Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Twelve
Get insights from 37 questions on Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Twelve, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Twelve
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
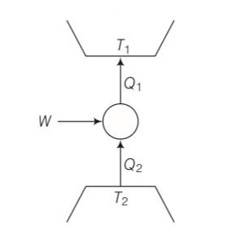
(a), (c) Q1= W+Q2
W=Q1-Q2>0
Q1>Q2>0
We can also write Q21
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
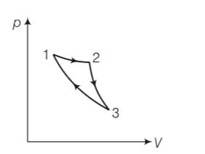
(a) the given process is a cyclic process i.e returns to the original state 1
Hence change in internal energy dU =0
dQ= dU+dW=0+dW
hence total heat supplied is converted to work done by the gas which is not possible by second law of thermodynamics.
(c) When the gas expands adiabatically from 2 to 3 . it is not possible to return to the same state without being heat supplied hence 3 to 1 cannot be adiabatic.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
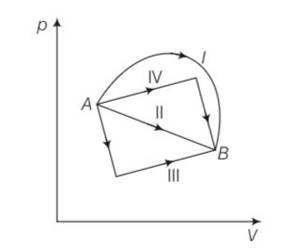
(b), (c) Change in internal energy for process A to B
dU=nCvdT=nCv (dT)=nCv (TB-TA)
work done from A to B = area under the PV curve which is maximum for path I
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a), (d) For isothermal dT= 0 so T=constant
For an ideal gas dU = change in internal energy = nCvdT=0
From first law of thermodynamics dQ= dU+dW
dQ= dW
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a), (b), (d) When the rod is hammered the external work is done on the rod which increases its temperature.
Heat is transferred to the gas in the small container by big reservoir at temperature T2
As the weight is added to the cylinder arrangement in the form of external pressure so it cannot reversed.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) Let us assume that T1, T2T3
According to questions there is no loss of heat in the surroundings
Heat lost by M3 = heat gained by M1+ heat gained by M2
M3s (T3-T)= M1s (T-T1)+M2s (T-T2)
T [M1+M2+M3]= M3T3+M1T1+M2T2
T =
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) Container A is isothermal and container B is adiabatic
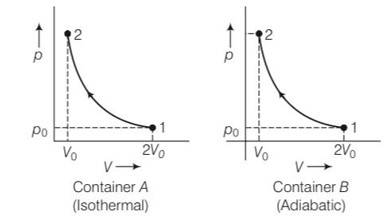
For isothermal process P1V1=P2V2
Po (2Vo)= P2 (Vo)
P2= 2Po
for adiabatic process
P1V1y= P2V2y
Po (2Vo)y=P2 (Vo)y
P2= ( )yPo= 2yPo
Hence ratio of final pressure =
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
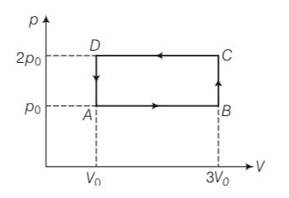
(b) Work done ABCD = area of rectangle ABCDA
= AB = (3Vo-Vo) (2po-po)
= 2V0 Po= 2poVo
And work done by the gas =- 2poVo
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
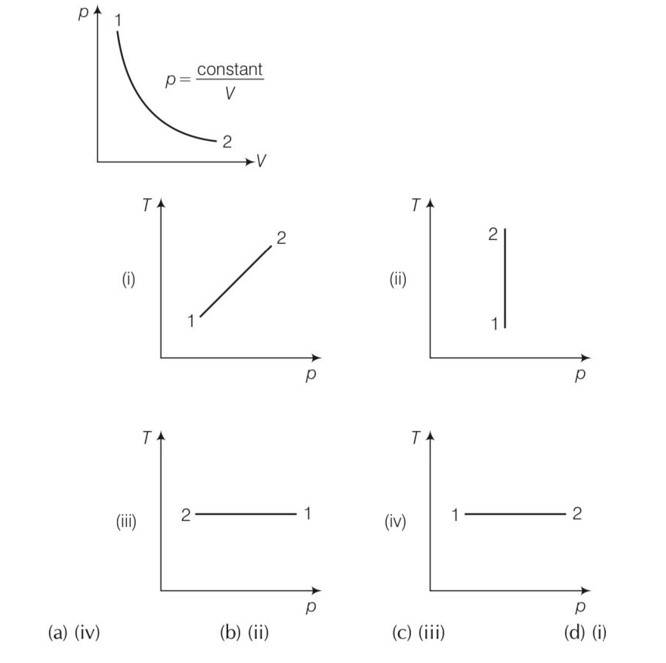
(c) As we know PV =constant
Hence we can say that gas is going through an isothermal process.
Clearly from the graph that between process 1 and 2 temperature is constant and the gas expands and pressure decreases. So density of 2 is less than 1 so option ii
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) Amount of sweat evaporated /minute =
=
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers