Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Get insights from 140 questions on Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
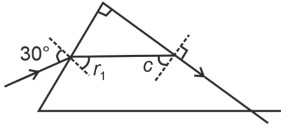
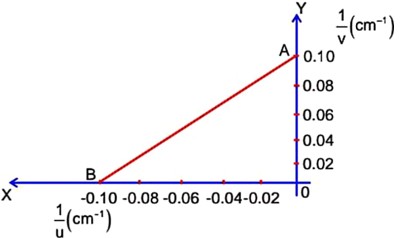
In prism,
…(i)
Apply Snell's law, on incidence surface
On squaring
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
A camera lens focuses the light onto a light-sensitive surface like film or a digital sensor for capturing an image. The camera lens gathers as much light as possible for forming a clear and bright image. This lens focuses the collected light on a specific point like camera's film or its digital sensor. The focus is achieved due to the curvature of lens and the arrangement of its optical elements. This lens refracts light rays so that they converge at focal plane where film/sensor is located.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
A telescope functions on the working principle of gathering light form distant source and then, forming image which can be magnified for observation. Based on their design, there are two types of telescopes including refracting telescopes and reflecting telescopes. A refracting telescope has a front lens called as objective lens. This front lens is a convex lens that collects light from distant objects and then bend it to the focal point. In a reflecting telescope, a concave mirror is the primary mirror that collects light and then, reflects it to a focal point.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
The following happens when light refracts from a prism:
- When a white light passes through prism, it is separated into its constituent colours. This separation occurs because different colours of light are refracted in different amounts. This is known as dispersion.
- Prism's refractive index varies with the wavelength of light. This causes shorter wavelengths to bend more than longer wavelengths. Due to the variation in bending, spread of colours is visible in rainbow.
- After being dispersed within the prism, light rays reach second surface of the prism. Here, light rays again undergo refraction as they exit the prism and re-enter air.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
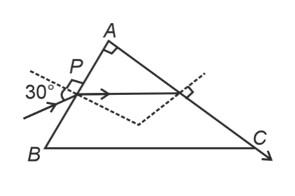
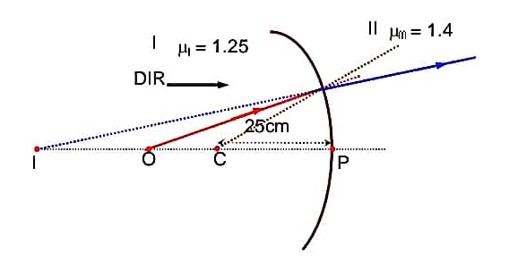
Since direction of incident ray (DIR) is from left to write, so considering refraction at point M, we can write
->
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
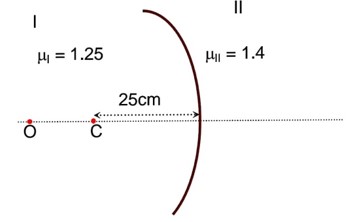
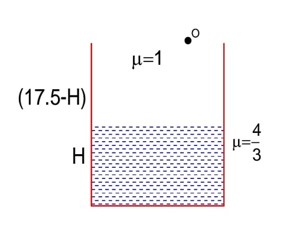
As observer is at O So height of water observed by observer
given diagram (17.5 - H) is height of observer
7H = 70
H = 10
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 685k Reviews
- 1800k Answers