Class 12th
Get insights from 12k questions on Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 9
Partial hydrolysis of XeF? gives XeO? F?
XeF? + 2H? O → XeO? F? + 4HF
Compound A is XeF? , so number of lone pair on Xe is 1.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
The reduction of aluminum oxide (Al? O? ) is performed through an electrolytic process in its molten state. This method is necessary because Al? O? is a highly ionic and stable compound.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 9
m=2 molal
ΔT? = 100.52 – 100 = 0.52°C
Using, ΔT? = iK? m
0.52 = I * 0.52 * 2
i = 0.5
Now using, α = (1-i) / (1-1/n)
Where, n=2 (dimerisation)
α = (1-0.5) / (1-0.5) = 1
So, percentage association = 100%
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
In a C? fullerene molecule, all 60 carbon atoms are identical. Each carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms via sigma bonds. The structure is composed of 20 six-membered rings and 12 five-membered rings.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
In diacetamide (CH? CO)? NH), the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom is delocalized through resonance with both adjacent carbonyl groups. This extensive resonance greatly decreases the electron density on the nitrogen atom.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 9
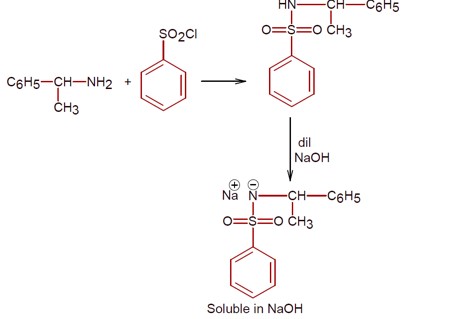
Only 1° amine react with benzene sulphonyl chloride to give a compound which is soluble in alkali
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 9
Metal sulphide sols are negatively charged while metal oxide sols are positively charged sols. So, CdS is negative while TiO? is positively charged sol.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
Colloidal particles are small enough to pass through an ordinary filter but can be stopped by an ultrafilter paper due to their specific particle size range.
New question posted
4 months agoNew answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
P (x) = f (x³) + xg (x³) is divisible by x²+x+1. The roots of x²+x+1=0 are the complex cube roots of unity, ω and ω².
P (ω) = f (ω³) + ωg (ω³) = f (1) + ωg (1) = 0 — (I)
P (ω²) = f (ω²)³) + ω²g (ω²)³) = f (1) + ω²g (1) = 0 — (II)
Subtracting (II) from (I): (ω - ω²)g (1) = 0. Since ω ≠ ω², we must have g (1) = 0.
Substituting g (1)=0 into (I) gives f (1) = 0.
We need to find P (1) = f (1³) + 1*g (1³) = f (1) + g (1).
P (1) = 0 + 0 = 0.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers