Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Tech
Get insights from 110 questions on Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Tech, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Tech
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New question posted
8 months agoNew answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a) They are structural isomers. The given compounds have the same molecular formula but they differ in the position of the functional group (here ketone group: first one at C-3 and second one at C-2 positions).
(b) They are geometrical isomers. Compounds having the same molecular formula, the same constitution, and the sequence of covalent bonds, but with the different relative position of their atoms in space are called geometrical isomers.
(c) They are resonance contributors because they differ in the position of electrons but not atoms.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
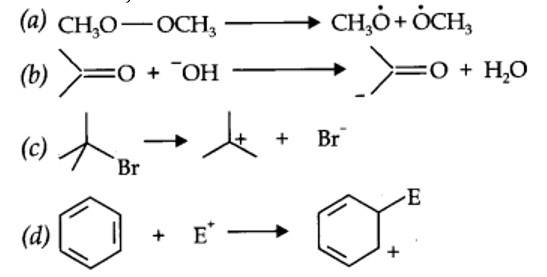
(a) Nucleophilic substitution (b) Electrophilic addition
(c) Bimolecular elimination (d) Nucleophilic substitution with rearrangement.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a) Here, HO– acts as a nucleophile as it is an electron-rich species, i.e., it is a nucleus-seeking species.
(b) Here, –CN acts as a nucleophile as it is an electron-rich species, i.e., it is a nucleus-seeking species.
(c) CH3C+O acts as an electrophile as it is an electron deficient species.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Electrophiles: The name electrophiles mean electron loving. Electrophiles are electron deficient. They may be positive ions or neutral molecules.
Ex: H+, Cl+, Br+, NO2+, R3C+, RN2+, AlCl3, BF3
Nucleophiles: The name nucleophiles means 'nucleus loving' and indicates that it attacks the region of low electron density (positive centres) in a substrate molecule. They are electron rich they may be negative ions or neutral molecules.
Ex: Cl– Br–, CN–, OH–, RCR2–, NH3, RNH2, H2O, ROH etc.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Due to hyperconjugation, alkyl groups act as electron donors when attached to a π - system as shown below:

New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Nitroethoxide ion (O2NCH2CH2O–) is more stable than ethoxide ion (CH3CH2O–) due to -I effect of nitro group which decreases the negative charge of oxide ion of nitroethoxide ion leading to stability. In contrast, CH3CH2 has +I-effect. It, therefore, tends to intensify the -ve charge and hence destabilizes it.
New question posted
8 months agoNew answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a) H-COOH
CH3—COOH
CH3CH2—COOH
CH3CH2CH2—COOH
CH3CH2CH2CH2—COOH
(b) CH3COCH3
CH3COCH2CH3
CH3COCH2CH2CH3
CH3COCH2CH2CH2CH3
CH3CO (CH3)4CH3
(c) H—CH=CH2
CH3CH=CH2
CH3CH2CH=CH2
CH3CH2CH2CH=CH2
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH=CH2
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a) 2, 2-Demethylpentane
(b) 2, 4, 7-Trimethyloctane. For two alkyl groups on the same carbon its locant is repeated twice, 2, 4, 7-locant set is lower than 2, 5, 7.
(c) 2- Chloro-4-methylpentane. Alphabetical order of substituents, (d) But-3-yn-1-ol. Lower locant for the principal functional group, i.e., alcohol.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers