Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 11th
Get insights from 2k questions on Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In order to calculate the lattice enthalpy of NaBr,
(i) Na (s) →Na (g) ; ΔsubH? =108.4 kJ/mol
(ii) Na→Na+ + e- ΔiH? = 496kJ/ mol
(iii) Br→ Br, Δdiss H? = 96kJ/ mol
(iv) Br+e-Br- ΔegH? = - 325 kJmol-1
? fH? =? subH? + Δdiss H + Δi H? + Δi H? + Δeg H? +? lattice H?
= -360.1 -108.4-96-496+325 = -735.5KJ/ mol
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The reaction presented in the question is
CH4 (g)→C (g) + 4H (g)
Now, ΔaH = 1665 kJ/mol
The mean bond enthalpy of the C-H bond should be used here. For the atomisation of 4 moles of C-H bonds, the value is 1665 kJ/mol. So, per mole energy = 1665/4 = 416.2 kJ / mol
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
According to Hess's law, ΔrH = ΔrH1+ ΔrH2+ΔrH3
This is so because during the reaction A→ B, B's formation undergoes various intermediate reactions, with the overall value of the enthalpy being ΔrH.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
ΔH for formation is given. For the reverse reaction, ΔHchanges sign as the reverse of exothermic reaction will be endothermic. So, ΔH for decomposition is - (-91.8)=91.8 for one mole. But here, two moles are decomposing,
ΔH=2*91.8=183.6KJ
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Standard molar enthalpy of formation, rH1- is just a special case of fH2-, where
one mole of a compound is formed from its constituent elements. In the above equation, enthalpy of formation and enthalpy of reaction is not the same.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Due to weak force of attraction between molecules, acetone requires less heat to vaporise. Hence, water has higher enthalpy of vaporization.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Enthalpy of a reaction is the energy change per mole for the process.
18 g of H2O = 1 mole ΔHvap = 40.79 kJ/ mol
Enthalpy change for vapourising 2 moles of H2O = 2 x 40.79 = 81.58 kJ ΔH°vap = 40.79 kJ mol-1.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
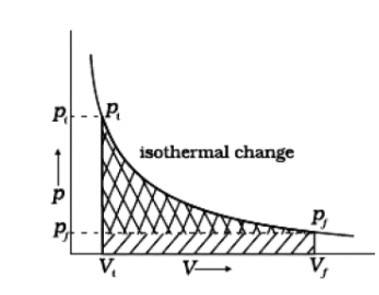
(i) Reversible work is represented by the combined areas
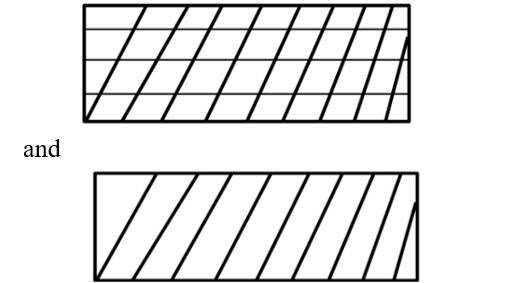
(ii) Work against constant pressure, Pf is represented by the area
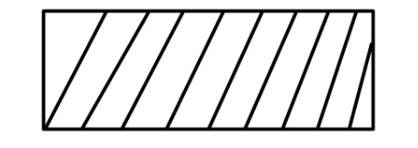
Work (i) > Work (ii).
The Approach While Dealing With the Concept of Thermodynamics
Since the concept of Thermodynamics and the terminologies of Chemistry are a bit new to the students, they should first learn the names of different chemical components and how to write the chemical equations properly through NCERT Exemplars and Solutions books.While writing the chemical equations, they might make some mistakes. To avoid making errors, they shoul
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
We know,
ΔStotal = ΔSsys + ΔSsurr
When a system is in thermal equilibrium with its surroundings, the surroundings' temperature is the same as the system's. Furthermore, a rise in the enthalpy of the surroundings equals a decrease in the system's enthalpy. As a result of the entropy shift in the environment,
ΔSsurr = ΔHsurr/T = -ΔHsys/T
ΔStotal = ΔSsys = (-ΔHsys/T)
Rearranging the above equation:
ΔStotal = TΔSsys - ΔHsys
For spontaneous process,
ΔStotal > 0, so
TΔSsys - ΔHsys> 0
⇒ ( - ΔHsys - TΔSsys) > 0
The above equation can be written as
- ΔG > 0
ΔG
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
A contrast is drawn in thermodynamics between extensive and intense qualities. An extensive property is one whose value is proportional to the amount or size of matter in the system. Extensive properties include mass, volume, internal energy, enthalpy, and heat capacity, to name a few.
Properties that are independent of the amount or size of matter present are known.
As though they were intensive properties Temperature, density, and pressure, for example, are intense properties. A molar property? m, is the value of an extensive property of the system for 1 mol of the sub
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 65k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 679k Reviews
- 1800k Answers