physics ncert solutions class 11th
Get insights from 951 questions on physics ncert solutions class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about physics ncert solutions class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Frequency of ultrasound, = 1000 kHz = Hz
Speed of sound in air, = 340 m/s
Speed of sound in water, = 1486 m/s
The wavelength of the reflected sound is given by the relation
= = 3.4 m
The wavelength of the transmitted sound wave is given by
= = 1.486 m
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a) For x =0 and t=0, the function (x – vt )2 becomes 0
Hence for x=0 and t=0, the function represents a point and not a wave.
(b) For x =0 and t=0, the function = log 0 =
Since the function does not converge to a finite value for x =0 and t = 0, it represents a travelling wave.
(c) For x = 0 and t = 0, the function = =
Since the function does not converge to a finite value for x = 0 and t = 0, it does not represent a travelling wave.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
In the equation ……(i)
Density = = where M = molecular weight of the gas, V = Volume of the gas, so we can write
…….(ii)
For ideal gas equation, PV = nRT, n = 1 so PV = RT
For constant T, PV = constant
In equation (ii), since PV = constant, and M constant, v is also constant. Hence, at a constant temperature, the speed of sound in a gaseous medium is independent of the change in the pressure of the gas.
From equation (i)
For 1 mole of an ideal gas, the gas equation can be written as PV = RT or P =
Substituting in equation (i), we get =
Since ,
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Length of the steel wire, l = 12 m
Mass of the steel wire, m = 2.1 kg
Velocity of the transverse wave, v = 343 m/s
Mass per unit length, = = = 0.175 kg/m
The velocity (v) of the transverse wave in the string is given by the relation:
, where T is the tension
T = = = 20588.575 N = 2.06 N
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Height of the tower, h = 300 m
Initial velocity of the stone, u = 0
Acceleration, a = g = 9.8 m/
Speed of sound in air, V = 340 m/s
The time taken by the stone (t), to strike the water can be calculated from the relation
s =us + a as
300 = 0 + or t = 7.82 s
Time taken by the sound to reach the top of the tower, = = = 0.88 s
Therefore, the time when the splash can be heard = 7.82 + 0.88 = 8.7 s
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Mass of the string, M = 2.5 kg
Tension in the string, T = 200 N
Length of the string, l = 20 m
Mass per unit length, = = = 0.125 kg/m
The velocity (v) of the transverse wave in the string is given by the relation:
= = 40 m/s
Therefore, time taken by the disturbance to reach the other end, t = = = 0.5 s
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Water pressure at the bottom, p = 1.1 Pa
Initial volume of the steel ball, V = 0.32
Bulk modulus of the steel, B = 1.6 N/
The ball falls at the bottom of the Pacific ocean which is 11 km beneath the surface
Let the change in volume of the ball on reaching the bottom of the trench be ΔV
We know, bulk modulus, B = or ΔV =
ΔV = = 2.2
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Diameter of the metal strip, d = 6.0 mm = 6 m
Radius, r = d/2 = 3 m
Maximum shearing stress = 6.9 Pa =
Maximum force = Maximum stress
= 6.9 = 6.9 = 1950.93 N
Since each rivet carries 1/4th of load,
Maximum tension on each rivet = 4 N = 7803.72 N
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Length of the mild steel wire, l = 1.0 m
Area of cross-section, A = 0.5 = 0.5
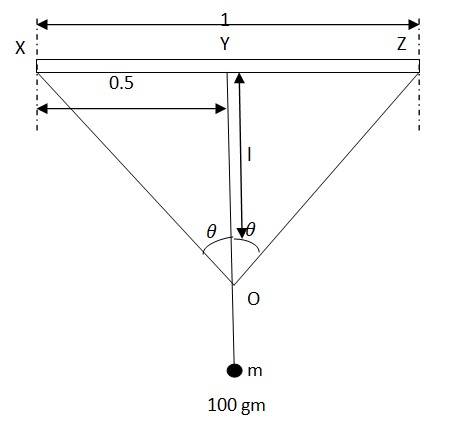
A mass of 100 gm is suspended at the midpoint.
m = 100 gm= 0.1 kg
Due to the weight, the wire dips, as shown in the figure.
Original length = XZ, depression = l
The final length of the wire after it dips = XO + OZ
Increase in length of the wire, Δl = (XO + OZ) – XZ ……(i)
From Pythagoras theorem
XO = OZ =
From equation (i)
Δl = 2 - 1.0 = 2 - 1.0 = - 1.0
Neglecting the smaller terms, we can write, Δl =
We know, Strain =
Let T be the tension in the wire, then
mg = 2T
From the figure
=&
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Cross-sectional area of wire A, = 1 = 1
Cross-sectional area of wire B, = 2 = 2
Young's modulus for steel, = 2 N/
Young's modulus for aluminium, = 7 N/
Stress in the wire = =
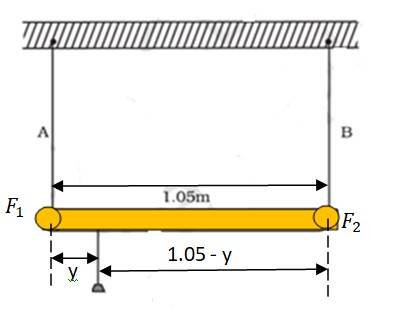
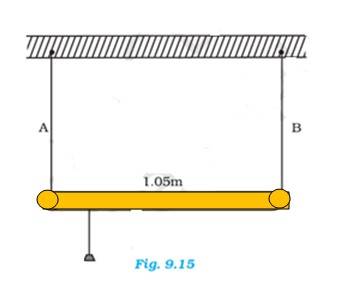
If the two wires have equal stresses, then
= or = = ………(i)
Where is the force exerted on steel wire and is the force exerted on aluminium wire
Taking a moment around the point of suspension, we get
=
= ……(ii)
Using equation (i) and (ii), we can
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers