Class 12th
Get insights from 12k questions on Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (d)
Acetanilide is less basic than aniline because electron density of nitrogen is lowered by acetyl group.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (a)
Aromatic primary amines cannot be prepared using Gabriel phthalimide synthesis as aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution with anion formed by phthalimide. Both the statement's assertion and reason are incorrect, hence the correct answer is a.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
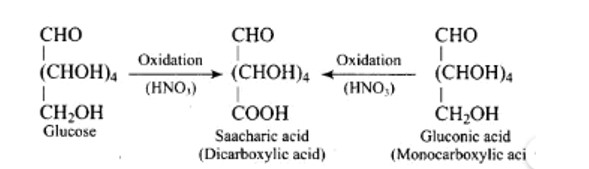
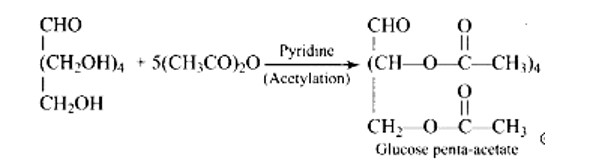
Glucose with acetic anhydride in the presence of pyridine or a few drops of concentrated H2SO4, leads to productions of penta-acetyl derivatives which shows that there are five hydroxyl groups. One hydroxyl group is a primary (1? ) alcoholic, whereas the other four (C2, C3, C4, and C5) hydroxyl or −OH groups are all labelled as secondary (2? ) alcoholics.
When glucose (or gluconic acid) is oxidized in the presence of HNO3, it produces saccharic acid (a dicarboxylic acid), showing that the primary (1? ) alcoholic group is oxidized to −COOH, but only under extreme of
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (d)
Fe+2HCl→FeCl2+2 [H] FeCl2+H2O (g)→FeO+2HCl
The nascent hydrogen formed act as reducing agent for the reduction of nitro compounds.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (b)
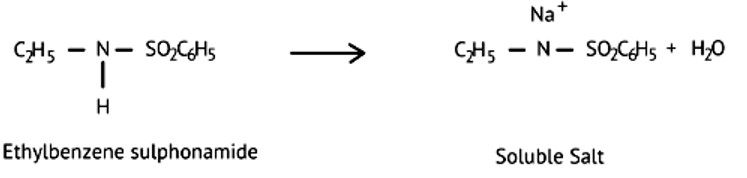
N, N-die ethyl benzene sulphonamide, there is no acidic hydrogen present on the N-atom which can make it soluble. Therefore, it is insoluble in alkali.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sugars are mainly classified into two configurations: D− configuration and L− configuration, each of which have individual distinct structures. These configurations are expressed in terms of the standard glyceraldehyde which are basically of two types:
D− (+)− Glyceraldehyde and L− (−)− Glyceraldehyde. The D− configuration has −OH attached to the carbon near to −CH2OH on the right, whereas the L− configuration has −OH attached to the carbon adjacent to −CH2OH on the left. The sugars are designated D− and L− depending on whether the molecul
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (d)
Ethylbenzene sulphonamide is soluble in alkali because it has acidic hydrogen.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Enzyme active sites bind the substrate molecule in a favourable location so that the reagent may attack it effectively. At each site in an enzyme, there is a substrate binding site to which the substrate binds and the reaction then proceeds.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Starch has α - glucose units, and cellulose has β−D− glucose units. In starch and glycogen, there is α−I glycosidic linkage, and in cellulose, there is glycosidic connection β - between glucose units.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Two monosaccharide molecules are linked by an oxide bond generated by the loss of a water molecule. Glycosidic linkage is the joining of two monosaccharide units by an oxygen atom.
Disaccharides, trisaccharides, and polysaccharides all have glycosidic linkage.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 684k Reviews
- 1800k Answers