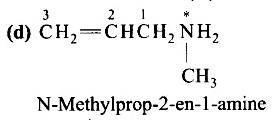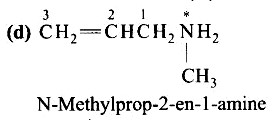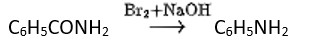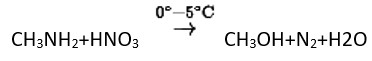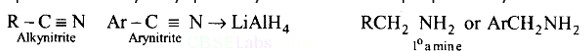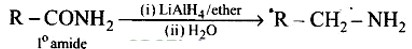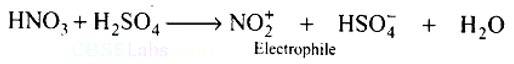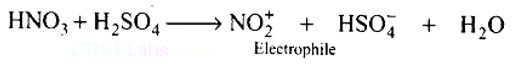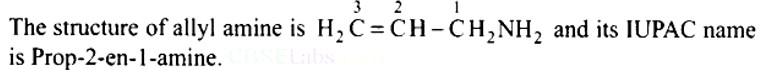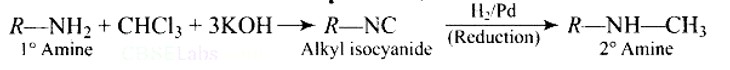- Amines Multiple Choice Questions
- Amines Short Type Questions
- Amines Matching Type Questions
- Amines Assertion and Reason Type Questions
- Animes Long Answer Type Questions
- JEE Mains Solutions 2022, 26th july , chemistry, second shift
- 27th July 2022 first shift
Amines Multiple Choice Questions
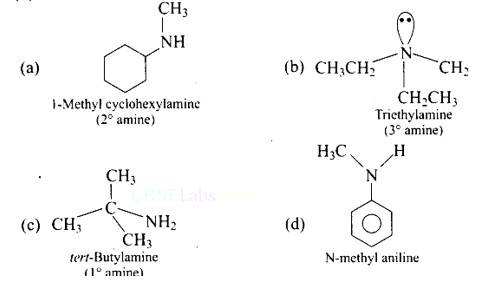
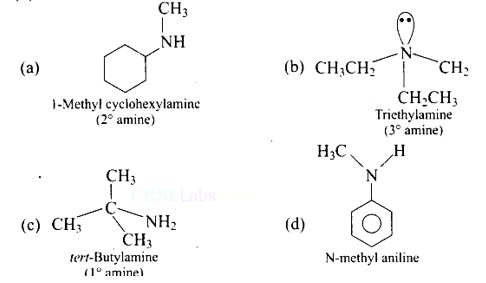
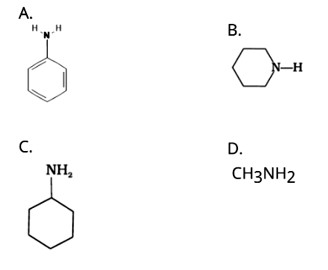
| 1. Which of the following is a 3° amine? (A) 1-methylcyclohexylamine (B) Triethylamine (C) Tert-butylamine (D) N-methylaniline |
| Ans: (B) Triethylamine The structure of the given amines are shown below. |
| 2. The correct IUPAC name for CH2=CH−CH2−NH−CH3 is (A) Allylmethylamine (B) 2-amino-4-pentene (C) 4-aminopent-l-ene (D) N-méthylprop-2-en-l-amine |
| Ans: Correct answer: (D) |
Commonly asked questions
Which of the following is a 3° amine?
(A) 1-methylcyclohexylamine
(B) Triethylamine
(C) Tert-butylamine
(D) N-methylaniline
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (B) Triethylamine
The structure of the given amines are shown below.
The correct IUPAC name for CH2=CH−CH2−NH−CH3 is
(A) Allylmethylamine
(B) 2-amino-4-pentene
(C) 4-aminopent-l-ene
(D) N-méthylprop-2-en-l-amine
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct answer: (D)
Amongst the following, the strongest base in an aqueous medium is.
(A) CH3NH2
(B) NCCH2NH2
(C) (CH3)2NH
(D) C6H5NHCH3
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (C)
Because of the electron-releasing nature of the alkyl group, it (R) pushes electrons towards nitrogen, making the unshared electron pair more available for sharing with the acid's proton. Furthermore, the +I effect of the alkyl group stabilizes the substituted ammonium ion formed from the amine by dispersing the positive charge.
As a result, alkylamines are more powerful bases than ammonia.
As a result, the basic nature of aliphatic amines should increase as the number of alkyl groups increases.
Which of the following is the weakest Brönsted base?
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (A)
The NH2 group is directly attached to the benzene ring in aniline and other aryl amines. As a result, the unshared electron pair on the nitrogen atom is conjugated with the benzene ring, making it less available for protonation.
Benzylamine may be alkylated as shown in the following equation:
C6H5CH2NH2+R−X→C6H5CH2NHR
Which of the following alkyl halides is best suited for this reaction through SN1 mechanism?
(A) CH3Br
(B) C6H5Br
(C) C6H5CH2Br
(D) C2H5Br
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (C)
SN1 reaction: A nucleophilic reaction that occurs in two steps, first is the bond-breaking step and the second is the production of the carbocation. The stability of carbocation formed in the second step determines the rate of reactivity of reactant toward SN1 reaction. Here, C6H5CH2Br,
In the process of ionization, removal of bromine, a stable Benzyl carbocation is produced. Therefore, it is best suited for reaction through the SN1 mechanism.
Which of the following reagents would not be a good choice for reducing an aryl nitro compound to an amine?
(A) H2 (excess) /Pt
(B) LiAlH4 in ether
(C) Fe and HCl
(D) Sn and HCl
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (B)
Lithium aluminum hydride in ether is a strong reducing agent that donates its H? hydride ion to any C=O containing a functional group. In addition to LiAlH4 to aryl nitro compounds, no reaction will be observed, the desired products of amines will not be produced, rather it will form diazobenzene products.
In order to prepare a primary amine from an alkyl halide with simultaneous addition of one CH2 group in the carbon chain, the reagent used as a source of nitrogen is
(A) Sodium amide, NaNH2
(B) Sodium azide, NaN3
(C) Potassium cyanide, KCN
(D) Potassium phthalimide, C6H4(CO2)N−K+
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (C)
Potassium cyanide, as cyanide on reduction with sodium metal in alcohol, produces amine with increased carbon atoms.
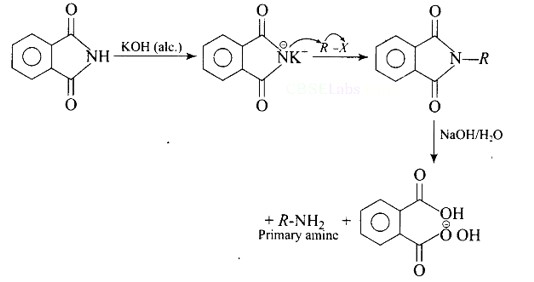
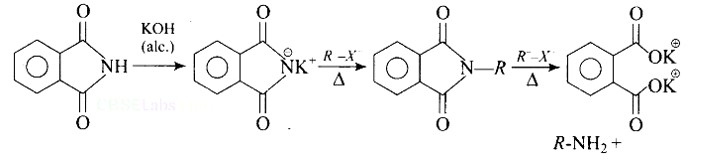
The source of nitrogen in Gabriel synthesis of amines is.
(A) Sodium azide, NaN3
(B) Sodium nitrite, NaNO2
(C) Potassium cyanide, KCN
(D) Potassium phthalimide, C6H4(CO2)N−K+
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (D)
Gabriel synthesis reaction:
Gabriel’s synthesis is a method for producing primary amines. When phthalimide is treated with ethanolic potassium hydroxide, it forms a potassium salt of phthalimide, which when heated with an alkyl halide and then alkaline hydrolyzed yields the corresponding primary amine. This method cannot produce aromatic primary amines because aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution with the anion formed by phthalimide.
Amongst the given set of reactants, the most appropriate for preparing 2? amine is.
(A) 2?R−Br+NH3
(B) 2?R−Br+NaCN followed by H2/Pt
(C) 1?R−NH2+RCHO followed by H2/Pt
(D) 1?R−Br+(2 mol)+ potassium phthalimide followed by H3O+/ heat
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: ( C)
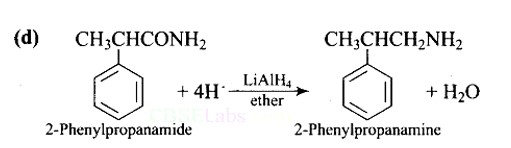
The best reagent for converting 2-phenylpro-panamide into-2-phenyl- propanamine is.
(A) Excess H2
(B) Br2 in aqueous NaOH
(C) Iodine in the presence of red phosphorus
(D) LiAlH4 in ether
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (D)
Lithium aluminium hydride in ether is a strong reducing agent that donates its hydride ion to any C=O containing functional groups into corresponding reduced compounds. Here, the amide group is converted to an amine functional group.
LiAlH4 in ether is the best reagent for converting 2-phenylpropanamide to 2-phenylpropanamine.
The best reagent for converting-2-phenylpro-panamide into 1-phenylethanamine is.
(A) Excess H2/Pt
(B) NaOH/Br2
(C) NaBH4/ methanol
(D) LiAlH4/ ether
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (B)
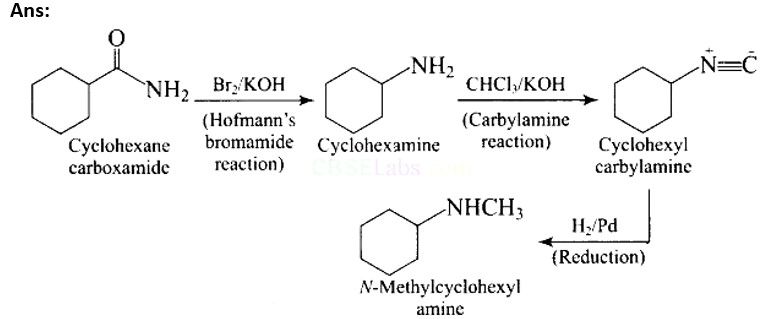
Hoffmann bromamide reaction- it is also called degradation reaction as in this reaction primary amide group is treated with halogen first (Br) then the halogen-substituted amide product is converted to a primary amine with the release of carbon dioxide gas.
Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction is shown by.
(A) ArNH2
(B) ArCONH2
(C) ArNO2
(D) ArCH2NH2
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (B)
Hoffmann invented a method for producing primary amines by treating an amide with bromine in an aqueous or ethanolic sodium hydroxide solution. An alkyl or aryl group migrates from the amide's carbonyl carbon to the nitrogen atom during this degradation reaction.
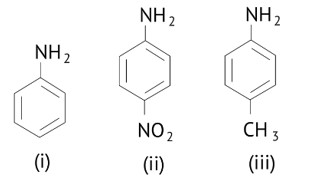
The correct increasing order of basic strength for the following compounds is
(A) (II) <( III )<( I )
(B) (III) <(I)<(II)
(C) (III) < (II) < (I)
(D) (II) <(I)<(III)
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (D)
The greater the electron density towards the ring, the greater its basic strength.
The electron withdrawing group reduces basic strength, whereas the electron donating group increases basic strength.
Methylamine reacts with HNO3 to form
(A) CH3−O−N=O
(B) CH3−O−CH3
(C) CH2OH
(D) CH3CHO
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (C)
Methyl amine reacts with HNO3 form methanol with release of nitrogen gas and water as side products.
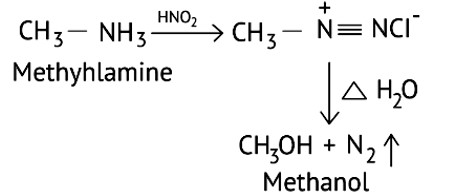
The gas evolved when methylamine reacts with nitrous acid is .
A) NH3
(B) N2
(C) H2
(D) C2H6
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (B)
Primary aliphatic amines react with nitrous acid to form aliphatic diazonium salts, which are unstable and release nitrogen gas and alcohol quantitatively.
In the nitration of benzene using a mixture of conc. H2SO4 and conc. HNO3, the species which initiates the reaction is.
(A) NO2
(B) NO+
(C) NO2+
(D) NH2
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (C)
In the process of nitration of benzene, firstly H2SO4 dissociates into H+ and HSO4−. The proton produced further reacts with HNO3 to give a positively charged complex that is unstable and dissociates into nitronium ions and water as products. The nitronium ion is an electron-deficient species i.e. electrophile that attacks the electron cloud of the benzene ring.
H2SO4 (conc.) ? H++HSO4−
H++HNO3? H2NO3+
H2NO3+? NO2+ + H2O
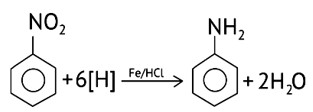
Reduction of aromatic nitro compounds using Fe and HCl gives.
(A) Aromatic oxime
(B) Aromatic hydrocarbon
(C) Aromatic primary amine
(D) Aromatic amide
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (C)
Using active metals like iron in acidic conditions can be efficiently used for the reduction of nitro compounds.
Under the acidic conditions, the intermediate compounds that may form are readily reduced to primary amine and pure product of primary amine is obtained.
The most reactive amine towards dilute hydrochloric acid is ___________.
Solution:
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (B)
Greater will be the basic character, greater will be its reactivity towards dilute hydrochloric acid. As, (B), secondary amine, it will be the most basic among all and hence the most reactive amine towards acid.
Acid anhydrides on reaction with primary amines give.
(A) Amide
(B) Imide
(C) Secondary amine
(D) Imine
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (A)
On Reaction of acid anhydrides with primary amines, amides are formed as the primary product along with carboxylic acid.
(RCO)2O + RNH2? RCONH2 + RCOOH
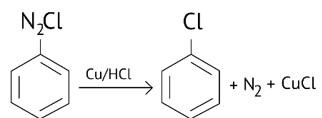
The reaction as ArN2Cl 
(A) Sandmeyer reaction
(B) Gatterman reaction
(C) Claisen reaction
(D) Carbylamine reaction
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (B)
Diazonium salts react with copper powder and halogen acid to form aryl halide.
Gattermann reaction is a Sandmeyer reaction variant in which Cu powder replaces CuCl.
This substitution produces aryl halide more easily and under milder conditions than the Sandmeyer reaction.
Best method for preparing primary amines from alkyl halides without changing the number of carbon atoms in the chain is
(A) Hoffmann bromamide reaction
(B) Gabriel phthalimide reaction
(C) Sandmeyer reaction
(D) Reaction with NH3
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (B)
The reaction of transformation of primary alkyl halides to primary amines using potassium phthalimide is the Gabriel phthalimide reaction.
Which of the following compounds will not undergo azo coupling reaction with benzene diazonium chloride?
(A) Aniline
(B) Phenol
(C) Anisole
(D) Nitrobenzene
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (D)
Weak electrophile such as Diazonium cation readily reacts with electron-rich compounds which are having electron-rich compounds such as hydroxyl group, amino group. They don't react with electron-withdrawing groups like nitro groups. Therefore, nitrobenzene will not undergo an azo coupling reaction with benzene diazonium chloride.
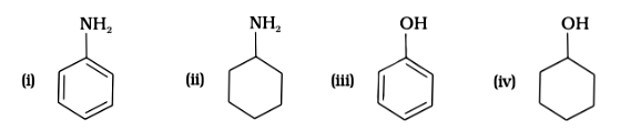
Which of the following compounds is the weakest Bronsted base?
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (D)
Since phenol is the strongest acid among the four options listed above, it is the weakest Brönsted base. The stronger the acid, the weaker the conjugate base.
