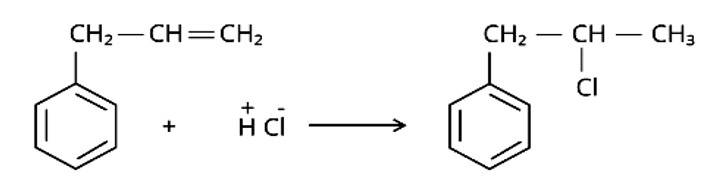
Arrange the compounds in increasing order of the rate of reaction towards nucleophilic substitution.
(i) (a) < (b) < (c)
(ii) (c) < (b) < (a)
(iii) (a) < (c) < (b)
(iv) (c) < (a) < (b)
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (iii).
Due to the resonance stabilisation of the benzene ring, the reactivity of aryl halides to nucleophilic substitution is exceedingly low. Because of resonance, the -Cl bond gains a partial double bond. The presence of an electron withdrawing -NO2 group at ortho or para positions on the ring enhances the reactivity of aryl halides. The presence of -NO2 near the C-Cl makes the molecule more reactive. The order of reactivity should be (b) > (c) > (a). The right option is (iii).
Assertion- Nitration of chlorobenzene leads to the formation of m-nitrochlorobenzene
Reason :−NO2 group is a m-directing group.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
(ii) Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
(iii) Assertion is correct but reason is wrong statement.
(iv) Assertion is wrong but reason is correct statement.
(v) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
This is a assertion and reason answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Because m-nitrochlorobenzene is not a stable molecule, the -NO2 group is a meta-directing group, and the reactions' products include nitro groups at the o- and p- positions.
Correct Answer: Option (iv)
Some alkylhalides undergo substitution whereas some undergo elimination reaction on treatment with bases. Discuss the structural features of alkyl halides with the help of examples which are responsible for this difference.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The structure of the alkyl halide as well as the chemicals used in the reaction dictate whether it undergoes substitution or elimination. The reactivity of alkyl halides to substitution processes can be examined to better understand their structural characteristics. The SN2 mechanism, which involves cleavage of the halide from the carbon atom and simultaneous attachment of the attacking nucleophile, is preferred by primary alkyl halides for substitution reactions.
Tertiary halides, on the other hand, go through an elimination process due to the production of stable carbocation. Tertiary halides also prefer to go through the SN1 reaction, which is a two-step reaction including the creation of a stable carbocation once the halide atom is cleaved. Depending on the solvent and temperature circumstances, secondary halides exhibit intermediate reactivity in both elimination and substitution processes.
The given reaction is for a primary alkyl halide undergoing SN2 substitution.
The provided reaction is for an SN2 substitution of a tertiary alkyl

Some halogen containing compounds are useful in daily life. Some compounds of this class are responsible for exposure of flora and fauna to more and more of UV light which causes destruction to a great extent. Name the class of these halocompounds. In your opinion, what should be done to minimise harmful effects of these compounds.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Multiple halogen groups are present in these carbon compounds, which have a wide range of applications in industry. Polyhalogen compounds are what they're called. The following are the different chemicals and their impact on life:
1. Dichloromethane, commonly known as methylene chloride, is a solvent that is used as a paint remover, an aerosol propellant, a process solvent in drug manufacturing, and a metal cleaning and finishing solvent. The central nervous system has been documented to be harmed by dichloromethane. Low amounts of this chemical might cause mild hearing and visual impairment, while larger levels in the air can induce dizziness, nausea, tingling, and numbness in the fingers and toes. Methylene chloride produces severe burning and moderate skin redness in humans when it comes into close contact with the skin. The cornea can be burned by direct contact with the eyes.
2. Trichloromethane or Chloroform: This is mostly utilised as a solvent for lipids, alkaloids, iodides, and other compounds, and it is also used to make Freon R-22. It used to be used as an anaesthetic in medicine, but now it's replaced with less harmful alternatives like ether. Chronic exposure to chloroform, which is transformed to phosgene and causes liver and kidney damage as well as skin ulcers, is deadly.
3. Tetrachloromethane, also known as carbon tetrachloride, was commonly utilised to make cleaning solutions, chlorofluorocarbons, and aerosol propellants. The use of CCl4 has resulted in the loss of the ozone layer, which shields the planet from UV radiation, leading to an increase in skin cancer and other diseases.
4. DDT, or p, p'-dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, was a commonly used pesticide. They're chlorinated organic pesticides that became popular after WWII due to their excellent effectiveness against malaria-causing mosquitoes and typhus-carrying lice. The major consequences began with insects developing resistance to DDT and a high toxicity to fish. The issue was exacerbated by DDT's chemical persistence and fat solubility. In terms of chemistry, DDT is not metabolised or solubilized well by mammals. The fatty tissues are where it is deposited and kept. DDT builds up within the animal over time if it is consumed at a constant pace, harming the ecosystem.
Why are aryl halides less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions than alkyl halides? How can we enhance the reactivity of aryl halides?
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Because of the following reasons, aryl halides are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution processes than alkyl halides:
(i) The halogen atom's electrons are conjugated to the aryl ring's -electrons, giving the C-X bond a partial double bond character. The whole molecule is then resonance stabilised, allowing for the formation of the following configurations. C-X bond cleavage in haloarenes is more difficult than in haloalkanes due to this bond creation.
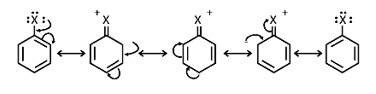
ii) The carbon linked to the halogen in haloalkanes is sp3 hybridised, whereas the carbon coupled to the halogen in haloarene is sp2 In haloalkanes, the sp2 hybridised carbon atom binds the halogen atom more firmly than a connection between sp3 carbon atom and halogen atom. Haloarenes have a shorter C-X bond than haloalkanes, making them more difficult to break.
(iii) Because the phenyl cation is not resonance stabilised, the SN1 mechanism of substitution cannot be used.
(iv) Because of the potential for repulsion between electron-rich arenes and approaching electron-rich nucleophiles, aryl halides are less reactive than alkyl halides.
The inclusion of an electron withdrawing group at the ortho- and para-positions can enhance the reactivity of aryl halides. At the meta-position, there is no impact. The presence of an electron withdrawing group, such as the nitro group, at ortho- and para- locations pulls electrons away from the benzene ring, making it easier for the nucleophile to attack haloarene. The carbanion is stabilised as a result of resonance. The -NO2 group stabilises the negative charge at ortho- and para-positions with regard to the halogen substituent, but none of the resonant structures in meta-nitrobenzene contain the negative charge on the carbon atom bearing the -NO2 group. As a result, the inclusion of a meta-position electron withdrawing group has no influence on the aryl halide's reactivity.
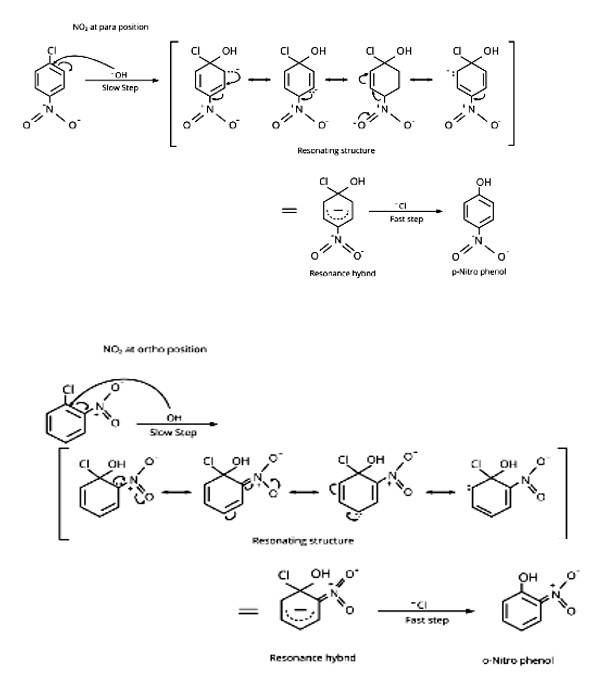
Aryl chlorides and bromides can be easily prepared by electrophilic substitution of arenes with chlorine and bromine respectively in the presence of Lewis acid catalysts. But why does preparation of aryl iodides requires presence of an oxidising agent?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Because HI is produced throughout the process, iodination reactions are reversible in nature. To keep the reaction moving ahead, we must remove the HI by an oxidation process using oxidising agents such as HIO4.
Out of o -and p -dibromobenzene which one has higher melting point and why?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The melting point of p-dibromobenzene is greater because p-symmetry of bromobenzene allows it to fit better in a crystal lattice. As a result, breaking the bonds between the molecules requires a greater temperature, resulting in a higher melting point.
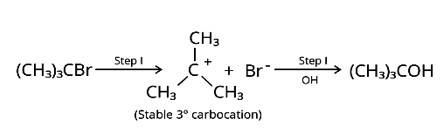
Which of the compounds will react faster in SN1reaction with the OH ion? CH3−CH2−Cl or C6H5−CH2−Cl
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In an SN1 reaction with the OH ion, C6H5−CH2−Cl will react quicker. This is owing to the carbocation's stability in the compound. The C6H5 group is already stable owing to resonance, and the CH2 attached will receive that stability after the cleavage in the first stage of the SN1 reaction, resulting in a stable C6H5CH2+ carbocation. CH3-CH2-Cl does not have the same sort of carbocation.
Why iodoform has appreciable antiseptic property?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Triiodomethane is the chemical name for iodoform. Because of its ability to liberate free iodine, it has antibacterial properties.
Haloarenes are less reactive than haloalkanes and haloalkenes. Explain.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The resonance stabilisation of the aryl ring is the main reason haloarenes are less reactive than haloalkanes and haloalkenes. The electron pairs on the halogen atom, for example, are conjugated with the ring's -electrons in C6H5 - Cl. The C-Cl link takes on a partial double bond character as a result of resonance, making it less reactive to nucleophilic substitution than haloalkanes and haloalkanes.
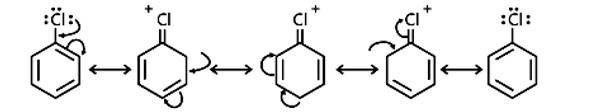
Discuss the role of Lewis acids in the preparation of aryl bromides and chlorides in the dark.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In the presence of Lewis acid catalysts (iron or iron chloride), aryl bromides and chlorides can be made by electrophilic replacement of arenas with bromine and chlorine, respectively.
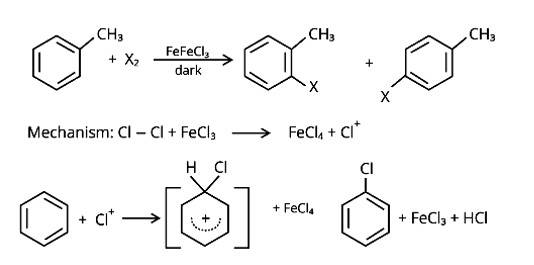
Which of the products will be major product in the reaction given below? Explain.
CH3CH = CH2 + HI → CH3CH2CH2 I + CH3CHICH3
(A) (B)
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
This addition reaction is carried out in accordance with Markovnikoff's rule, which states that in a double bond, the hydrogen from the hydrogen halide is added to the carbon atom with the most hydrogen atoms attached to it, while the halogen atom is attached to the carbon atom with the fewest hydrogens attached to it. The main product in the combination will be the molecule that follows this guideline. As a result, the molecule (B) will be the reaction's main product.
Why is the solubility of haloalkanes in water very low?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Because energy is required to overcome the attractions between the haloalkane molecules as well as to break the hydrogen bonds between water molecules in order to dissolve a haloalkane in water, haloalkanes are only weakly soluble in water. New attractions between the haloalkane and the water molecules, on the other hand, release less energy since they are weaker than the water's initial hydrogen bonds.
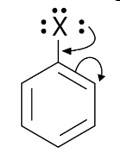
Draw other resonance structures related to the following structure and find out whether the functional group present in the molecule is ortho, para directing or meta directing.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
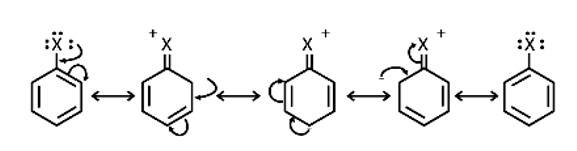
Because electron density is higher at ortho and para locations, the functional groups contained in these compounds are ortho-para directed.
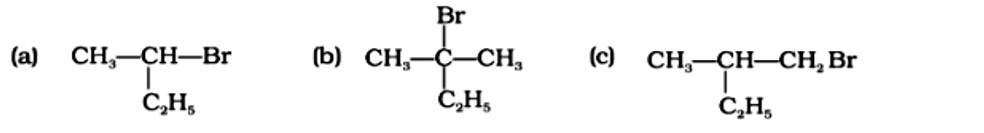
Classify the following compounds as primary, secondary and tertiary halides.
(i) 1 -Bromobut-2-ene
(ii) 4-Bromopent-2-ene
(iii) 2-Bromo-2-methylpropane
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) 1-Bromobut-2-ene: It is a primary halide.
(ii) 4-Bromopent-2-ene: Here Bromine is attached to the secondary carbon. Hence, it is a secondary halide.
(iii) 2-Bromo-2-methylpropane: Here Bromine is attached to the tertiary carbon. Hence, it is a tertiary halide.
Compound 'A' with molecular formula C4H9Br is treated with aq. KOH solution. The rate of this reaction depends upon the concentration of the compound 'A' only. When another optically active isomer 'B' of this compound was treated with aq. KOH solution, the rate of reaction was found to be dependent on concentration of compound and KOH both.
(i) Write down the structural formula of both compounds ' A' and ' B '.
(ii) Out of these two compounds, which one will be converted to the product with inverted configuration.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) Because the rate of reaction of compound ‘A' with aqueous KOH is solely dependent on the concentration of ‘A, ' the reaction mechanism is SN1and ‘A' is 2-Bromo-2-methylpropane (tertiary bromide).
‘B', on the other hand, is an isomer of ‘A' and is optically active. As a result, ‘B' has to be 2-Bromobutane. Because the rate of reaction of ‘B' with aqueous KOH is determined by its concentration, the reaction mechanism is SN2.
(ii) Compound ‘B' will have an inverted conformation as a result of the SN2 reaction, resulting in an inverted product.
Structure ‘A’ is and structure ‘B’ is
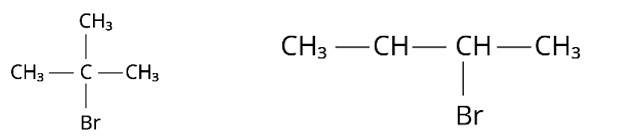
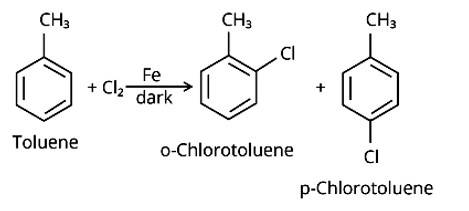
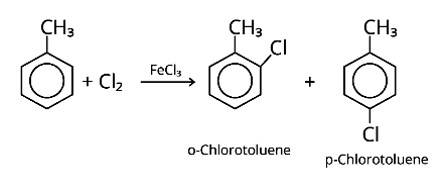
Write the structures and names of the compounds formed when compound "A' with molecular formula, C7H8 is treated with Cl2 in the presence of FeCl3.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
When an arene is treated with Cl2 in the presence of FeCl3, the electrophilic addition reaction chlorinates the arene to produce aryl chloride. As a result, the chemical provided is C6H5-CH3, often known as toluene. o-chlorotoluene and p-chlorotoluene are the results of electrophilic substitution chlorination.
Identify the products A and B formed in the following reaction:
(a) CH3−CH2−CH=CH−CH3 + HCl?A+B
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The addition reaction of the alkene produces two products, as indicated below.
CH3−CH2−CH=CH−CH3 + HCl→ A + B
Which of the following compounds will have the highest melting point and why?
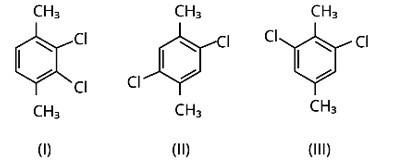
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Because both methyl groups and chlorine atoms are symmetrically positioned at para-positions in compound (II), these molecules fit better in the crystal lattice than other isomers, and hence have the greatest melting point.
Write down the structure and IUPAC name for neo-pentylbromide.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The IUPAC name for this compound is 1-Bromo-2,2-dimethylpropane
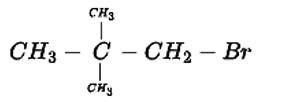
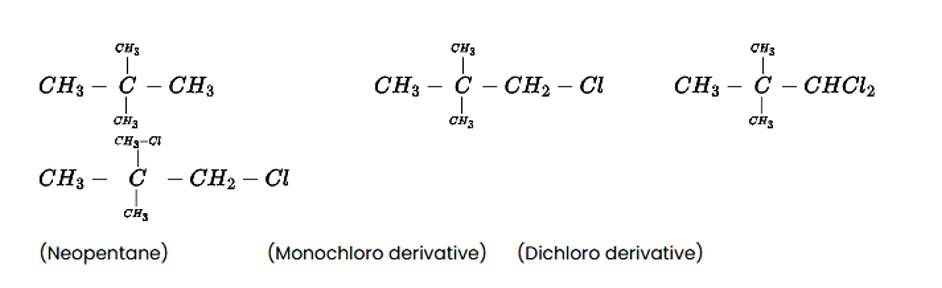
A hydrocarbon of molecular mass 72gmol−1 gives a single monochloro derivative and two dichloro derivatives on photo chlorination. Give the structure of the hydrocarbon.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The alkane C5H12 is a hydrocarbon with a molecular mass of 72gmol?1. On photo-chlorination, the tert-isomer of pentane yields a single monochloro derivative and two dichloro derivatives. The following is the structure of the alkane and its chloride derivatives.
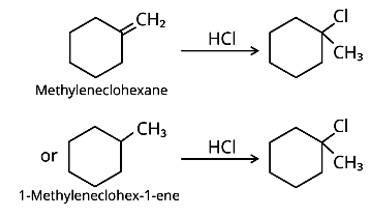
Name the alkene which will yield 1-chloro-1-methylcyclohexane by its reaction withHCl. Write the reactions involved.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Methylenecyclohexane and 1-methylcyclohex-1-ene are two chemicals that can produce 1-chloro-1-methylcyclohexane.
Which of the following haloalkanes reacts with aqueous ??? most easily? Explain giving reason.
(i) 1 -Bromobutane
(ii) 2 -Bromobutane
(iii) 2-Bromo-2-methylpropane
(iv) 2-Chlorobutane
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Nucleophilic substitutions occur when haloalkanes react with aqueous KOH. The tertiary halide 2-Bromo-2-methylpropane will react with aq. KOH the easiest of the compounds because the initial step involves cleavage of the alkyl and halide groups, resulting in the production of the extremely stable carbocation.
Why can aryl halides not be prepared by reaction of phenol with HCl in the presence of ZnCl2
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Phenol will not react with HCl in the presence of ZnCl2. This is owing to the presence of partial double bond properties between the benzene ring and O, which will result in resonance between the benzene ring and the OH - group. As a result, no aryl halide will be made.
Which of the following compounds would undergo SN1 reaction faster and why?
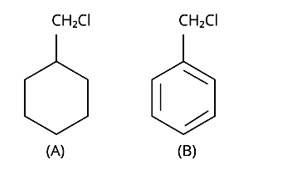
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Due to the resonance stabilisation of the benzyl ring, compound (B) would conduct the SN1 reaction faster than compound (A). The carbocation C6H5CH2Cl+ is very stable when the -Cl from the ring is cleaved, and it is driven to carry out the SN1 reaction.
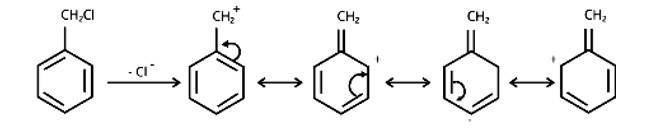
Allyl chloride is hydrolysed more readily than n -propyl chloride. Why?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In nature, allyl chloride becomes very reactive due to the production of carbocation, which is extremely stable due to resonance. Due to carbocation, there will be no such stability in the case of n-propyl chloride.
Why is it necessary to avoid even traces of moisture during the use of a Grignard reagent?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
RMgX+H2O→RH+Mg (OH)X
Because the Grignard reagents are very reactive in nature, even residues of moisture must be avoided. Even minute amounts of water can cause these reagents to generate hydrocarbons.
How do polar solvents help in the first step in SN1 mechanism?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The SN1 mechanism advances through the production of carbocation. The breakage of the C-halogen bond occurs during this phase. The solution of the halide ions is done with the protons of the protic solvent as a result. In this approach, polar solvents aid in the ionisation process by solvating the ions and stabilising them.
Write a test to detect the presence of double bond in a molecule.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The bromine water test and Bayer's test are two methods for detecting the presence of an unsaturated double bond in an organic molecule.
Bromine is added to the carbon atoms across the double bond in the bromine water test when the molecule is introduced to bromine water. Bromine water changes colour from orange to brown to colourless at the end of the process.
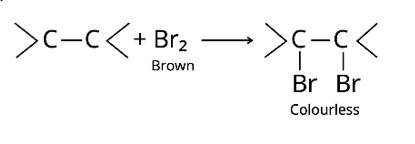
The alkaline KMnO4 is employed in Bayer's test to detect unsaturated carbon with a double bond. The chemical produces [O], which hydrolyzes the carbons across the double bond, resulting in a purple-to-colorless solution containing the two molecules.
2KMnO4+H2O→2KOH+2MnO2+3 [O]
Diphenyls are potential threat to the environment. How are these produced from arylhalides?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Diphenyls, such as p, p-dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT), which have been employed as organic pesticides, are a possible hazard to the environment since it was shown to have significant toxicity towards fish during its early years of widespread use, and many insects acquired resistance to it. The issue was exacerbated by DDT's chemical persistence and fat solubility. In terms of chemistry, DDT is not metabolised or solubilized well by mammals. The fatty tissues are where it is deposited and kept. DDT builds up within the animal over time if it is consumed at a constant pace, harming the ecosystem.
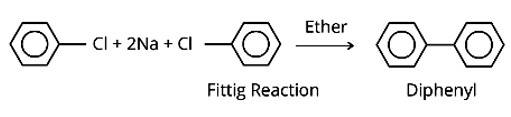
The following two techniques can be used to make di-phenyls from aryl halides:
(i) The aryl halides are reacted with sodium metal in the presence of dry ether to generate substituted aryl compounds, such as biphenyl compounds, in the Fittig reaction.
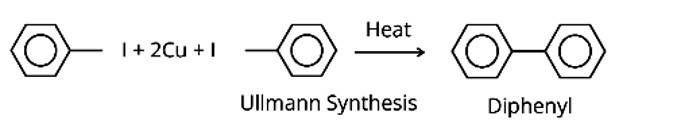
(ii) Aryl halides are heated in the presence of Cu to create biphenyl/diphenyl compounds in the Ullmann synthesis, which is a coupling process.
What are the IUPAC names of the insecticide DDT and benzene hexachloride? Why is their use banned in India and other countries?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The IUPAC names for DDT and benzene hexachloride are 2, 2-bis (4-chlorophenyl)-1, 1-trichloroethane and 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6-hexachlorocyclohexane, respectively.
They are poisonous and non-bio digestible at the same time. They are fat soluble, and their concentration in the food chain continues to rise. As a result, they are prohibited in India and other nations.
Elimination reactions (especially \beta -elimination) are as common as the nucleophilic substitution reaction in case of alkyl halides. Specify the reagents used in both cases.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Nucleophilic substitution and elimination (β-elimination) reactions are both possible with alkyl halides.
Although, with the appropriate reaction conditions and reagent selection, a specific product can be produced. In most cases, the elimination reaction is best suited to strong and bigger bases, as well as high temperatures. The substitution reaction, on the other hand, is best for weaker and smaller bases at lower temperatures.
CH3CH2Br+alc.KOH![]() KCH2=CH2 + HBr
KCH2=CH2 + HBr
CH3CH2Br + aqKOH→CH3CH2OH + KBr
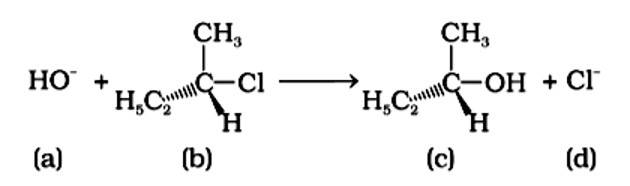
Tert-Butyl Bromide reacts with aq. NaOH by SN1 mechanism while n-butyl bromide reacts by SN2 mechanism. Why?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Tert-butyl bromide is substituted via the SN1 process because it may produce a stable carbocation in the first step after the halide group is cleaved. The nucleophile OH - interacts with the carbocation next. The primary halide n-butylbromide, on the other hand, is unable to create a stable carbocation, thus it undergoes the SN2 process, which is a one-step substitution involving OH - attack and concomitant X - leaving to generate n-butyl alcohol.
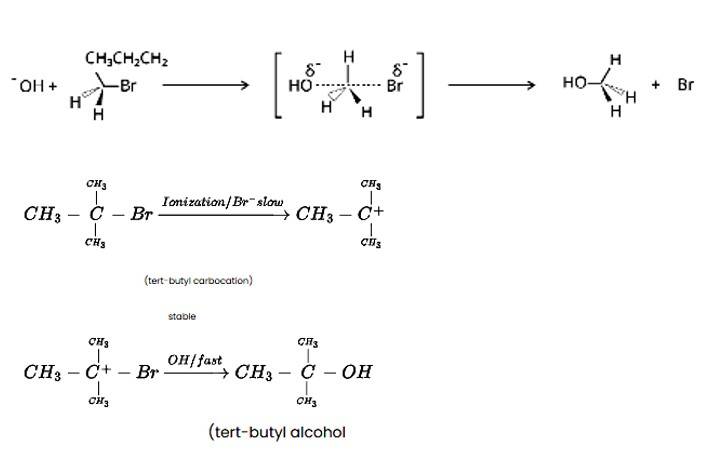
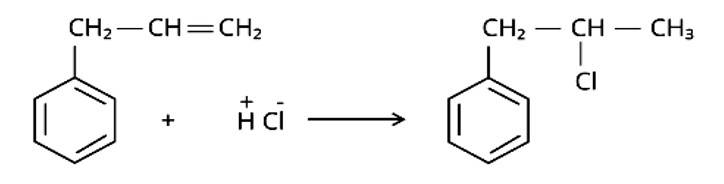
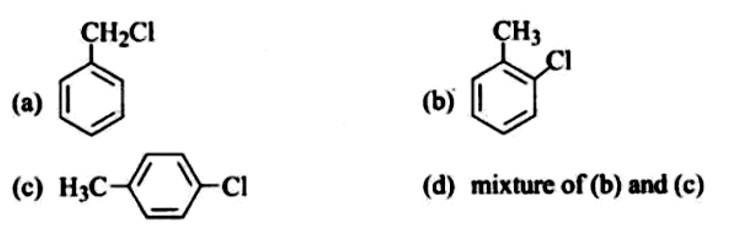
Predict the major product formed when HCl is added to isobutylene. Explain the mechanism involved.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The reaction of HCl and isobutylene is given as:
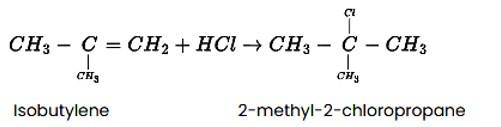
Steps in reaction involves are:
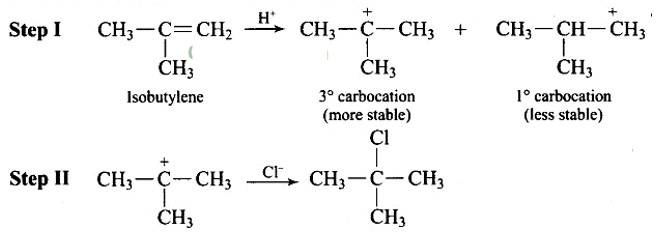
Discuss the nature of C—X bond in the haloarenes.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Resonance effect: Because the C – X bond has the characteristics of a partial double bond, it is extremely difficult to break.
(i) The C - X bond in haloarenes is extremely less reactive to nucleophilic groups
(ii) The C atom linked to the halogen is sp2 hybridised in the C – X bond. Carbon that has been sp2 hybridised with a higher s-character is more electronegative in nature and can retain the electron pair of the C - X bond more tightly than carbon that has been sp3 hybridised with a lower s -character in haloalkanes.
How can you obtain iodoethane from ethanol when no other iodine containing reagent except NaI is available in the laboratory?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In the presence of ZnCl2, ethanol can be treated with HCl to produce chloroethane. Iodoethane is formed when chloroethane reacts with NaI.
C2H5OH+HCl→ZnCl2? C2H5Cl→ NaI ? C2H5I
Cyanide ion acts as an ambident nucleophile. From which end it acts as a stronger nucleophile in aqueous medium? Give reason for your answer.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ambident nucleophiles are groups that include two nucleophilic centres, such as cyanide and nitrile. In the cyanide group, linkage can occur from both the carbon and nitrogen ends. The carbon end functions as a greater nucleophile in an aqueous media because it leads to the creation of a C-C sbond, which is stronger than a N-C bond in the identical molecule.
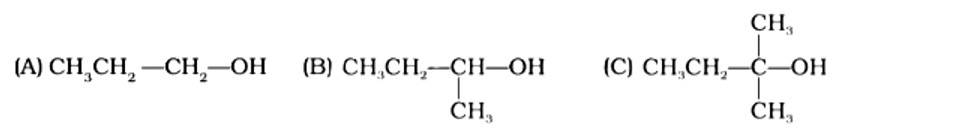
The order of reactivity of following alcohols with halogen acids is
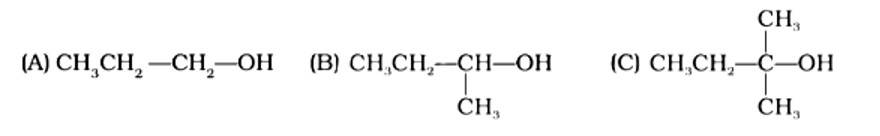
(i) (A) > (B) > (C)
(ii) (C) > (B) > (A)
(iii) (B) > (A) > (C)
(iv) (A) > (C) > (B)
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (ii). Haloalkanes are made by combining alcohols with halogen acids, in which the hydroxyl group of the alcohol is replaced by the halogen. Primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols are represented by options (A), (B), and (C). Tertiary alcohols are more reactive than secondary and primary alcohols, and they generate haloalkanes from haloacids without the need of catalysts at ambient temperature. Alcohols have a reactivity order of 3? >2? >1? . As a result, the proper option is (ii).
Which of the following alcohols will yield the corresponding alkyl chloride on reaction with concentrated HCl at room temperature?
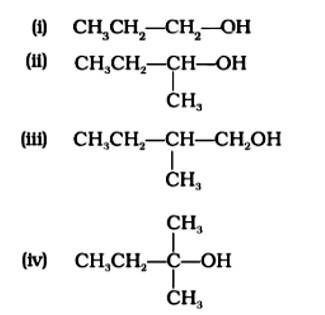
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (iv) Because the tertiary carbocation is the most stable, it interacts the most with concentrated HCl. As a result, for tertiary alcohol, room temperature is sufficient for the reaction. However, for primary and secondary alcohols, the presence of a catalyst (ZnCl2) is required.
As a result, option (iv) is accurate.
Toluene reacts with a halogen in the presence of iron (III) chloride giving ortho and para halo compounds. The reaction is
(i) Electrophilic elimination reaction
(ii) Electrophilic substitution reaction
(iii) Free radical addition reaction
(iv) Nucleophilic substitution reaction
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (ii). Toluene is an aromatic hydrocarbon (C6H5-CH3) that may be treated with halogens and utilised in an electrophilic substitution process to create aryl halides in the presence of the Lewis acid catalyst iron (III) chloride. In the absence of light, the reaction is carried out using chlorine or bromine, and the products are o- and p- haloarenes.
Which of the following is halogen exchange reaction?
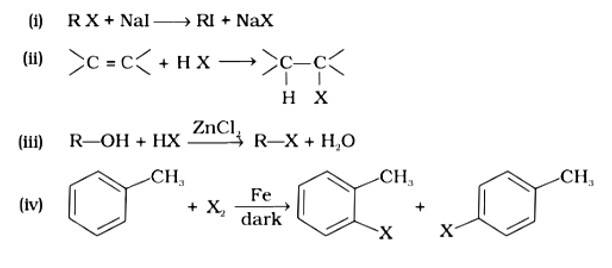
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (i)
The correct answer is option (i). Option (i) is an example of a Finklestein reaction, which is a halogen exchange reaction that produces alkyl iodide by treating alkyl halides with NaI in dry acetone. Option (ii) is an addition reaction in which an alkene is transformed to the equivalent alkyl halide. Option (iii) is a substitution reaction, whereas option (iv) is an electrophilic substitution reaction.
Which reagent will you use for the following reaction?
(i) Light
(ii) NaCl+H2SO4
(iii) Cl2 gas in dark
(iv) Cl2 gas in the presence of iron in dark
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The correct Answer is Option (i).
Chlorination in the presence of UV light can be used to produce alkyl chlorides from alkanes. Under the action of UV radiation, the chlorine molecule generates free radicals, which react with alkanes to create a mixture of isomeric mono- and poly haloalkanes.
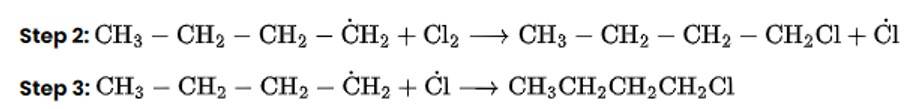
Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their densities.
(i) (a) < (b) < (c) < (d)
(ii) (a) < (c) < (d) < (b)
(iii) (d) < (c) < (b) < (a)
(iv) (b) < (d) < (c) < (a)
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (i).
Alkyl halides have a higher density than water. Their densities are determined by the masses of the halogen atoms, the number of halogen atoms, and the number of carbon atoms. Simply expressed, Br has an atomic mass of 79 while Cl has an atomic mass of 35. (d) will be the heaviest of the molecules, followed by (c), (b), and (a). Because density is exactly proportional to mass, the order of decreasing densities will be the same. The right answer is (i).
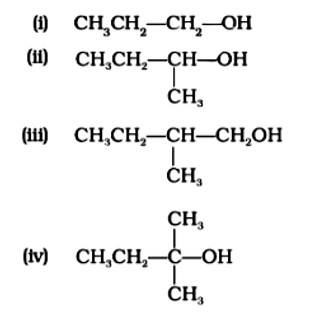
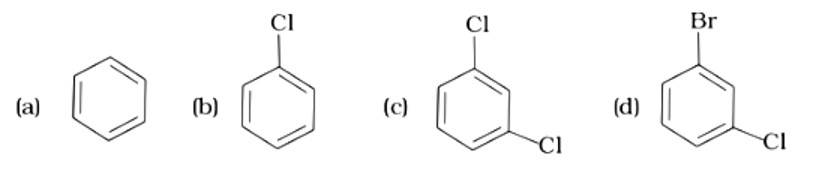
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their boiling points.
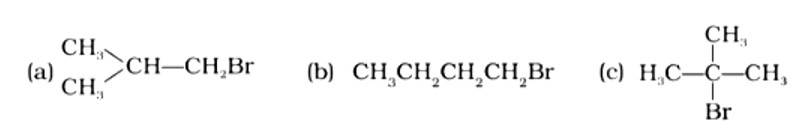
(i) (b) < (a) < (c)
(ii) (a) < (b) < (c)
(iii) (c) < (a) < (b)
(iv) (c) < (b) < (a)
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (iii).
Isomeric alkyl halides' boiling points are related to their branching, with a reduction in B.P. as branching increases. As a result, the boiling point of the tertiary isomer is the lowest, while that of the primary isomer is the highest. Thus, the order of lowering boiling points is (b) > (a) > (c).
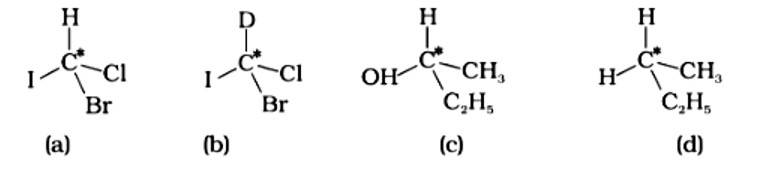
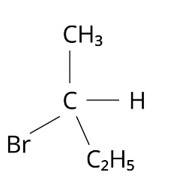
In which of the following molecules carbon atom marked with asterisk (*) is asymmetric?
(i) (a), (b), (c), (d)
(ii) (a), (b), (c)
(iii) (b), (c), (d)
(iv) (a), (c), (d)
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The correct answer is (ii).The mirror copies of the molecules (a), (b), and (c) are non-superimposable. Because all four species linked to the carbon atom are identical, molecule (d) cannot have an asymmetric carbon atom, thus the mirror image of (d) when rotated 180? is superimposable on the original picture.
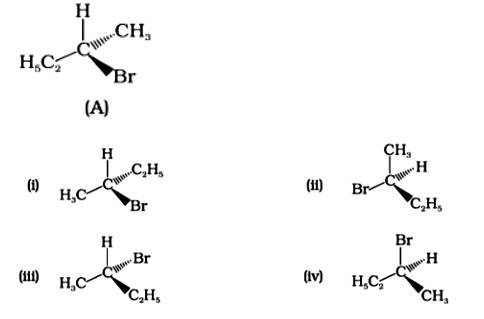
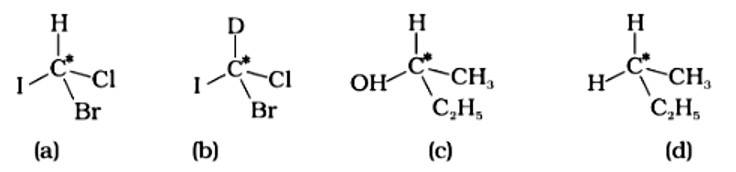
Which of the following structures is enantiomeric with the molecule (A) given below :
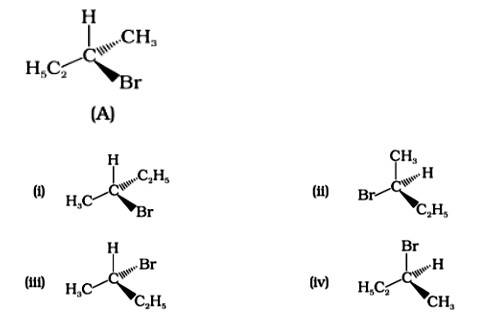
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (i).
Enantiomers are stereoisomers of a substance that are not superimposable on each other. The carbon atom in the molecule (A) is asymmetric. The molecule's mirror image (i) and 180? rotation cannot be superimposed on each other (A). The molecules (ii), (iii), and (iv) can all be superimposed on one other (A). The molecules (iii) and (iv) have 180? rotations that are superimposable on one another (A).
Which of the following is an example of vic-dihalide?
(i) Dichloromethane
(ii) 1,2 -dichloroethane
(iii) Ethylidene chloride
(iv) Allyl chloride
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (iv).
Geminal halides or gem-dihalides and vicinal halides or vic-dihalides are dihaloalkanes with the same halogen. Vic-dihalides are dihaloalkanes with halogen atoms on two adjacent carbon atoms, whereas Gem-dihalides are molecules with halogen atoms on two adjacent carbon atoms. Gem-dihalides are called alkylidene halides in the conventional naming system, whereas vic-dihalides are called alkylene dihalides. Because dichloromethane has just one carbon, it cannot contain neighbouring halogen atoms. Two carbon atoms are sandwiched between two halogen atoms in 1,2-dichloroethane. Ethylidene chloride is a gem-dihalide, as its name implies. There is only one chlorine atom in allyl chloride.
The position of −Br in the compound in CH3CH=CHC(Br)(CH3)2 can be classified as
(i) Allyl
(ii) Aryl
(iii) Vinyl
(iv) Secondary
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The correct answer is Option (i).
When the halogen atom is linked to an sp3-hybridised carbon atom next to an allylic carbon, a carbon-carbon double bond is formed.
Aryl halides are produced when a halogen atom is directly linked to an aromatic ring's sp2-hybridised carbon atom.
When a halogen atom is linked to a sp2-hybridised carbon atom in a carbon-carbon double bond, vinylic bonds are produced. Simply defined, it's an ethylene molecule with one hydrogen atom substituted by another -R group.
When the halogen is attached to a secondary carbon atom in the molecule, secondary bonds form. The −Br is linked to a tertiary carbon atom in the supplied molecule, which is then bonded to an sp3-hybridised carbon-carbon double bond. As a result, this −Br has an allylic position.
Chlorobenzene is formed by reaction of chlorine with benzene in the presence of .Which of the following species attacks the benzene ring in this reaction?
(i) Cl−
(ii) Cl+
(iii) AlCl3
(iv) [AlCl4]−
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The correct answer is option ii.
Aluminum chloride is a Lewis acid catalyst that functions similarly to FeCl3. By chlorinating benzene in the presence of AlCl3, benzene is transformed to chlorobenzene. Electrophilic substitution is used to carry out the reaction. Cl2 forms a coordination complex with AlCl3 called Cl + AlCl4- , which has a small positive charge on Cl and is negatively charged on AlCl4- . This Cl+ then interacts with the benzene ring's aromatic double bond to generate an addition product, followed by deprotonation to produce chlorobenzene, AlCl3, and HCl as side products. The best choice is (ii).
Ethylidene chloride is a/an
(i) Vic-dihalide
(ii) Gem-dihalide
(iii) Allylic halide
(iv) Vinylic halide
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (ii).
Dihaloalkanes with two halogen atoms of the same kind bonded to the same carbon atom are known as gem-dihalides. Alkylidene dihalides is the most frequent naming scheme for gem-dihalides. As a result, ethylidene dichloride is a gem-dihalide. The best choice is (ii).
A primary alkyl halide would prefer to undergo
(i) SN1 reaction
(ii) SN2 reaction
(iii) ?-Elimination
(iv) Racemisation
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (ii).
When an alkyl halide with -hydrogen atoms reacts with a base or a nucleophile, depending on the nature of the alkyl halide, the strength of the base or nucleophile, the size of the molecules, and the reaction circumstances, it can undergo a specific kind of reaction. A substitution or elimination process can be followed by an alkyl halide, as well as the two kinds of substitution, SN1 and SN2. Because the entering nucleophile cannot engage with the bulky substituents on or near the carbon atom, the main alkyl halide prefers the SN2reaction. As a result, primary alkyl halides and methyl halides have the greatest proclivity for SN2 reactions.
Which of the following alkyl halides will undergo SN1 reaction most readily?
(i) (CH3)3C−F
(ii) (CH3)3C −Cl
(iii) (CH3)3C −Br
(iv) (CH3)3C −I
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (iv).
SN1 reactions occur mostly in polar protic solvents such as H2O and follow first-order kinetics. This indicates that the reaction rate is solely determined by one reactant. Because of the great stability of the generated carbocation, this reaction favours tertiary alkyl halides. When a molecule is polarised in water, it generates a carbocation as well as a halide ion. The halides' reactivity is R-I > R-Br > R-Cl > > R-F. As a result, (CH3)3C-I will be the most likely to undergo the reaction.
Which is the correct IUPAC name for :
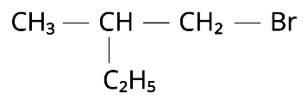
(i) 1-Bromo-2-ethylpropane
(ii) 1 -Bromo-2-ethyl-2-methylethane
(iii) 1 -Bromo-2-methylbutane
(iv) 2-Methyl-1-bromobutane
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (iii)
The correct answer is option iii.
First, we must determine which carbon chain is the longest. After that, we should have CH3-CH2-CH (CH3)-CH2-Br as the real structure. -Br, because the functional halide group is linked to the first carbon atom, we begin numbering there. The methyl group branch is joined to the chain's second carbon atom. Butane is named from the number of carbons in the unbranched parent chain, which is four. 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane is the name of the molecule. Option (iii) is the right answer.
What should be the correct IUPAC name for diethylbromomethane?
(i) 1 -Bromo- 1,1 -diethylmethane
(ii) 3-Bromopentane
(iii) 1-Bromo-1-ethylpropane
(iv) 1-Bromopentane
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (ii).
We may conclude from the given compound's common name that there are two -C2H5 groups and one -Br group linked to a CH4 molecule. Bromomethane would be represented by the symbol CH3-Br. Two ethyl groups can be replaced for the hydrogens in the methyl molecule to make diethylbromomethane (C2H5)CH (C2H5)Br. The longest parent chain must be identified in order to offer an IUPAC name. The parent chain is CH3-CH2-CH (Br)-CH2-CH3, with the -Br group from either side connected to the third carbon atom. Because the parent chain has five carbons, the molecule is termed 3-bromopentane.
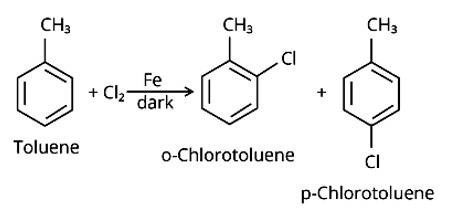
The reaction of toluene with chlorine in the presence of iron and in the absence of light yields:

This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (iv).
By electrophilic substitution, aromatic arenes react with chlorine in the presence of Lewis acid catalysts such as iron (III) chloride, yielding ortho and para isomers of haloarenes. (ii) and (iii) are both products of the reaction. Cl2 forms a coordination complex with FeCl3, creating the Cl + FeCl4 - complex, which has a small positive charge on Cl and a negative charge on FeCl4 - . This Cl+ then interacts with the aromatic double bonds of the toluene molecule to create an addition product, which is subsequently deprotonated to form a mixture of o-, p-, and m- chlorotoluene isomers. Because the m- isomer is highly unstable, the product is not accessible in the o- and p- forms.
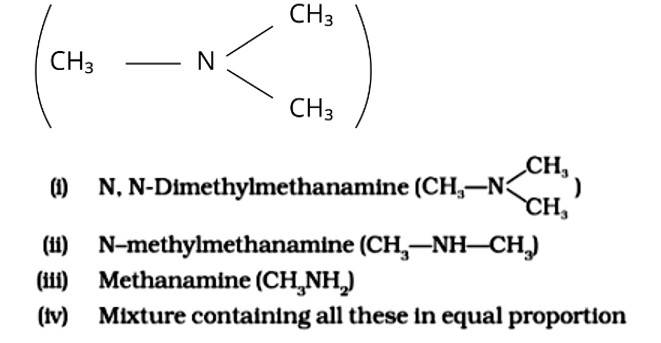
Chloromethane on treatment with excess of ammonia yields mainly
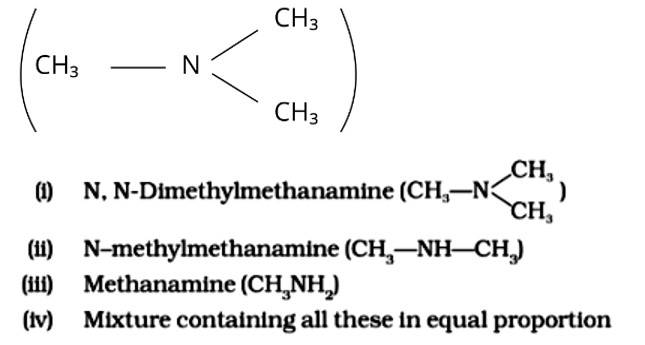
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (iii).
Because it possesses unpaired electrons, the ammonia molecule is a nucleophile in nature. By nucleophilic substitution, this nucleophile attacks the chloromethane molecule and forms methyl amine or methanamine. The carbon atom in the molecule is partially positive due to the electronegativity of the linked halide, which is partially negative. The positive ion is attacked by the electron-rich nucleophile, causing the halide ion to be detached from the molecule. The proper response is (iii).
Molecules whose mirror image is non super-imposable over them are known as chiral. Which of the following molecules is chiral in nature?
(i) 2-Bromobutane
(ii) 1-Bromobutane
(iii) 2-Bromopropane
(iv) 2-Bromopropan-2-ol
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (i).
The structure of 2-Bromobutane is depicted in the diagram below. Because all of the groups connected to the central carbon atom differ, the mirror image of the molecule cannot be superimposed on the original molecule.
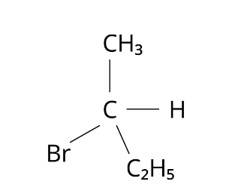
The structure of 1-Bromobutane is shown in the diagram below. Because there are just three groups that vary from one another, the molecule is not chiral in nature.
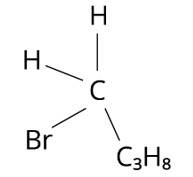
The structure of 2-Bromopropan-2-ol, shown below, has two identical species and hence cannot be chiral.

Reaction of C6H5CH2Br with aqueous sodium hydroxide follows
(i) SN1 mechanism
(ii) SN2 mechanism
(iii) Any of the above two depending upon the temperature of reaction
(iv) Saytzeff rule
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (i).
When benzyl chloride is treated with aqueous sodium hydroxide, where -OH is the nucleophile, a nucleophilic substitution reaction occurs, resulting in the formation of benzyl alcohol. The benzene ring is resonance stabilised here, and this stability is extended to the connected methylene group, giving a positive charge to -CH2, making the whole carbocation stable when the link between benzyl and bromide is broken. This is an SN1 reaction with two stages that is followed due to the stability of the carbocation. This is a coordinated reaction that takes place in two phases. The halide group first exits the carbocation, and then the nucleophile binds to the cation, producing alcohol. The right answer is (i).
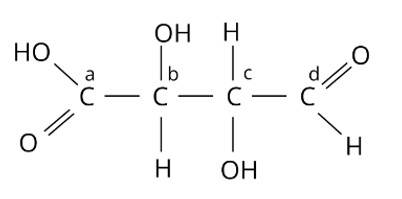
Which of the carbon atoms present in the molecule given below are asymmetric?
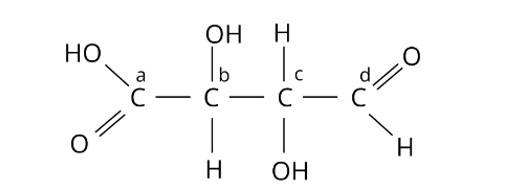
(i) a, b, c, d
(ii) b, c
(iii) a, d
(iv) a, b, c
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (ii).
Chiral molecules are made up of one carbon atom surrounded by four different species. Because of the presence of two or more identical groups, such as hydrogens, all straight chain molecules cannot be chiral. Even carbons with double or triple bonds to a group are not considered chiral. Through covalent connections, an asymmetric carbon must be surrounded by four distinct species. As a result, atoms b and c are asymmetric. The correct answer is option (ii).
Which of the following compounds will give racemic mixture on nucleophilic substitution by OH− ion?
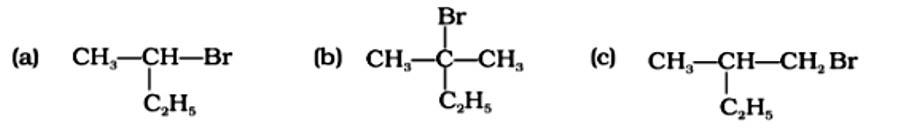
(i) (a)
(ii) (a), (b), (c)
(iii) (b), (c)
(iv) (a), (c)
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (i).
A racemic mixture is one that contains two enantiomers in equal quantities but has no optical activity because the opposing optical rotations of the two enantiomers cancel each other out. The optically active reactant undergoes the SN1 reaction in order for a racemic mixture to form following nucleophilic substitution. Option (a) is a chiral carbon atom that will undergo the SN1 process, resulting in a racemic mixture. Option (b) does not include an asymmetric carbon, but option (c) has a secondary carbon asymmetric atom that is less reactive to an SN1 substitution. The right answer is (i).
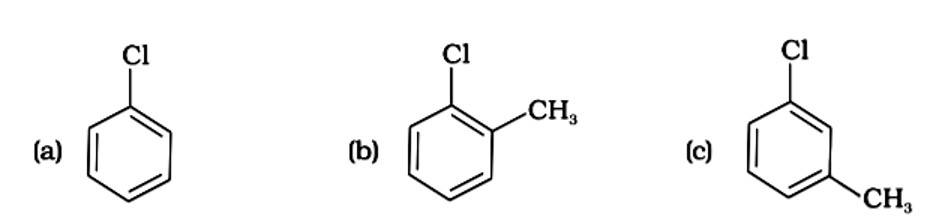
(i) (a) < (b) < (c)
(ii) (a) < (c) < (b)
(iii) (c) < (b) < (a)
(iv) (b) < (c) < (a)
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (iv).
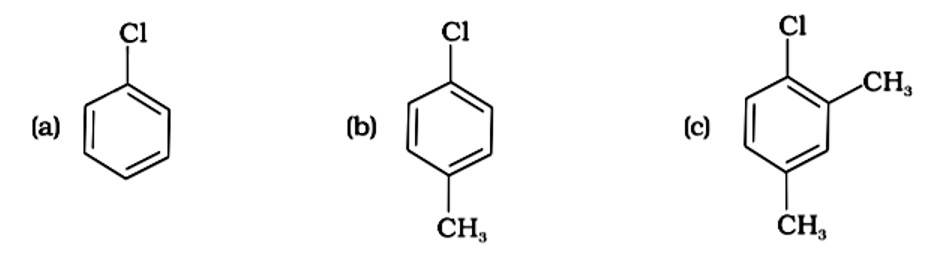
Because the -CH3 group is an electron releasing group, it reduces the reactivity of aryl halides in the ortho and para locations. As a result, aryl halides without electron releasing groups are more reactive. As a result, the order of reactivity is (a) > (c) > (d) (b). The right answer is (iv).
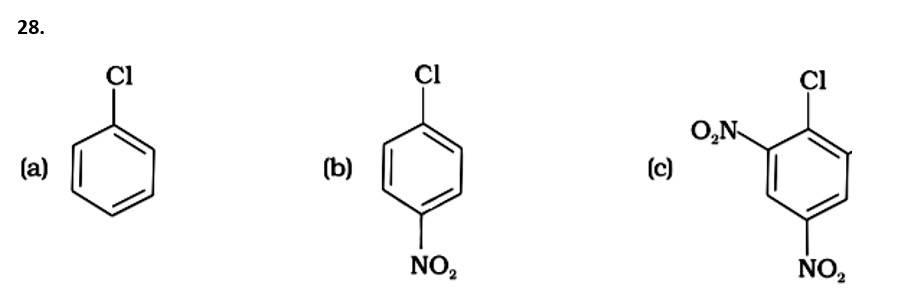
(i) (c) < (b) < (a)
(ii) (b) < (c) < (a)
(iii) (a) < (c) < (b)
(iv) (a) < (b) < (c)
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is option (iv).
( - NO2) is an electron-withdrawing group that induces nucleophilic substitution when it is in the ortho and para positions. When this identical electron-drawing group is in the meta position, its impact is much reduced. The reactivity of aryl halides rises as the number of electron-withdrawing groups increases. As a result, the greater the number of electron-drawing groups, the greater the rate of nucleophilic substitution.
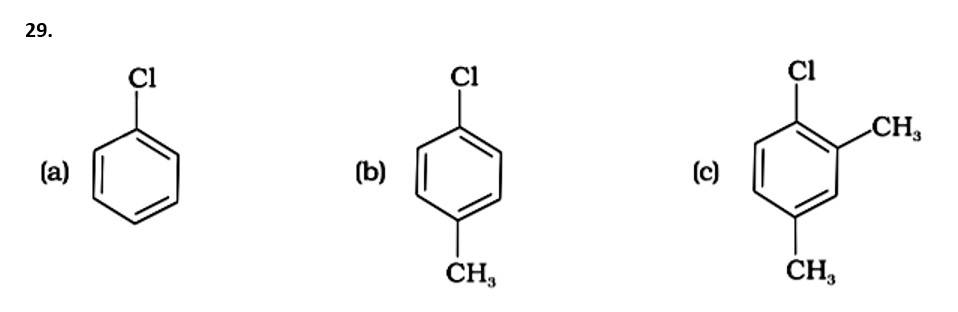
(i) (a) < (b) < (c)
(ii) (b) < (a) < (c)
(iii) (c) < (b) < (a)
(iv) (a) < (c) < (b)
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (iii).
The presence of electron releasing groups increases the reactivity of aryl halides; the fewer the electron releasing groups, the slower the rate of nucleophilic substitution. As a result, an increase in methyl groups decreases reactivity. The sequence of reactivity is (a) > (b) > (c). The right answer is (iii).
Which is the correct increasing order of boiling points of the following compounds?
1-Iodobutane, 1-Bromobutane, 1-Chlorobutane, Butane
(i) Butane < 1-Chlorobutane < 1-Bromobutane < 1-Iodobutane
(ii) 1-Iodobutane < 1-Bromobutane < 1-Chlorobutane < Butane
(iii) Butane < 1-Iodobutane < 1-Bromobutane < 1-Chlorobutane
(iv) Butane < 1-Chlorobutane < 1-Iodobutane < 1-Bromobutane
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (i).
The intermolecular force of attraction will grow as the surface area increases. As a result, the boiling point rises as well. The boiling point of a comparable alkyl halide rises with increasing molecular mass. Iodine has the greatest atomic mass. As a result, 1-iodobutane has the greatest boiling point.
Which is the correct increasing order of boiling points of the following compounds?
1-Bromoethane, 1-Bromopropane, 1-Bromobutane, Bromobenzene
(i) Bromobenzene < 1-Bromobutane < 1-Bromopropane < 1-Bromoethane
(ii) Bromobenzene < 1-Bromoethane < 1-Bromopropane < 1-Bromobutane
(iii) 1-Bromopropane < 1-Bromobutane < 1-Bromoethane < Bromobenzene
(iv) 1-Bromoethane < 1-Bromopropane < 1-Bromobutane < Bromobenzene
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (iv).
If the halogen atom in all of the supplied alkyl halides is the same kind, the boiling point of a compound rises as the number of alkyl groups added increases. As the quantity and size of molecules and electrons grow, so do their attractions. As a result, the greater the boiling point, the larger the molecular weight of the alkyl halide. The boiling points of the following compounds are listed in ascending order: 1-Bromoethane 1-Bromopropane 1-Bromobutane Bromobenzene The right answer is (iv).
In the following questions two or more options may be correct.
Consider the following reaction and answer the questions.
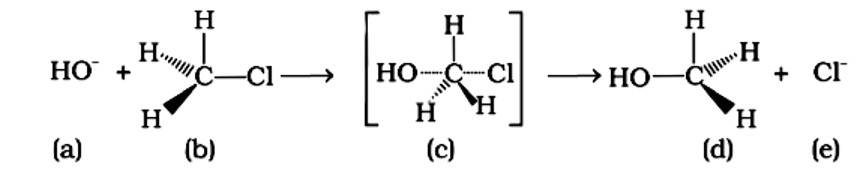
Which of the statements are correct about the above reaction?
(i) (a) and (e) both are nucleophiles.
(ii) In (c) carbon atom is sp3 hybridised.
(iii) In (c) carbon atom is sp2 hybridised.
(iv) (a) and (e) both are electrophiles.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
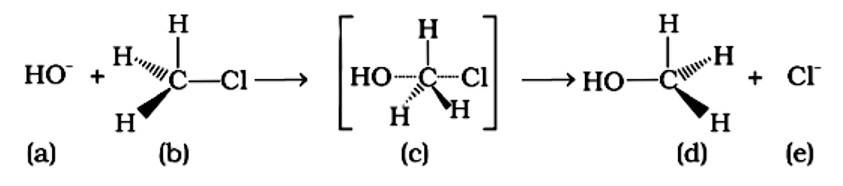
An SN2 nucleophilic substitution reaction occurs when CH3Cl interacts with the hydroxide ion to produce CH3OH. Both OH - and Cl - are nucleophiles with an excess of electrons in this reaction. Because the binding of OH - and the leaving of Cl - occurs simultaneously in the transition state (c), the carbon atom is linked to just three hydrogens. As a result, the carbon atom becomes sp2 hybridised. Aand (C) are the right statements.
Correct Answer: Option (A) and (C)
Which of the following statements are correct about this reaction?
(i) The given reaction follows the SN2 mechanism.
(ii) (b) and (d) have the opposite configuration.
(iii) (b) and (d) have the same configuration.
(iv) The given reaction follows the SN1 mechanism.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
An SN2 reaction, also known as a nucleophilic substitution, is the reaction in question. The entering nucleophile causes the groups surrounding the carbon atom to migrate in the opposite direction of the nucleophile, causing the configuration of alkyl halides to invert. As a result, (b) and (d) will be in the opposite order. This reaction is also SN2 since there is just one phase in which OH- is added and Cl- is removed at the same time. (i) and (ii) are the right answers.
Correct Answer: Option (A) and (B)
Which of the following statements are correct about the reaction intermediate?
(i) Intermediate (c) is unstable because in this carbon is attached to 5 atoms.
(ii) Intermediate (c) is unstable because carbon atom is sp2 hybridised.
(iii) Intermediate (c) is stable because carbon atom is sp2 hybridised.
(iv) Intermediate (c) is less stable than the reactant (b).
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Because the carbon atom is transiently linked to five atoms, the intermediate (iii) is less stable than reactant (ii), which is coupled to four groups.
Based on the following reaction.
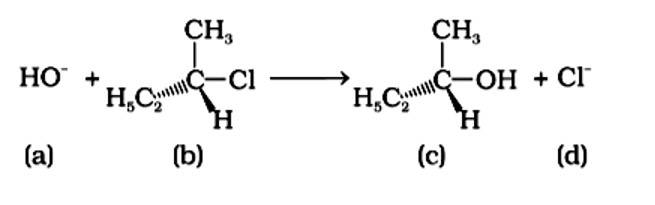
Which of the following statements are correct about the mechanism of this reaction?
(i) A carbocation will be formed as an intermediate in the reaction.
(ii) OH–will attach the substrate (b) from one side and Cl- will leave it simultaneously from the other side.
(iii) An unstable intermediate will be formed in which OH– and Cl– will be attached by weak bonds.
(iv) The reaction proceeds through an SN1 mechanism.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Because it is a tertiary alkyl halide, the described reaction is a nucleophilic substitution that follows the SN1 mechanism. It's a two-step process. The first step is the gradual breaking of a polarised C-Br bond, which results in the formation of a carbocation and a bromide ion. To complete the substitution, the stable intermediate carbocation is attacked by the nucleophile OH−. (i) and (iv) are the right statements.
Correct Answer: option (A) and (iv)
Which of the following statements are correct about the kinetics of this reaction?
(i) The rate of reaction depends on the concentration of only (b).
(ii) The rate of reaction depends on the concentration of both (a) and (b).
(iii) Molecularity of reaction is one.
(iv) Molecularity of reaction is two.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The reaction is of the type SN1 nucleophilic substitution. This sort of reaction is governed by second order kinetics, in which the rate of reaction is determined only by the concentration of the reactant. A reaction's molecularity is defined as the number of molecules involved in the rate-determining phase. Because of second order kinetics, the moleculeity of this reaction is one. (i) and (iii) are the right answers .
Correct Answer: Option (A) and (C)
Haloalkanes contain halogen atom (s) attached to the sp3 hybridised carbon atom of an alkyl group. Identify haloalkane from the following compounds.
(i) 2-Bromopentane
(ii) Vinyl chloride (chloroethene)
(iii) 2-chloroacetophenone
(iv) Trichloromethane
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (i) and (iv) have a halogen atom linked to an sp3 hybridised carbon that is single-bonded to other groups. The other possibilities are sp2 hybridised because they are linked to carbon atoms, which are coupled to other groups in double bonds. Option I and (iv) are both correct.
Correct Answer: Option (i) and (iv)
Ethylene chloride and ethylidene chloride are isomers. Identify the correct statements.
(i) Both the compounds form the same product on treatment with alcoholic KOH.
(ii) Both the compounds form the same product on treatment with aq.NaOH.
(iii) Both the compounds form the same product on reduction.
(iv) Both the compounds are optically active.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Isomers are ethylene chloride ClCH2-CH2Cl and ethylidene dichloride CH3-CHCl2. Because the carbon atoms are not surrounded by distinct groups, neither molecule is optically active. When haloalkanes are treated with alcoholic KOH, they undergo an elimination process in which a hydrogen atom from the -carbon atom and a halogen atom from the -carbon atom are eliminated. To form the ethyne molecule, each of these chemicals lose hydrogen and chlorine atoms. When exposed to aqueous NaOH, the molecules undergo nucleophilic substitution, with the –Cl groups being replaced by -OH molecules. The results will differ due to the locations of the halides on various carbon atoms.
Correct Answer: Option (i) and (iii)
Which of the following compounds are gem-dihalides?
(i) Ethylidene chloride
(ii) Ethylene dichloride
(iii) Methylene chloride
(iv) Benzyl chloride
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Dihaloalkanes with two halogen atoms linked to the same carbon atom are known as gem-dihalides. Alkylidene halides are another name for them. The chemical ethylene dichloride is a vicinal dihalide, meaning that chlorine atoms are linked to neighbouring carbon atoms. There is only one chlorine atom in benzoyl chloride. According to the molecule's nomenclature, ethylidene chloride is a gem-dihalide. The IUPAC terminology for methylene chloride is dichloromethane. Two chlorine atoms are joined to a single carbon atom in this compound.
Correct Answer: Option (i) and (iii)
Which of the following are secondary bromides?
(i) (CH3)2 CHBr
(ii) (CH3)3CCH2Br
(iii) CH3CH(Br)CH2CH3
(iv) (CH3)2CBrCH2CH3
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Checking with the carbon atom it is connected to is one way to see if a compound has a secondary bromide. In a molecule, a secondary carbon group is linked to one hydrogen atom and three non-hydrogen groups. As a result of the foregoing possibilities, secondary bromides are formed when the -Br group is linked to the -CH group. (i) and (iii) are the right answers.
Correct Answer: Option (i) and (iii)
Which of the following compounds can be classified as aryl halides?
(i) p-ClC6H4CH2CH(CH3)2
(ii) p-CH3CHCl(C6H4 )CH2CH3
(iii) o-BrH2C-C6H4CH(CH3)CH2CH3
(iv) C6H5 -Cl
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Aryl halides are halides in which the halogen atom is directly linked to the aromatic ring's sp2 hybridised carbon atom. Only (i) and (iv) contain halogen atoms directly linked to aryl rings among the choices. As a result, they are known as aryl halides. (i) and (ii) are the right answers (iv).
Correct Answer: Option (i) and (iv)
Alkyl halides are prepared from alcohols by treating with
(i) HCl + ZnCl2
(ii) Redp+Br2
(iii) H2SO4 + KI
(iv) All the above
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
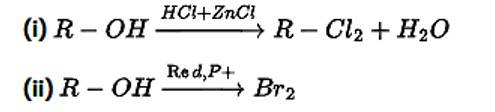
Correct Answer: Option (i) and (ii)
Alkyl fluorides are synthesised by heating an alkyl chloride/bromide in presence of ____________ or ____________.
(i) CaF2
(ii) CoF2
(iii) Hg2F2
(iv) Na
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Heat an alkyl chloride/bromide in the presence of a metallic fluoride such as AgF, Hg2F2, CoF2, or SbF3 to produce alkyl fluorides. Swarts reaction is the name given to this reaction. CoF2 and Hg2F2 are the only choices that work as reagents. NaF is not suitable because the end products of NaF + RCl→ RF + NaCl are soluble in the solvent, i.e. water, making separation difficult. As a result, the right alternatives are (ii) and (iii).
Correct Answer: Option (ii) and (iii)
Match the compounds given in Column I with the effects given in Column II.
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(i) Chloramphenicol |
(a) Malaria |
|
(ii) Thyroxine |
(b) Anaesthetic |
|
(iii) Chloroquine |
(c) Typhoid fever |
|
(iv) Chloroform |
(d) Goiter |
|
(e) Blood substituent |
This is a matching answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The medicinal uses are linked to the halogen derivatives. Chloramphenicol is an antibiotic used to treat typhoid fever, thyroxine is a hormone whose dysregulation causes goitre, chloroquine is a malaria medication, and chloroform is often used as an anaesthetic.
Correct Answer: (i) → (c) (ii) → (d) (iii) → (a) (iv) → (b)
Match the items of Column I and Column II.
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(i) SN1 reaction |
(a) vic-dibromides |
|
(ii) Chemicals in fire extinguisher |
(b) gem-dihalides |
|
(iii) Bromination of alkenes |
(c) Racemisation |
|
(iv) Alkylidene halides |
(d) Saytzeff rule |
|
(v) Elimination of HX from alkylhalide |
(e) Chlorobromocarbons |
This is a matching answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Racemization is the process of converting enantiomers into a racemic mixture, which is a mixture comprising two optically active enantiomers in equal quantities, from the results of the SN1 reaction. Chemical fire extinguishers are chlorobromocarbons.
Bromination of alkenes produces vic-dibromides, which are formed when halogen atoms of the same kind are linked to nearby carbon atoms of the molecule. Alkylidene dihalides, sometimes called gem-dihalides, are dihalides that have two halogen atoms bonded to the same carbon atom. The Saytzeff rule governs the removal of HX from alkyl halides: “In dehydrohalogenation processes, the desired product is that alkene with the greatest number of alkyl groups linked to the doubly bound carbon atoms.”
Correct Answer: (i) → (c) (ii) → (e) (iii) → (a) (iv) → (b) (v) → (d)
Match the structures of compounds given in Column I with the classes of compounds given in Column II.
|
Column I |
Column II |
| (i) |
(a) Aryl halide |
|
(ii) |
(b) Alkyl halide |
(iii) 
|
(c) Vinyl halide |
|
(iv) |
(d) Allyl halide |
This is a matching answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Because it includes a halogen atom bound to an sp3 hybridised carbon atom, which is subsequently linked to additional alkyl groups, the first molecule is an alkyl halide.
An allyl halide is a compound in which the halogen atom is linked to a carbon atom that is bound to an sp3 hybridised carbon atom that is attached to a carbon-carbon double bond.
The third molecule is an aryl halide, which is a chemical in which the halogen atom is sp2 hybridised with an aromatic ring carbon atom.
In a carbon-carbon double bond, the halogen atom is linked to a sp2 hybridised carbon atom in the fourth molecule, a vinyl halide.
Correct Answer: (i) → (b) (ii) → (d) (iii) → (a) (iv) → (c)
Match the reactions given in Column I with the types of reactions given in Column II.
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
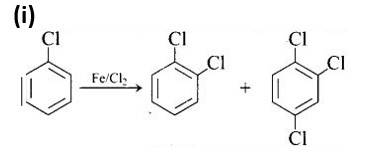
|
(a) Nucleophilic aromatic |
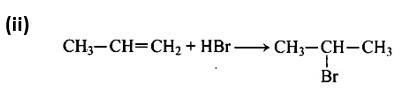 |
(b) Electrophilic aromatic substitution |
 |
(c) Saytzeff elimination |
 |
(d) Electrophilic addition |
|
|
(e) Nucleophilic substitution |
This is a matching answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The first reaction is an electrophilic substitution process in which Cl+ from the Cl2 and FeCl3 combination attacks and substitutes the benzene ring.
Following Markownikoff's rule, the second reaction is an electrophilic addition reaction in which HBr is added across the double bond.
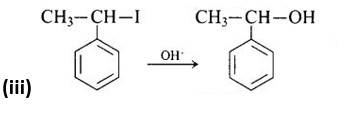
The third reaction is a nucleophilic substitution process that uses the SN1 mechanism to replace the -I group with -OH.
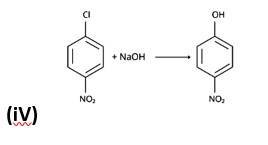
The nucleophilic aromatic substitution process, in which the -Cl group is replaced by -OH, is the fourth reaction.The fifth reaction is a dehydrohalogenation reaction, in which the alkyl halide is eliminated by Saytzeff.
Correct Answer: (i) → (b) (ii) → (d) (iii) → (e) (iv) → (a) (v) → (c)
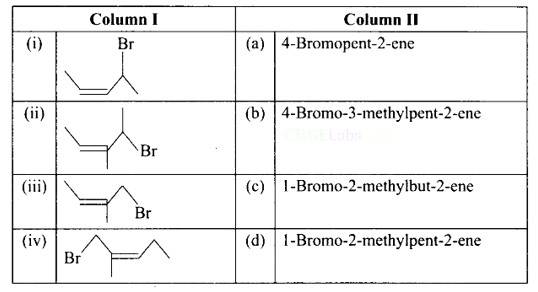
Match the structures given in Column I with the names in Column II.
This is a matching answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) A: 4-bromopent-2-ene.
(ii) B: 4-bromo-3-methylpent-2-ene.
(iii) C: 1-bromo-2-methylbut-2-ene.
(iv) D: 1 -bromo-2-methylpent-2-ene.
Correct Answer: (i) → (a) (ii) → (c) (iii) → (b) (iv) → (d)
Match the reactions given in Column I with the names given in Column II.
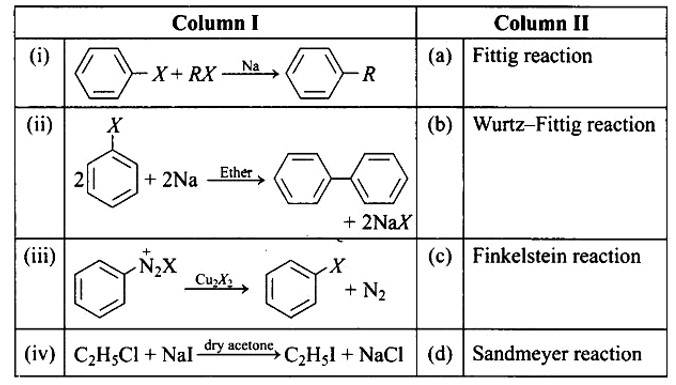
This is a matching answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In the presence of Na metal in dry ether, an alkyl halide and an aryl halide combine to create alkyl arene in the Wurtz-Fittig reaction.
The Fittig reaction, which involves a coupling reaction between two aryl halides in dry ether in the presence of Na metal, yielding diaryl compounds, is the second reaction.
The Sandmeyer reaction produces aryl halides from primary amines by converting them to diazonium salts and treating them with cuprous bromide.
The Finkelstein reaction, which produces alkyl iodides by reacting alkyl chlorides or bromides with NaI in dry acetone, is the fourth process.
Correct Answer: (i) → (b) (ii) → (a) (iii) → (d) (iv) → (c)
In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion : Phosphorus chlorides (tri and penta) are preferred over thionyl chloride for the preparation of alkyl chlorides from alcohols.
Reason : Phosphorus chlorides give pure alkyl halides.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
(ii) Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
(iii) Assertion is correct but reason is wrong statement.
(iv) Assertion is wrong but reason is correct statement.
(v) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
This is a assertion and reason answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Thionyl chloride is favoured over phosphorus chlorides because the by-products produced, in addition to the alkyl halides, include SO2 and HCl, which are gaseous and so may escape the reaction, leaving just pure halides.
Correct Answer: Option (ii)
Assertion: The boiling points of alkyl halides decrease in the order: RI>RBr>RCl>RF
Reason : The boiling points of alkyl chlorides, bromides and iodides are considerably higher than that of the hydrocarbon of comparable molecular mass.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
(ii) Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
(iii) Assertion is correct but reason is wrong statement.
(iv) Assertion is wrong but reason is correct statement.
(v) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
This is a assertion and reason answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Because of the size of the halogen atom, the boiling temperatures of alkyl halides drop in the specified sequence. With the greatest atomic number, iodide has the most electrons, resulting in increased Van Der Waals forces and a higher boiling point.
Correct Answer: Option (v)
Assertion: KCN reacts with methyl chloride to give methyl isocyanide
Reason: CN− is an ambident nucleophile.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
(ii) Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
(iii) Assertion is correct but reason is wrong statement.
(iv) Assertion is wrong but reason is correct statement.
(v) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
This is a assertion and reason answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Haloalkanes react with AgCN to produce alkyl isocyanides as the primary product, whereas KCN produces alkyl cyanides.
Correct Answer: Option (iv)
Assertion: tert-Butyl bromide undergoes Wurtz reaction to give 2,2,3,3-tetramethylbutane.
Reason : In the Wurtz reaction, alkyl halides react with sodium in dry ether to give hydrocarbons containing double the number of carbon atoms present in the halide.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
(ii) Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
(iii) Assertion is correct but reason is wrong statement.
(iv) Assertion is wrong but reason is correct statement.
(v) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
This is a assertion and reason answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Because tertiary butyl bromide interacts with NaI in dry ether to create 2, 3, 3-tetramethylbutane, it undergoes the Wurtz reaction to yield 2, 3, 3-tetramethylbutane.
Correct Answer: Option (i)
Assertion: Presence of a nitro group at ortho or para position increases the reactivity of haloarenes towards nucleophilic substitution.
Reason : Nitro group, being an electron withdrawing group decreases the electron density over the benzene ring.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
(ii) Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
(iii) Assertion is correct but reason is wrong statement.
(iv) Assertion is wrong but reason is correct statement.
(v) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
This is a assertion and reason answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The nitro group on the ortho and para positions of haloarenes acts as an electron-withdrawing group, making it more reactive to nucleophilic substitution reactions due to the electron deficit.
Correct Answer: Option (i)
Assertion : In monohaloarenes, further electrophilic substitution occurs at ortho and para positions.
Reason : Halogen atom is a ring deactivator.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
(ii) Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
(iii) Assertion is correct but reason is wrong statement.
(iv) Assertion is wrong but reason is correct statement.
(v) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
This is a assertion and reason answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Because halogen atoms are ortho and para directing, rather than ring deactivators, further electrophilic substitution occurs at ortho and para locations.
Correct Answer: Option (v)
Assertion: Aryl iodides can be prepared by reaction of arenes with iodine in the presence of an oxidising agent.
Reason : Oxidising agent oxidises I2 into HI.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
(ii) Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
(iii) Assertion is correct but reason is wrong statement.
(iv) Assertion is wrong but reason is correct statement.
(v) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
This is a assertion and reason answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Oxidising chemicals such as HIO3 oxidise HI to I2 because the presence of HI causes the aryl iodides to revert to arenes in their absence.
Correct Answer: Option (iii)
Assertion- It is difficult to replace chlorine by −OH in chlorobenzene in comparison to that in chloroethane.
Reason: Chlorine-carbon (C−Cl) bond in chlorobenzene has a partial double bond character due to resonance.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
(ii) Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
(iii) Assertion is correct but reason is wrong statement.
(iv) Assertion is wrong but reason is correct statement.
(v) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
This is a assertion and reason answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Due to resonance, a partial double bond character occurs in the bond between the C and Cl atoms in chlorobenzene, and we all know that changing a partial double bond character is more difficult than replacing a single bond as in the C - Cl bond in chloroethane.
Correct Answer: Option (i)
Assertion : Hydrolysis of (−)−2-bromooctane proceeds with inversion of configuration.
Reason : This reaction proceeds through the formation of a carbocation.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
(ii) Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
(iii) Assertion is correct but reason is wrong statement.
(iv) Assertion is wrong but reason is correct statement.
(v) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
This is a assertion and reason answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The SN2 mechanism is demonstrated by the hydrolysis of alkyl halides with inversion of configuration. This is a one-step method that does not need the production of carbocation.
Correct Answer: Option (iii)
A certain element crystallises in a bcc lattice of unit cell edge length 27 Å . If the same element under the same conditions crystallises in the fcc lattice, the edge length of the unit cell in Å will be ___________. (Round off to the nearest Integer).
[Assume each lattice point has a single atom] [Assume √3 = 1.73, √2 = 1.41]
Edge length in bcc, a? = 27 Å
Let, Edge length in fcc be a? Å
Now, the same element crystallises in bcc as well as fcc.
For bcc: 4r = √3 a? ⇒ r = (√3 / 4) a?
For fcc: 4r = √2 a? ⇒ r = a? / (2√2)
So, (√3 / 4) a? = a? / (2√2)
(√3 / 4) × 27 = a? / (2√2)
a? = 33.13 Å
The nearest integer is 33.
2MnO-4 + bC2O2-4 + cH+ xMn2+ + yCO2 + zH2O
If the above equation is balanced with integer coefficients, the value of c is_________.
(Round off to the nearest Integer).
The balanced equation is:
2MnO? + 5C? O? ²? + 16H? → 2Mn²? + 10CO? + 8H? O
So, the value of c (coefficient for H? ) = 16.
Two salts A2X and MX have the same value of solubility product of 4.0 x 10-12. The ratio of their molar solubilities i.eS A2X/S MX = ____________.
(Round off to the Nearest Integer).
Solubility product of A? X = 4S? ³
Where S? is the solubility of salt A? X.
Solubility product of MX = S? ²
Where S? is the solubility of MX.
Given 4S? ³ = 4 × 10? ¹² ⇒ S? = 10? M
Given S? ² = 4 × 10? ¹² ⇒ S? = 2 × 10? M
So, S? / S? = 10? / (2 × 10? ) = 50
Complete combustion of 750g of an organic compound provides 420 g of CO2 and 210 g of H2O.
The percentage composition of carbon and hydrogen in organic compound is 15.3 and _________ respectively. (Round off to the nearest Integer).
Moles of carbon in organic compound = Moles of carbon in CO?
n_c = 420 / 44 moles
Mass of carbon in organic compound = (420 / 44) × 12 = 114.54 g
Moles of hydrogen in compound = 2 × moles of H? O
n_H = 2 × (210 / 18) moles
Mass of hydrogen = 2 × (210 / 18) g = 23.33 g
% of H = (23.33 / 750) × 100 = 3.11%
The nearest integer is 3.
A 6.50 molal solution of KOH (aq) has a density of 1.89 g cm-3. The molarity of the solution is________ mol dm-3. (Round off to the nearest Integer).
[Atomic masses : K = 39.0u, O = 16.0u, H= 1.0u]
A 6.5 molal solution means 6.5 moles of KOH is in 1 kg (1000 g) of solvent (H? O).
Moles of solute, n_B = 6.5
Mass of solute, W_B = 6.5 × 56 = 364 g
Mass of solvent, W_A = 1000 g
Mass of solution = 1364 g
Volume of solution = 1364 / 1.89 mL
Now, molarity = [6.5 / (1364 / 1.89)] × 1000 M = 9 M
AB2 is 10% dissociated in water to A2+ and B-. The boiling point of a 10.0 molal aqueous solution of AB2 is_________ °C. (Round off to the nearest Integer).
[Given : Molal elevation constant of water Kb = 0.5 K kg mol-1, boiling point of pure water = 100°C]
m = 10 molal
K_b = 0.5 K kg mol? ¹
Using: ΔT_b = I K_b m
and α = (i - 1) / (n - 1)
n for AB? is 3; α = 0.1
0.1 = (i - 1) / (3 - 1) ⇒ I = 1.2
ΔT_b = 1.2 × 0.5 × 10 = 6 °C
So, boiling point of solution = 100 + 6 = 106 °C
For the reaction A(g) B(g) at 495 K, ΔrGo = -9.478kJ/mol. If we start the reaction in a closed container at 495 K with 22 millimoles of A, the amount of B in the equilibrium mixture is __________ millimoles
(Round off to the nearest Integer). [R=8.314 J/mol K; ln 10 = 2.303]
ΔG° = -9.478 kJ/mol
Using ΔG° = -2.303 RT log K_p
-9.478 × 10³ = -2.303 × 8.314 × 495 log K_p
1 = log K_p ⇒ K_p = 10
Here, for the given reaction A (g)? B (g), K_p = K_c
Initial A = 22 mmol
At equilibrium A = 22 - x mmol; B = x mmol
K_c = [B] / [A] = (x/V) / (22-x)/V) = x / (22-x) = 10
x = 10 (22-x) ⇒ x = 220 - 10x ⇒ 11x = 220 ⇒ x = 20
So, mmol of B at equilibrium are 20.
The equivalents of ethylene diamine required to replace the neutral ligands from the coordination sphere of the trans-complex of CoCl3.4NH3 is _________.
(Round off to the Nearest Integer).
The complex CoCl? ·4NH? is represented as [CoCl? (NH? )? ]Cl.
Here, 4 NH? are neutral monodentate ligands. So, 2 equivalents of ethylene diamine replace 4NH? since ethylene diamine is a didentate ligand.
The decomposition of formic acid on gold surface follows first order kinetics. If the rate constant at 300 K is 1.0x10-3 /s and the activation energy Ea = 11.488 kJ/mol, the rate constant at 200 K is ___________ x10-5 /s. (Round off to the nearest Integer).
[Given R = 8.314 J/molK]
T? = 300 K; K? = 1 × 10? ³ s? ¹
T? = 200 K; K? =?
E_a = 11.488 kJ/mol
Using Arrhenius equation:
log (K? /K? ) = (E_a / 2.303R) × [ (T? - T? ) / (T? )]
log (K? / 10? ³) = (11.488 × 10³ / (2.303 × 8.314) × [ (-100) / (6 × 10? )]
log (K? / 10? ³) = -1
K? / 10? ³ = 10? ¹
K? = 10? s? ¹ or K? = 10 × 10? s? ¹
When light of wavelength 248 nm falls on a metal of threshold energy 3.0eV, the de-Broglie wavelength of emitted electrons is__________ Angstrom.
K.E = φ - φ?
φ? = 3 eV = 3 × 1.6 × 10? ¹? J = 4.8 × 10? ¹? J
φ = hc/λ = (6.63 × 10? ³? × 3 × 10? ) / (248 × 10? ) J = 8 × 10? ¹? J
K.E = 8 × 10? ¹? - 4.8 × 10? ¹? = 3.2 × 10? ¹? J
Now using, λ = h / √ (2 K.E m)
λ = (6.63 × 10? ³? ) / √ (2 × 3.2 × 10? ¹? × 9.1 × 10? ³¹) m
λ = (6.63 × 10? ³? ) / (7.63 × 10? ²? ) m = 0.87 × 10? m = 8.7 Å
So, the nearest integer is 9.
28th June 2022(First Shift)
28th June 2022(First Shift)
Commonly asked questions
Given below are two statements:
Statement I : is square planar and diamagnetic complex, with dsp2 hybridizatin for Ni but is tetrahedral, paramagnetic and with sp3 hybridization for Ni.
Statement II : both have same d-electron configuration have same geometry and are paramagnetic.
In light the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
CN is strong field ligand
Here; is square planar and diamagnetic.
Ni = 4s23d8Co is strong field ligand.
Here ; is tetrahedral and diamagnetic
has 3d8 configuration while has 3d10 configuration.
The major product (P) in the reaction
Consider the image below
The correct structure of product ‘A’ formed in the following reaction, 
Consider the following image
Identify the major product formed in the following sequence of reactions:
Consider the image below
The incorrect statement about the imperfections in solids is
· Density of solid decreases in Schottky defect and vacancy defect.
· Density of solid increases in interstitial defect.
· Density of solid remain unchanged in Frenkel defect.
Dihydrogen reacts with CuO to give
A 2.0g sample containing MnO2 is treated with HCl liberating Cl2. The Cl2 gas is passed into a solution of Kl and 60.0mL of 0.1M Na2S2O3 is required to titrate the liberated iodine. The percentage of MnO2 in the sample is_______. (Nearest integer)
[Atomic masses (in u) Mn = 55; Cl = 35.5; O = 16, I = 127, Na = 23, K = 39, S = 32]
Here, meq of MnO2 = meq of Na2S4O6
Mass of MnO2 in sample = 0.261 g
Percentage of MnO2 in sample =
= 13.05%
The quantity of electricity in Faraday needed to reduce 1 mol of to Cr3+ is________.
Here, 6F electricity is required to reduce 1 mol
For a first order reaction A→B, the rate constant, k = 5.5 × 10-14s-1. The time required for 67% completion of reaction is x × 10-1 times the half life of reaction. The value of x is ________ (Nearest integer)
(Given : log 3 = 0.4771)
Rate constant, k = 5.5 × 10-14 s-1.
=
From (i) & (ii)
= 1.58 t50%
So; t67% is 15.8 × 10-1 times half life.
X = 16 (the nearest integer)
Number of complexes which will exhibit synergic bonding amongst and is_______________.
All metal carbonyls have synergic bonds.
In the estimation of bromine, 0.5g of an organic compound gave 0.40g of silver bromide. The percentage of bromine in the given compound is____________% (Nearest integer)
(Relative atomic masses of Ag and Br are 18 u and 80 u, respectively).
Organic compound → AgBr (s)
0.5 g 0.40 g
Here; Moles of Br in organic compound = Moles of Br in Ag Br
= Moles of AgBr
=
Mass of Br in organic compound =
The Zeta potential is related to which property of colloids
Potential difference between fixed layer and mobile layer of lyophobic colloid is called zeta potential or electro kinetic potential.
This potential difference is related to charge on the surface of colloidal particles.
Element “E” belongs to the period 4 and group 16of the periodic table. The valence shell electron configuration of the element, which is just above “E” in the group is
General valence shell electronic configuration of group 16 elements is ns2np4. For 3rd period element which is above element “E” is 3s23p4
Given are two statements one is labeled as Assertion A and other is labeled as Reason R.
Assertion A : Magnesium can reduce Al2O3 at a temperature below 1350°C, while above 1350°C aluminium can reduce MgO
Reason R : The melting and boiling points of magnesium are lower thatn those of aluminium.
In light of the above statements, choose most appropriate answer for the options given below
Below 1350° C, Mg can reduce Al2O3 and above 1350°C, Al can reduce MgO (from Ellingham diagram).
Melting and boiling point of Mg are lower than that of Al.
Nitrogen gas is obtained by thermal decomposition of
N2 gas is obtained by thermal decomposition of Ba (N3)2 as,
Given below are two statements:
Statement I : The pentavalent oxide of group-15 element, E2O5, is less acidic than trivalent oxide, E2O3, of the same element.
Statement II : The acidic character of trivalent oxide of group 15 elements, E2O3 decreases down the group.
In light of the above statements, choose most appropriate answer form the options given below
Pentavalent oxides of group – 15 elements, E2O5 is more acidic than trivalent oxides, E2O3 of the same element.
Acidic strength of trivalent oxides decreases down the group as metallic strength increases.
Which one of the lanthanoids given below is the most stable in divalent form?
Valence shell electronic configuration of Eu in +2 O.S is,
It has half filled f-sub shell and stable.
Which amongst the following is not a pesticide?
DDT, organophosphates and dieldrin are pesticides.
Which one of the following techniques is not used to spot components of a mixture separated in thin layer chromatographic plate?
In thin layer chromatography, the spots of colourless compounds, which are invisible to eyes can be detected by putting the plate under UV light.
Another detection technique is to place the plate in a covered jar containing I2 (s). Sometimes an appropriate reagent may also be sprayed on the plate, ninhydrin in case of amino acids
Which one of the following structures are aromatic in nature?
A primary aliphatic amine on reaction with nitrous acid in cold (273K) and there after raising temperature of reaction mixture to room temperature (298K), gives a / an
1° aliphatic amine Diazonium salt Alcohol
Which one of the following is NOT a copolymer?
Copolymer is the polymer formed by two or more monomers having multiple bonds.
Buna – S, PHBV and butadiene – styrene are copolymers. Neoprene is homopolymer.
Stability of α- Helix structure of proteins depends upon
Helix (2°) structure of protein is stabilized by intermolecular H-bonding.
The formula of the purple colour formed in Laissaigne’s test for sulphur using sodium nitroprusside is
If the work function of a metal is 6.63 × 10-19J, the maximum wavelength of the photon required to remove a photoelectron from the metal is _______nm. (Nearest integer)
[Given h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js, and c = 3 × 108 ms-1]
Work function,
Threshold wavelength
Using ;
= 300 × 109 m = 300 nm
The hybridization of P exhibited in PF5 is spxdy. The value of y is
Hybridization of P in PF5 is sp3d, so value of y = 1.
4.0 L of an ideal gas is allowed to expand isothermally into vacuum until the total volume is 20L. The amount of heat absorbed in this expansion is _________L atm.
For expansion in vacuum, workdone, w = 0
For isothermal process,
According to first law of thermodynamics,
The vapour pressure of two volatile liquid A and B at 25°C are 50 Torr and 100 Torr, respectively. If the liquid mixture contains 0.3 mole fraction of A, then the mole fraction of liquid B in the vapour phase is The value of x is____________.
Mole fraction of A in liquid phase, xA = 0.3
Mole fraction of B in liquid phase, xB = 0.7
Now;
= 100 × 0.7 = 70 torr
Mole fraction of B in vapour phase,
X = 14
The solubility product of a sparingly soluble salt A2X3 is 1.1 × 10-23. If specific conductance of the solution is 3 × 10-1, the limiting molar conductivity of the solution is x × 10-3 S m2 mol-1. The value of x is_________.
Using ; ksp = 108 S5
1.1 × 10-23 = 108 S5
S =
Specific conductance,
= 3 × 10-3 Sm2 mol-1
So; x = 3
Which one of the following compounds in inactive towards SN1 reaction?
Consider the image below
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Multiple Choice Type Questions
| 1. The order of reactivity of following alcohols with halogen acids is (i) (A) > (B) > (C) (ii) (C) > (B) > (A) (iii) (B) > (A) > (C) (iv) (A) > (C) > (B) |
| Ans: The Correct Answer is Option (ii). Haloalkanes are made by combining alcohols with halogen acids, in which the hydroxyl group of the alcohol is replaced by the halogen. Primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols are represented by options (A), (B), and (C). Tertiary alcohols are more reactive than secondary and primary alcohols, and they generate haloalkanes from haloacids without the need of catalysts at ambient temperature. Alcohols have a reactivity order of 3∘>2∘>1∘. As a result, the proper option is (ii). |
| 2. Which of the following alcohols will yield the corresponding alkyl chloride on reaction with concentrated HCl at room temperature? |
| Ans: The Correct Answer is Option (iv)Because the tertiary carbocation is the most stable, it interacts the most with concentrated HCl. As a result, for tertiary alcohol, room temperature is sufficient for the reaction. However, for primary and secondary alcohols, the presence of a catalyst (ZnCl2) is required. As a result, option (iv) is accurate. |
| 3. Identify the compound Y in the following reaction. |
| Ans: The correct answer is (i). Sandmeyer's reaction can be used to synthesise haloarenes from amines. A primary aromatic amine that has been dissolved or suspended in cold aqueous mineral acid is treated with sodium nitrite to create a diazonium salt in this procedure. When this freshly produced salt is combined with cuprous chloride, the diazonium group is replaced with - Cl, resulting in aryl chloride. Option I is the chemical Y, which is an aryl chloride. |
| 4. Toluene reacts with a halogen in the presence of iron (III) chloride giving ortho and para halo compounds. The reaction is (i) Electrophilic elimination reaction (ii) Electrophilic substitution reaction (iii) Free radical addition reaction (iv) Nucleophilic substitution reaction |
| Ans: The Correct Answer is Option (ii). Toluene is an aromatic hydrocarbon (C6H5---CH3) that may be treated with halogens and utilised in an electrophilic substitution process to create aryl halides in the presence of the Lewis acid catalyst iron (III) chloride. In the absence of light, the reaction is carried out using chlorine or bromine, and the products are o- and p- haloarenes. |
| 5. Which of the following is halogen exchange reaction? |
| Correct Answer: option (i) Ans: The correct answer is option (i). Option (i) is an example of a Finklestein reaction, which is a halogen exchange reaction that produces alkyl iodide by treating alkyl halides with NaI in dry acetone. Option (ii) is an addition reaction in which an alkene is transformed to the equivalent alkyl halide. Option (iii) is a substitution reaction, whereas option (iv) is an electrophilic substitution reaction. |
| 6.Which reagent will you use for the following reaction? (i) light (ii) NaCl+H2SO4 (iii) Cl2 gas in dark (iv) Cl2 gas in the presence of iron in dark |
| Ans: The correct Answer is Option (i). Chlorination in the presence of UV light can be used to produce alkyl chlorides from alkanes. Under the action of UV radiation, the chlorine molecule generates free radicals, which react with alkanes to create a mixture of isomeric mono- and poly haloalkanes. |
| 7. Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their densities. |
| Ans: The Correct Answer is Option (i). Alkyl halides have a higher density than water. Their densities are determined by the masses of the halogen atoms, the number of halogen atoms, and the number of carbon atoms. Simply expressed, Br has an atomic mass of 79 while Cl has an atomic mass of 35. (d) will be the heaviest of the molecules, followed by (c), (b), and (a). Because density is exactly proportional to mass, the order of decreasing densities will be the same. The right answer is (i). |
| 8. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their boiling points. |
| Ans: The Correct Answer is Option(iii). Isomeric alkyl halides' boiling points are related to their branching, with a reduction in B.P. as branching increases. As a result, the boiling point of the tertiary isomer is the lowest, while that of the primary isomer is the highest. Thus, the order of lowering boiling points is (b) > (a) > (c). |
| 9. In which of the following molecules carbon atom marked with asterisk (*) is asymmetric? (i) (a), (b), (c), (d) (ii) (a), (b), (c) (iii) (b), (c), (d) (iv) (a), (c), (d) |
| Ans: The correct answer is (ii).The mirror copies of the molecules (a), (b), and (c) are non-superimposable. Because all four species linked to the carbon atom are identical, molecule (d) cannot have an asymmetric carbon atom, thus the mirror image of (d) when rotated 180∘ is superimposable on the original picture. |
| 10. Which of the following structures is enantiomeric with the molecule (A) given below : |
| Ans: The Correct Answer is Option (i). Enantiomers are stereoisomers of a substance that are not superimposable on each other. The carbon atom in the molecule (A) is asymmetric. The molecule's mirror image (i) and 180∘ rotation cannot be superimposed on each other (A). The molecules (ii), (iii), and (iv) can all be superimposed on one other (A). The molecules (iii) and (iv) have 180∘ rotations that are superimposable on one another (A). |
| 11. Which of the following is an example of vic-dihalide? (i) Dichloromethane (ii) 1,2 -dichloroethane (iii) Ethylidene chloride (iv) Allyl chloride |
| Ans: The Correct Answer is Option (iv). Geminal halides or gem-dihalides and vicinal halides or vic-dihalides are dihaloalkanes with the same halogen. Vic-dihalides are dihaloalkanes with halogen atoms on two adjacent carbon atoms, whereas Gem-dihalides are molecules with halogen atoms on two adjacent carbon atoms. Gem-dihalides are called alkylidene halides in the conventional naming system, whereas vic-dihalides are called alkylene dihalides. Because dichloromethane has just one carbon, it cannot contain neighbouring halogen atoms. Two carbon atoms are sandwiched between two halogen atoms in 1,2-dichloroethane. Ethylidene chloride is a gem-dihalide, as its name implies. There is only one chlorine atom in allyl chloride. |
| 12. The position of −Br in the compound in CH3CH=CHC(Br)(CH3)2 can be classified as (i) Allyl (ii) Aryl (iii) Vinyl (iv) Secondary |
| Ans: The correct answer isOption (i). When the halogen atom is linked to an sp3-hybridised carbon atom next to an allylic carbon, a carbon-carbon double bond is formed. Aryl halides are produced when a halogen atom is directly linked to an aromatic ring's sp2-hybridised carbon atom. When a halogen atom is linked to a sp2-hybridised carbon atom in a carbon-carbon double bond, vinylic bonds are produced. Simply defined, it's an ethylene molecule with one hydrogen atom substituted by another --R group. When the halogen is attached to a secondary carbon atom in the molecule, secondary bonds form. The −Br is linked to a tertiary carbon atom in the supplied molecule, which is then bonded to an sp3-hybridised carbon-carbon double bond. As a result, this −Br has an allylic position. |
| 13. Chlorobenzene is formed by reaction of chlorine with benzene in the presence of .Which of the following species attacks the benzene ring in this reaction? (i) Cl− (ii) Cl+ (iii) AlCl3 (iv) [AlCl4]− |
| Ans: The correct answer is option ii. Aluminum chloride is a Lewis acid catalyst that functions similarly to FeCl3. By chlorinating benzene in the presence of AlCl3, benzene is transformed to chlorobenzene. Electrophilic substitution is used to carry out the reaction. Cl2 forms a coordination complex with AlCl3 called Cl + AlCl4- , which has a small positive charge on Cl and is negatively charged on AlCl4- . This Cl+ then interacts with the benzene ring's aromatic double bond to generate an addition product, followed by deprotonation to produce chlorobenzene, AlCl3, and HCl as side products. The best choice is (ii). |
| 14. Ethylidene chloride is a/an (i) vic-dihalide (ii) gem-dihalide (iii) allylic halide (iv) vinylic halide |
| Ans: The Correct Answer is Option (ii). Dihaloalkanes with two halogen atoms of the same kind bonded to the same carbon atom are known as gem-dihalides. Alkylidene dihalides is the most frequent naming scheme for gem-dihalides. As a result, ethylidene dichloride is a gem-dihalide. The best choice is (ii). |
| 15. What is 'A' in the following reaction? |
| Ans: The correct answer is Option (iii). Markonikov's rule can be used to explain the results. The hydrogen from HCl is added to the carbon immediately bonded to the most hydrogen atoms, whereas the --Cl is attached to the carbon directly bonded to the least hydrogens, according to the rule. As a result, the right response is (iii). |
| 16. A primary alkyl halide would prefer to undergo (i) SN1 reaction (ii) SN2 reaction (iii) 𝛂-Elimination (iv) Racemisation |
| Ans: The Correct Answer is Option (ii). When an alkyl halide with -hydrogen atoms reacts with a base or a nucleophile, depending on the nature of the alkyl halide, the strength of the base or nucleophile, the size of the molecules, and the reaction circumstances, it can undergo a specific kind of reaction. A substitution or elimination process can be followed by an alkyl halide, as well as the two kinds of substitution, SN1 and SN2. Because the entering nucleophile cannot engage with the bulky substituents on or near the carbon atom, the main alkyl halide prefers the SN2reaction. As a result, primary alkyl halides and methyl halides have the greatest proclivity for SN2 reactions. |
| 17. Which of the following alkyl halides will undergo SN1 reaction most readily? (i) (CH3)3C−F (ii) (CH3)3C −Cl (iii) (CH3)3C −Br (iv) (CH3)3C −I |
| Ans: The Correct Answer is Option (iv). SN1 reactions occur mostly in polar protic solvents such as H2O and follow first-order kinetics. This indicates that the reaction rate is solely determined by one reactant. Because of the great stability of the generated carbocation, this reaction favours tertiary alkyl halides. When a molecule is polarised in water, it generates a carbocation as well as a halide ion. The halides' reactivity is R--I > R--Br > R--Cl > > R--F. As a result, (CH3)3C---I will be the most likely to undergo the reaction. |
| 18. Which is the correct IUPAC name for : (i) 1-Bromo-2-ethylpropane (ii) 1 -Bromo-2-ethyl-2-methylethane (iii) 1 -Bromo-2-methylbutane (iv) 2-Methyl-1-bromobutane |
| Correct Answer: Option (iii) Ans: The correct answer is option iii. First, we must determine which carbon chain is the longest. After that, we should have CH3---CH2---CH(CH3)---CH2---Br as the real structure. --Br, because the functional halide group is linked to the first carbon atom, we begin numbering there. The methyl group branch is joined to the chain's second carbon atom. Butane is named from the number of carbons in the unbranched parent chain, which is four. 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane is the name of the molecule. Option (iii) is the right answer. |
| 19. What should be the correct IUPAC name for diethylbromomethane? (i) 1 -Bromo- 1,1 -diethylmethane (ii) 3-Bromopentane (iii) 1-Bromo-1-ethylpropane (iv) 1-Bromopentane |
| Ans: The Correct Answer is Option (ii). We may conclude from the given compound's common name that there are two --C2H5 groups and one --Br group linked to a CH4 molecule. Bromomethane would be represented by the symbol CH3---Br. Two ethyl groups can be replaced for the hydrogens in the methyl molecule to make diethylbromomethane (C2H5)CH(C2H5)Br. The longest parent chain must be identified in order to offer an IUPAC name. The parent chain is CH3---CH2---CH(Br)---CH2---CH3, with the --Br group from either side connected to the third carbon atom. Because the parent chain has five carbons, the molecule is termed 3-bromopentane. |
| 20. The reaction of toluene with chlorine in the presence of iron and in the absence of light yields: |
| Ans: The Correct Answer is Option (iv). By electrophilic substitution, aromatic arenes react with chlorine in the presence of Lewis acid catalysts such as iron (III) chloride, yielding ortho and para isomers of haloarenes. (ii) and (iii) are both products of the reaction. Cl2 forms a coordination complex with FeCl3, creating the Cl + FeCl4 - complex, which has a small positive charge on Cl and a negative charge on FeCl4 - . This Cl+ then interacts with the aromatic double bonds of the toluene molecule to create an addition product, which is subsequently deprotonated to form a mixture of o-, p-, and m- chlorotoluene isomers. Because the m- isomer is highly unstable, the product is not accessible in the o- and p- forms. |
| 21. Chloromethane on treatment with excess of ammonia yields mainly |
| Ans: The Correct Answer is Option (iii). Because it possesses unpaired electrons, the ammonia molecule is a nucleophile in nature. By nucleophilic substitution, this nucleophile attacks the chloromethane molecule and forms methyl amine or methanamine. The carbon atom in the molecule is partially positive due to the electronegativity of the linked halide, which is partially negative. The positive ion is attacked by the electron-rich nucleophile, causing the halide ion to be detached from the molecule. The proper response is (iii). |
| 22. Molecules whose mirror image is non super-imposable over them are known as chiral. Which of the following molecules is chiral in nature? (i) 2-Bromobutane (ii) 1-Bromobutane (iii) 2-Bromopropane (iv) 2-Bromopropan-2-ol |
| Ans: The Correct Answer is Option (i). The structure of 2-Bromobutane is depicted in the diagram below. Because all of the groups connected to the central carbon atom differ, the mirror image of the molecule cannot be superimposed on the original molecule. The structure of 1-Bromobutane is shown in the diagram below. Because there are just three groups that vary from one another, the molecule is not chiral in nature. The structure of 2-Bromopropan-2-ol, shown below, has two identical species and hence cannot be chiral. |
| 23. Reaction of C6H5CH2Br with aqueous sodium hydroxide follows (i) SN1 mechanism (ii) SN2 mechanism (iii) Any of the above two depending upon the temperature of reaction (iv) Saytzeff rule |
| Ans: The Correct Answer is Option (i). When benzyl chloride is treated with aqueous sodium hydroxide, where --OH is the nucleophile, a nucleophilic substitution reaction occurs, resulting in the formation of benzyl alcohol. The benzene ring is resonance stabilised here, and this stability is extended to the connected methylene group, giving a positive charge to --CH2, making the whole carbocation stable when the link between benzyl and bromide is broken. This is an SN1 reaction with two stages that is followed due to the stability of the carbocation. This is a coordinated reaction that takes place in two phases. The halide group first exits the carbocation, and then the nucleophile binds to the cation, producing alcohol. The right answer is (i). |
| 24. Which of the carbon atoms present in the molecule given below are asymmetric? (i) a, b, c, d (ii) b, c (iii) a, d (iv) a, b, c |
| Ans: The Correct Answer is Option (ii). Chiral molecules are made up of one carbon atom surrounded by four different species. Because of the presence of two or more identical groups, such as hydrogens, all straight chain molecules cannot be chiral. Even carbons with double or triple bonds to a group are not considered chiral. Through covalent connections, an asymmetric carbon must be surrounded by four distinct species. As a result, atoms b and c are asymmetric. The correct answer is option (ii). |
| 25. Which of the following compounds will give racemic mixture on nucleophilic substitution by OH− ion? |
| Solution: Ans: The Correct Answer is Option (i). A racemic mixture is one that contains two enantiomers in equal quantities but has no optical activity because the opposing optical rotations of the two enantiomers cancel each other out. The optically active reactant undergoes the SN1 reaction in order for a racemic mixture to form following nucleophilic substitution. Option (a) is a chiral carbon atom that will undergo the SN1 process, resulting in a racemic mixture. Option (b) does not include an asymmetric carbon, but option (c) has a secondary carbon asymmetric atom that is less reactive to an SN1 substitution. The right answer is (i). |
| In the questions, 26 to 29 arrange the compounds in increasing order of the rate of reaction towards nucleophilic substitution. |
| Ans: The Correct Answer is Option (iii). Due to the resonance stabilisation of the benzene ring, the reactivity of aryl halides to nucleophilic substitution is exceedingly low. Because of resonance, the --Cl bond gains a partial double bond. The presence of an electron withdrawing --NO2 group at ortho or para positions on the ring enhances the reactivity of aryl halides. The presence of --NO2 near the C---Cl makes the molecule more reactive. The order of reactivity should be (b) > (c) > (a). The right option is (iii). |
|
(i) (a) < (b) < (c) (ii) (a) < (c) < (b) (iii) (c) < (b) < (a) (iv) (b) < (c) < (a) |
| Ans: The Correct Answer is Option (iv). Because the --CH3 group is an electron releasing group, it reduces the reactivity of aryl halides in the ortho and para locations. As a result, aryl halides without electron releasing groups are more reactive. As a result, the order of reactivity is (a) > (c) > (d) (b). The right answer is (iv). |
|
(i) (c) < (b) < (a) (ii) (b) < (c) < (a) (iii) (a) < (c) < (b) (iv) (a) < (b) < (c) |
| Solution: Ans: The Correct Answer is option (iv). ( - NO2) is an electron-withdrawing group that induces nucleophilic substitution when it is in the ortho and para positions. When this identical electron-drawing group is in the meta position, its impact is much reduced. The reactivity of aryl halides rises as the number of electron-withdrawing groups increases. As a result, the greater the number of electron-drawing groups, the greater the rate of nucleophilic substitution. |
|
(i) (a) < (b) < (c) (ii) (b) < (a) < (c) (iii) (c) < (b) < (a) (iv) (a) < (c) < (b) |
| Ans: The Correct Answer is Option (iii). The presence of electron releasing groups increases the reactivity of aryl halides; the fewer the electron releasing groups, the slower the rate of nucleophilic substitution. As a result, an increase in methyl groups decreases reactivity. The sequence of reactivity is (a) > (b) > (c). The right answer is (iii). |
| 30. Which is the correct increasing order of boiling points of the following compounds? 1-Iodobutane, 1-Bromobutane, 1-Chlorobutane, Butane (i) Butane < 1-Chlorobutane < 1-Bromobutane < 1-Iodobutane (ii) 1-Iodobutane < 1-Bromobutane < 1-Chlorobutane < Butane (iii) Butane < 1-Iodobutane < 1-Bromobutane < 1-Chlorobutane (iv) Butane < 1-Chlorobutane < 1-Iodobutane < 1-Bromobutane |
| Ans: The Correct Answer is Option (i). The intermolecular force of attraction will grow as the surface area increases. As a result, the boiling point rises as well. The boiling point of a comparable alkyl halide rises with increasing molecular mass. Iodine has the greatest atomic mass. As a result, 1-iodobutane has the greatest boiling point. |
| 31. Which is the correct increasing order of boiling points of the following compounds? 1-Bromoethane, 1-Bromopropane, 1-Bromobutane, Bromobenzene (i) Bromobenzene < 1-Bromobutane < 1-Bromopropane < 1-Bromoethane (ii) Bromobenzene < 1-Bromoethane < 1-Bromopropane < 1-Bromobutane (iii) 1-Bromopropane < 1-Bromobutane < 1-Bromoethane < Bromobenzene (iv) 1-Bromoethane < 1-Bromopropane < 1-Bromobutane < Bromobenzene |
| Ans: The Correct Answer is Option (iv). If the halogen atom in all of the supplied alkyl halides is the same kind, the boiling point of a compound rises as the number of alkyl groups added increases. As the quantity and size of molecules and electrons grow, so do their attractions. As a result, the greater the boiling point, the larger the molecular weight of the alkyl halide. The boiling points of the following compounds are listed in ascending order: 1-Bromoethane 1-Bromopropane 1-Bromobutane Bromobenzene The right answer is (iv). |
| In the following questions two or more options may be correct. Consider the following reaction and answer the questions no. 32–34. 32. Which of the statements are correct about the above reaction? (i) (a) and (e) both are nucleophiles. (ii) In (c) carbon atom is sp3 hybridised. (iii) In (c) carbon atom is sp2 hybridised. (iv) (a) and (e) both are electrophiles. |
| Ans: An SN2 nucleophilic substitution reaction occurs when CH3Cl interacts with the hydroxide ion to produce CH3OH. Both OH - and Cl - are nucleophiles with an excess of electrons in this reaction. Because the binding of OH - and the leaving of Cl - occurs simultaneously in the transition state (c), the carbon atom is linked to just three hydrogens. As a result, the carbon atom becomes sp2 hybridised. Aand (C) are the right statements. Correct Answer: Option (A) and (C) |
| 33. Which of the following statements are correct about this reaction? (i) The given reaction follows the SN2 mechanism. (ii) (b) and (d) have the opposite configuration. (iii) (b) and (d) have the same configuration. (iv) The given reaction follows the SN1 mechanism. |
| Ans: An SN2 reaction, also known as a nucleophilic substitution, is the reaction in question. The entering nucleophile causes the groups surrounding the carbon atom to migrate in the opposite direction of the nucleophile, causing the configuration of alkyl halides to invert. As a result, (b) and (d) will be in the opposite order. This reaction is also SN2 since there is just one phase in which OH- is added and Cl- is removed at the same time. (i) and (ii) are the right answers. Correct Answer: Option (A) and (B) |
| 34. Which of the following statements are correct about the reaction intermediate? (i) Intermediate (c) is unstable because in this carbon is attached to 5 atoms. (ii) Intermediate (c) is unstable because carbon atom is sp2 hybridised. (iii) Intermediate (c) is stable because carbon atom is sp2 hybridised. (iv) Intermediate (c) is less stable than the reactant (b). |
| Ans: Because the carbon atom is transiently linked to five atoms, the intermediate (iii) is less stable than reactant (ii), which is coupled to four groups. |
| Answer Q. No. 35 and 36 based on the following reaction. 35. Which of the following statements are correct about the mechanism of this reaction? (i) A carbocation will be formed as an intermediate in the reaction. (ii) OH–will attach the substrate (b) from one side and Cl- will leave it simultaneously from the other side. (iii) An unstable intermediate will be formed in which OH– and Cl– will be attached by weak bonds. (iv) The reaction proceeds through an SN1 mechanism. |
| Ans: Because it is a tertiary alkyl halide, the described reaction is a nucleophilic substitution that follows the SN1 mechanism. It's a two-step process. The first step is the gradual breaking of a polarised C---Br bond, which results in the formation of a carbocation and a bromide ion. To complete the substitution, the stable intermediate carbocation is attacked by the nucleophile OH−. (i) and (iv) are the right statements. Correct Answer: option (A) and (iv) |
| 36. Which of the following statements are correct about the kinetics of this reaction? (i) The rate of reaction depends on the concentration of only (b). (ii) The rate of reaction depends on the concentration of both (a) and (b). (iii) Molecularity of reaction is one. (iv) Molecularity of reaction is two. |
| Ans: The reaction is of the type SN1 nucleophilic substitution. This sort of reaction is governed by second order kinetics, in which the rate of reaction is determined only by the concentration of the reactant. A reaction's molecularity is defined as the number of molecules involved in the rate-determining phase. Because of second order kinetics, the moleculeity of this reaction is one. (i) and (iii) are the right answers . Correct Answer: Option (A) and (C) |
| 37. Haloalkanes contain halogen atom (s) attached to the sp3 hybridised carbon atom of an alkyl group. Identify haloalkane from the following compounds. (i) 2-Bromopentane (ii) Vinyl chloride (chloroethene) (iii) 2-chloroacetophenone (iv) Trichloromethane |
| Ans: Option (i) and (iv) have a halogen atom linked to an sp3 hybridised carbon that is single-bonded to other groups. The other possibilities are sp2 hybridised because they are linked to carbon atoms, which are coupled to other groups in double bonds. Option I and (iv) are both correct. Correct Answer: Option (i) and (iv) |
| 38. Ethylene chloride and ethylidene chloride are isomers. Identify the correct statements. (i) Both the compounds form the same product on treatment with alcoholic KOH. (ii) Both the compounds form the same product on treatment with aq.NaOH. (iii) Both the compounds form the same product on reduction. (iv) Both the compounds are optically active. |
| Ans: Isomers are ethylene chloride ClCH2---CH2Cl and ethylidene dichloride CH3---CHCl2. Because the carbon atoms are not surrounded by distinct groups, neither molecule is optically active. When haloalkanes are treated with alcoholic KOH, they undergo an elimination process in which a hydrogen atom from the -carbon atom and a halogen atom from the -carbon atom are eliminated. To form the ethyne molecule, each of these chemicals lose hydrogen and chlorine atoms. When exposed to aqueous NaOH, the molecules undergo nucleophilic substitution, with the –Cl groups being replaced by --OH molecules. The results will differ due to the locations of the halides on various carbon atoms. Correct Answer: Option (i) and (iii) |
| 39. Which of the following compounds are gem-dihalides? (i) Ethylidene chloride (ii) Ethylene dichloride (iii) Methylene chloride (iv) Benzyl chloride |
| Ans:Dihaloalkanes with two halogen atoms linked to the same carbon atom are known as gem-dihalides. Alkylidene halides are another name for them. The chemical ethylene dichloride is a vicinal dihalide, meaning that chlorine atoms are linked to neighbouring carbon atoms. There is only one chlorine atom in benzoyl chloride. According to the molecule's nomenclature, ethylidene chloride is a gem-dihalide. The IUPAC terminology for methylene chloride is dichloromethane. Two chlorine atoms are joined to a single carbon atom in this compound. Correct Answer: Option (i) and (iii) |
| 40. Which of the following are secondary bromides? (i) (CH3)2 CHBr (ii) (CH3)3CCH2Br (iii) CH3CH(Br)CH2CH3 (iv) (CH3)2CBrCH2CH3 |
| Ans: Checking with the carbon atom it is connected to is one way to see if a compound has a secondary bromide. In a molecule, a secondary carbon group is linked to one hydrogen atom and three non-hydrogen groups. As a result of the foregoing possibilities, secondary bromides are formed when the --Br group is linked to the --CH group. (i) and (iii) are the right answers. Correct Answer: Option (i) and (iii) |
| 41. Which of the following compounds can be classified as aryl halides? (i) p-ClC6H4CH2CH(CH3)2 (ii) p-CH3CHCl(C6H4 )CH2CH3 (iii) o-BrH2C-C6H4CH(CH3)CH2CH3 (iv) C6H5 -Cl |
| Ans: Aryl halides are halides in which the halogen atom is directly linked to the aromatic ring's sp2 hybridised carbon atom. Only (i) and (iv) contain halogen atoms directly linked to aryl rings among the choices. As a result, they are known as aryl halides. (i) and (ii) are the right answers (iv). Correct Answer: Option (i) and (iv) |
| 42. Alkyl halides are prepared from alcohols by treating with (i) HCl + ZnCl2 (ii) Redp+Br2 (iii) H2SO4 + KI (iv) All the above |
| Ans:
Alcohols produce matching alkyl halides when they are treated with various reagents. Alcohols, red phosphorous, and bromine treated with alcohol produce alkyl chlorides and alkyl bromide, respectively, when treated with HCl+ZnCl2. H2SO4 + KI cannot be used to convert an alcohol to alkyl iodide because they will convert KI to the equivalent acid, HI, which will then be oxidised to I2. As a result, the right statements are (i) and (ii). Correct Answer: Option (i) and (ii) |
| 43. Alkyl fluorides are synthesised by heating an alkyl chloride/bromide in presence of ____________ or ____________. (i) CaF2 (ii) CoF2 (iii) Hg2F2 (iv) Na |
| Ans: Heat an alkyl chloride/bromide in the presence of a metallic fluoride such as AgF, Hg2F2, CoF2, or SbF3 to produce alkyl fluorides. Swarts reaction is the name given to this reaction. CoF2 and Hg2F2 are the only choices that work as reagents. NaF is not suitable because the end products of NaF + RCl→ RF + NaCl are soluble in the solvent, i.e. water, making separation difficult. As a result, the right alternatives are (ii) and (iii). Correct Answer: Option (ii) and (iii) |
JEE Mains 2022
JEE Mains 2022
Commonly asked questions
In the given reaction,
X + Y + 3Z XYZ3
If one mole of each of X and Y with 0.05 mol of Z gives compound XYZ3. (Given: Atomic masses of X, Y and Z are 10, 20 and 30 amu, respectively.) The yield of XYZ3 is_____________g.
(Nearest integer)
x + y + 3z = xyz3
1 mole 1 mole 0.05 mole
here z is limiting reagent.
mole z gives 1 mole xyz3
mass of xyz3 = n × molecular mass
=
= 0.5 × 4 = 2g
An element M crystallises in a body centred cubic unit cell with a cell edge of 300 pm. The density of the element is 6.0g cm-3. The number of atoms in 180g of the element is_________× 1023 (Nearest integer)
B.C.C structure
a = 300 pm = 300 × 10-12 m
d = 6g/cm3
z = 2
= 3.69 × 6.022 × 1023
= 22.22 × 1023
the nearest integer = 22
The number of paramagnetic species among the following is
B2, Li2, C2, , , and .
Paramagnetic
Diamagnetic
Paramagnetic
Paramagnetic
Paramagnetic molecules are
150g of acetic acid was contaminated with 10.2g ascorbic acid to lower down its freezing point by (x × 10-1)°C. The value of x is _________. (Nearest integer)
(Given Kf = 3.9 K kg mol-1; molar mass of ascorbic acid = 176 g mol-1]
3.9 × 0.386
Ans =15
Ka for butyric acid (C3H7COOH) is 2 × 10-5. The pH of 0.2 M solution of butyric acid is ____________× 10-1 (Nearest integer)
[Given log2 = 0.30]
Ka for C3H7COOH = 2 × 10-5
=5 – 0.3 = 4.7
pH of 0.2 (M) solution =
Ans 27
For the given first order reaction
A -> B
The half life of the reaction is 0.3010 min. The ration of the initial concentration of reactant to the concentration of reactant at time 2.0 min will be equal to________________. (Nearest integer)
t1/2 = 0.301 min
t = 2 min
Ans. 100
The number of interhalogens from the following having square pyramidal structure is:
CIF3, IF7, BrF5, BrF3, I2Cl6, IF5, ClF, ClF5
IF7 -> Pentagonal bipyramidal (sp3d3)
BrF5 -> Square pyramidal (sp3d2)
BrF3 -> T-Shaped (sp3d)
I2Cl6 -> Triangular bipyramidal (sp3d)
Square Pyramidal (sp3d2)
ClF -> (sp3)
ClF5 -> Square Pyramidal (sp3d2)
Br5, IF5 & ClF5 -> Square Pyramidal
The disproportionation of in acidic medium resultant in the formation of two manganese compounds A and B. If the oxidation state of Mn is B is smaller than that of A, then the spin-only magnetic moment value of B in BM is___________.
(Nearest integer)
Oxidation state of Mn in B < A
B is MnO2
Oxidation state of Mn = +4
unpaired electron = 3
Spin only magnetic moment
Total number of relatively more stable isomer(s) possible for octahedral complex will be________________.
More stable isomers = 3 (trans isomers)
On complete combustion of 0.492g of an organic compound containing C, H and O, 0.7938 g of CO2 and 0.4428 g of H2O was produced. The % composition of oxygen in the compounds is____________.
% of C in organic compound
=
=
= 100 – 54 = 46%
Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Ten Exam