Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Get insights from 140 questions on Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
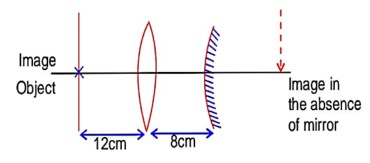
As image coincides with the object, image formed by convex lens should be at the centre of curvature of the convex mirror. If the convex mirror is removed, then, also, image formed the convex lens is at the same location.
Distance of image from object = 12 + 8 + 2 * 15 = 50 cm
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
For mirror
Velocity of image w.r.t. mirror
Velocity of object w.r.t. mirror
m magnification
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Velocity of light in medium 2
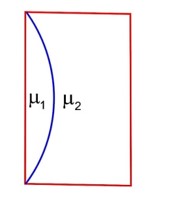
By snell's law for total internal Reflection
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
The Class 12 Physics Ch 10 Wave Optics includes a significant weightage in CBSE Class 12 Physics Exams which carries around 10 to 12 marks. Topics like Diffraction, Polarization, and Young's Double-Slit Experiment are oftenly asked in theory-based and numerical questions in CBSE Board exams and other competitive exams and therefore it is an important chapter for exams preparation.
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
To imporve the understanding of Class 12 Chapter 10 Wave Optics, students must follow the tips given below during their preparation time:
Students must read NCERT thoroughly to understand the fundamental concepts.
Students must solve all NCERT exercises and examples given in the textbook.
Students must consider NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Ch 10 Wave Optics to clarify doubts and learn step-by-step problem-solving.
Students must practice previous years' question papers and mock tests to gain confidence with their conceptual understanding and with the exam pattern.
Students can also watch videos to get familiar with the visualize opti
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 685k Reviews
- 1800k Answers