Alternating Current
Get insights from 94 questions on Alternating Current, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Alternating Current
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
An inductor opposes flow of current through it by developing a back emf according to Lenz's law. The induced voltage has a polarity so as to maintain the current at its present value. If the current is decreasing, the polarity of the induced emf will be so as to increase the current and vice -versa.
Since, the induced emf is proportional to the rate of change of current, it will provide greater reactance to the flow of current if the rate of change is faster, i.e., if the frequency is higher. The reactance of an inductor, therefore, is proportional to the frequency. Mat
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
A capacitor does not allow flow of direct current through it as the resistance across the gap is infinite. When an alternating voltage is applied across the capacitor plates, the plates are alternately charged and discharged. The current through the capacitor is a result of this changing voltage (or charge).
Thus, a capacitor will pass more current through it if the voltage is changing at a faster rate, i.e. if the frequency of supply is higher. This implies that the reactance offered by a capacitor is less with increasing frequency.
Mathematically, the reactance can be
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ps=60W, Is= 0.54 A
P=VI, V= 60/0.54= 110V
Voltage in the secondary is less than voltage in primary so transformer is step down transformer
As transformation ratio is, k = Es/Ep= Ip/Is
110/220=Ip/0.54A
Ip= 0.27A
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
L= 0.01H
R= 1ohm
Voltage =200V
Frequency = 50Hz
Z= = = =3.3ohm
tan = = 3.14
= tan-13.14=72
=72
= /w= = s
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
For a Direct Current (DC),
1ampere= 1coulomb/sec
An AC current changes direction with the source frequency and the attractive force would average to zero. Thus, the AC ampere must be defined in terms of some property that is independent of the direction of current.
Joule's heating effect is such property and hence it is used to define rms value of AC.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) We know that P= VI
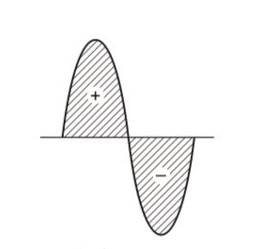
that is curve of power will be having maximum amplitude, equals to multiplication of amplitudes of voltage (V)and current (I) curve. So, the curve will be represented by A.
(b) As shown by shaded area in the diagram, the full cycle of the graph consists of one positive and one negative symmetrical area. Hence average power over a cycle is zero.

(c) As the average power is zero, hence the device may be inductor (L) or capacitor (C) or the series combination of L and C.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar

New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
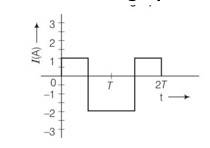
Irms= = = 1.58A = 1.6 approx
This value is indicating in graph
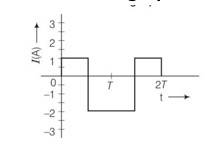
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
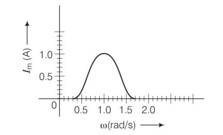
In the figure
Band width = w2-w1 where these two corresponds to frequencies at which magnitude of current is 1/ times of maximum value
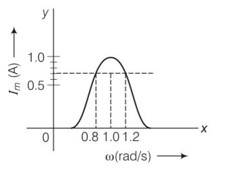
Irms= = 1/ = 0.7A
From the diagram the corresponding frequencies are 0.8 and 1.2rad/s
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
E=E0sinwt
And current I=I0sin (wt )
Power, P= EI = E0sinwt = E0I0sinwtsin (wt+ )
= [cos ]………… (1)
Pav= cos =VrmsIrmscos ………. (2)
From eqn 1 ……But when cos < cos (2wt+
P<0 power can be nagative of an AC source
From eqn 2……… Pav>0
cos =R/Z>0 average power can not be negative
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers