Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Get insights from 133 questions on Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
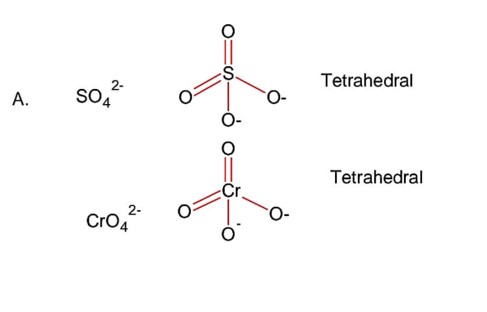
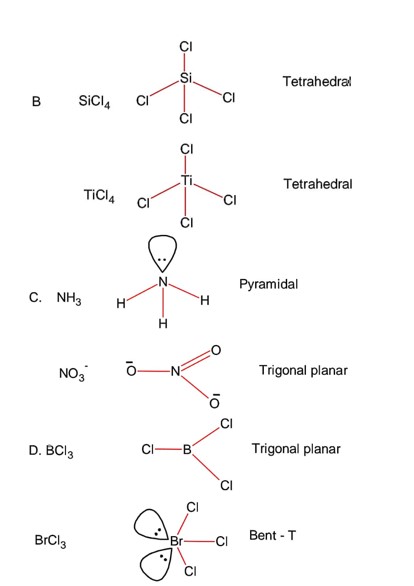
Kindly consider the following figure
As bond order is increasing it implies bond strength is increasing. As bond order is increasing it implies bond strength is increasing.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
Total number of electron in Ti = 22
Total number of electron in Ti? = 22 – 4 = 18 So EAN value of Ti = 18 + 12 + 4 = 34
New answer posted
4 months agoIf Hund's rule is violated, then which among the following will become diamagnetic from paramagnetic
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 9
Number of electrons in
are e- deficient molecules. B2H6 is dimer of BH3, both compound has 6e- only.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 9
Bond strength Bond order
NO ® Number of electron = 7 + 8 = 15
B.O. Similar to
B.O. of N2 = 3 B.O of C2 =
Removal of e- form antibonding molecular orbital increases bond order.
In NO & O2 has valance e- in p orbital.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
E.C = σ1s² σ1s² σ2s² σ2s² σ2p? ² π2p? ² = π2p? ² π2p? ² = π2p? ²
Total electrons in BMO = 10
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers