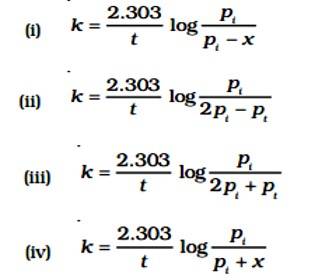Chemical Kinetics
Get insights from 144 questions on Chemical Kinetics, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Chemical Kinetics
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New question posted
7 months agoNew answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option C
Rate of Disappearance = = - =
=
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option A
Because reactant concentrations fall as reactants are transformed to products, reaction rates decrease over time. When reactant concentrations are raised, reaction rates generally increase
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option B
Reaction occurring at the smallest time interval is known as instantaneous rate of reaction. For e.g the instantaneous rate of reaction at 40s is the rate of reaction during a small interval of time close to 40s. Volume changes during a small-time interval close to the 40s.
Instantaneous rate can be determined graphically by drawing a tangent on the curve
Instantaneous reaction=
Option B is incorrect since the line travels through the graph but does not link to any of the Y axis lines. As a result, option B is incorrect.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option C
Option (c) is the only one of the four assertions that is incorrect. In rate law expression, the order of reaction is equal to the sum of the power of concentration of the reactants.
xA + yB→zC
r = k (A)x (B)y
Order x + y
The order of the reactions can also be a fraction. In a balanced chemical equation, the order of reaction may or may not be equal to the total of the stoichiometric coefficients of the reactants.
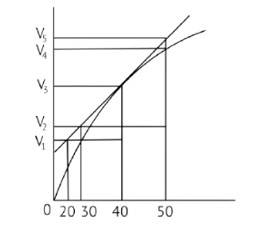
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option C
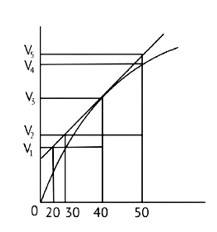
In the given graph V is the volume in the Y axis and time is in X axis
Zn + dil.HCl→ZnCl2 + H2↑
Average rate = 40s
Average rate of reaction =
Analyzing the graph line where time and volume intersect.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option D
k = Ae -
From this equation
Kα
When Activation energy Ea decreases, rate constant k
increases.
Hence, Rate constant increases exponentially with decreasing activation energy and increasing temperature.
New answer posted
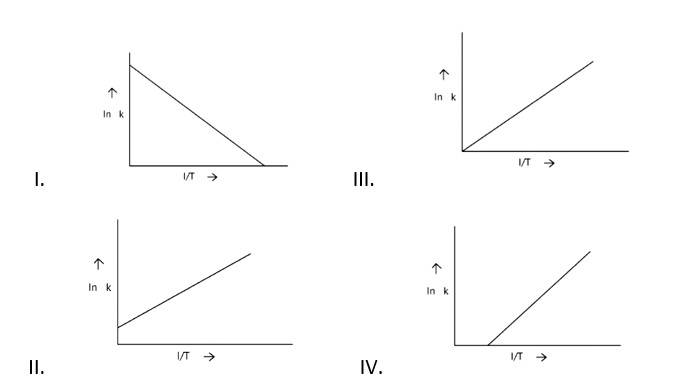
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option A
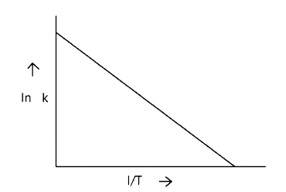
Arrhenius equation Ae -
K = rate constant
A= frequency factor
Ea= Activation Energy
R= gas constant
T= temperature
ln k = lnA -
When the temperature rises, ln falls.
∴ ln kv/s , is a negative slope.
ln A is intercepted by k, and its magnitude decreases with time.
∴ Negative slope is obtained.
When compared to the other possibilities, T is increasing over time, which is incorrect.
ln k = + lnA
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option B
Given:
A (g) → B (g) + C (g)
pi= Initial pressure
(Time) t = 0
A (g) → B (g) + C (g)
pi →0atm + 0atm
t, (pi - x)atm
pt = (pi - x)atm + x + x = pi + x
pA = (pi - x)
The value of x changes when it is substituted.
pA = pi - (pt - pi) = 2pi - pt
K = log
New answer posted
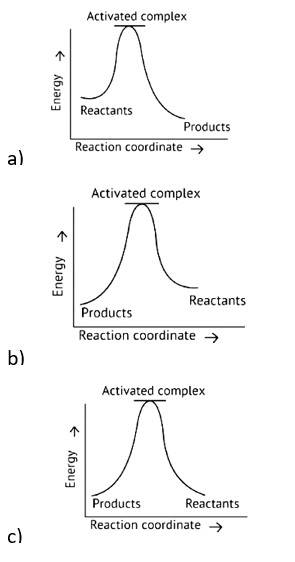
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option A
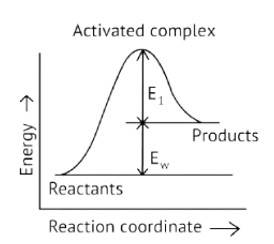
Activation Energy → The amount of energy required to overcome the obstacle and generate a product
The activation energy of a forward reaction can be seen in the [Eaf = E1 + E2] (This is an endothermic reaction.
Therefore, [Eaf > Eab]
The energy of the product is high, while the energy of the reactant is low.
The lower the energy, the more stable and positive the situation becomes.
Δ? = posistive
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 685k Reviews
- 1800k Answers