Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Get insights from 2.6k questions on Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
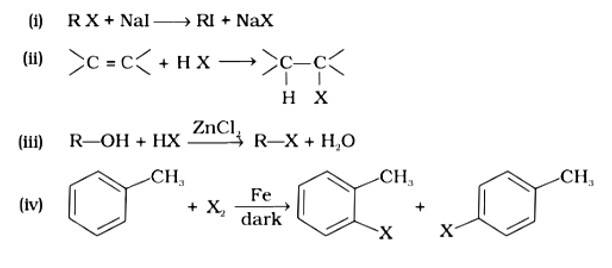
Option (i)
The correct answer is option (i). Option (i) is an example of a Finklestein reaction, which is a halogen exchange reaction that produces alkyl iodide by treating alkyl halides with NaI in dry acetone. Option (ii) is an addition reaction in which an alkene is transformed to the equivalent alkyl halide. Option (iii) is a substitution reaction, whereas option (iv) is an electrophilic substitution reaction.
New question posted
4 months agoNew answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (ii). Toluene is an aromatic hydrocarbon (C6H5-CH3) that may be treated with halogens and utilised in an electrophilic substitution process to create aryl halides in the presence of the Lewis acid catalyst iron (III) chloride. In the absence of light, the reaction is carried out using chlorine or bromine, and the products are o- and p- haloarenes.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
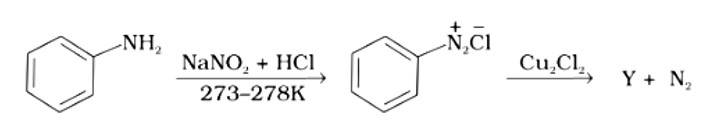
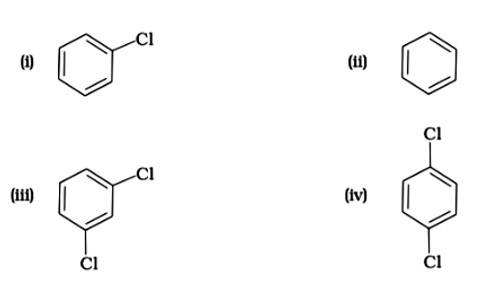
The correct answer is (i). Sandmeyer's reaction can be used to synthesise haloarenes from amines. A primary aromatic amine that has been dissolved or suspended in cold aqueous mineral acid is treated with sodium nitrite to create a diazonium salt in this procedure. When this freshly produced salt is combined with cuprous chloride, the diazonium group is replaced with - Cl, resulting in aryl chloride. Option I is the chemical Y, which is an aryl chloride.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct Answer is Option (iv) Because the tertiary carbocation is the most stable, it interacts the most with concentrated HCl. As a result, for tertiary alcohol, room temperature is sufficient for the reaction. However, for primary and secondary alcohols, the presence of a catalyst (ZnCl2) is required.
As a result, option (iv) is accurate.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
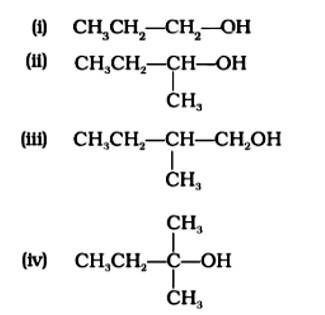
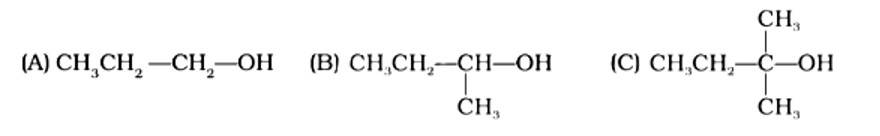
The Correct Answer is Option (ii). Haloalkanes are made by combining alcohols with halogen acids, in which the hydroxyl group of the alcohol is replaced by the halogen. Primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols are represented by options (A), (B), and (C). Tertiary alcohols are more reactive than secondary and primary alcohols, and they generate haloalkanes from haloacids without the need of catalysts at ambient temperature. Alcohols have a reactivity order of 3? >2? >1? . As a result, the proper option is (ii).
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ambident nucleophiles are groups that include two nucleophilic centres, such as cyanide and nitrile. In the cyanide group, linkage can occur from both the carbon and nitrogen ends. The carbon end functions as a greater nucleophile in an aqueous media because it leads to the creation of a C-C sbond, which is stronger than a N-C bond in the identical molecule.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In the presence of ZnCl2, ethanol can be treated with HCl to produce chloroethane. Iodoethane is formed when chloroethane reacts with NaI.
C2H5OH+HCl→ZnCl2? C2H5Cl→ NaI ? C2H5I
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
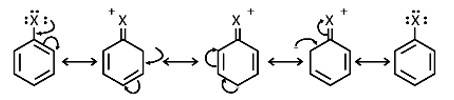
Resonance effect: Because the C – X bond has the characteristics of a partial double bond, it is extremely difficult to break.
(i) The C - X bond in haloarenes is extremely less reactive to nucleophilic groups
(ii) The C atom linked to the halogen is sp2 hybridised in the C – X bond. Carbon that has been sp2 hybridised with a higher s-character is more electronegative in nature and can retain the electron pair of the C - X bond more tightly than carbon that has been sp3 hybridised with a lower s -character in haloalkanes.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The reaction of HCl and isobutylene is given as:
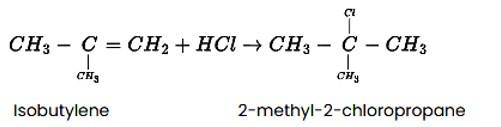
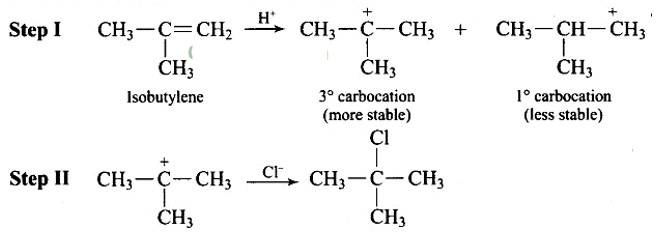
Steps in reaction involves are:
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 65k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 679k Reviews
- 1800k Answers