Amines have a strong tendency to accept electrons thus they are a strong bronsted base while phenol is the strongest acid among all, therefore as per the relation of conjugative strong acids and weak bases, phenol is the weakest base.
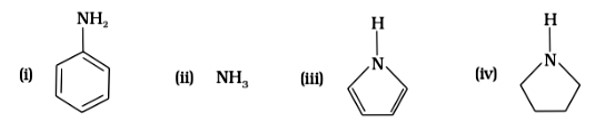
Among the following amines’ the strongest Bronsted base is
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (D)
Pyrrolidine is the strongest of two bases because the lone pair of nitrogen does not involve sin resonance, and the presence of two alkyl basic compounds increases the basic strength among the given four compounds.
The correct decreasing order of basic strength of the following species is
H2O,NH3,OH−,NH2−
(A) NH2− >OH∗>NH3>H2O
(B) OH− >NH2− >H2O > NH3
(C) NH3 >H2O > NH2− >OH−
(D) H2O > NH3 > OH − > NH2−
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (A)
The basic strength of an atom is determined by its electron-donating capacity; in this case, the amide is the most basic due to the presence of a negative charge and two lone pairs of electrons on the nitrogen atom.
Which of the following should be most volatile?
(A) II
(B) IV
(C) I
(D) III
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (B)
Among primary, secondary, and tertiary amines, tertiary amines are the most volatile compounds as they don't have any strong intermolecular H-bonding between N-H like the primary and secondary amines have.
So due to weak dipole-dipole interactions, (B) will be the most volatile.
Which of the following methods of preparation of amines will not give the same number of carbon atoms in the chain of amines as in the reactant?
(A) Reaction of nitrile with LiAlH4
(B) Reaction of amide with LiAlH4 followed by treatment with water.
(C) Heating alkyl halide with potassium salt of phthalimide followed by hydrolysis
(D) Treatment of amide with bromine in aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (D)
Aliphatic and arylalkyl primary amines can be prepared by the reduction of the corresponding nitriles with LiAlH4
Heating alkyl halide with primary, secondary and tertiary amine can be prepared by reduction of LiAlH4 followed by treatment with water.
Heating alkyl halide with potassium salt of phthalimide followed by hydrolysis produces primary amine. This process is known as Gabriel phthalimide reaction. The number of carbon atoms in the chain of amines of product is same as reactant.
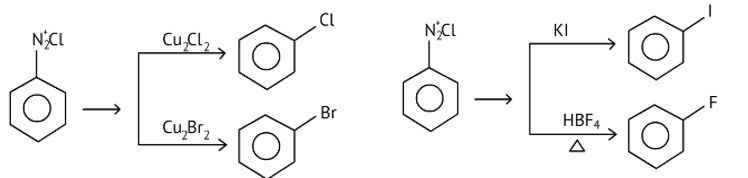
Which of the following cannot be prepared by Sandmeyer’s reaction?
(A) Chlorobenzene
(B) Bromobenzene
(C) Iodobenzene
(D) Fluorobenzene
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (C and D)
Chlorobenzene and bromobenzene are prepared by the sandmeyer's reaction.
While fluorobenzene and iodobenzene are prepared by simple heating of diazonium salt with aqueous KI Solution.
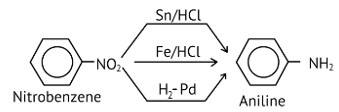
Reduction of nitrobenzene by which of the following reagents give aniline?
(A) Sn/HCl
(B) Fe/HCl
(C) H2−Pd
(D) Sn/NH4OH
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (A, B & C)
Nitro compounds are reduced to amines by passing hydrogen gas through an acidic medium containing finely divided nickel, palladium, or platinum, as well as by reduction with metals in an acidic medium.
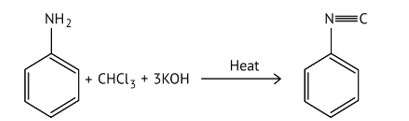
Which of the following species are involved in the carbylamine test?
(A) R-NC
(B) CHCl3
(C) COCl2
(D) NaNO2+HCl
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (A and B)
When aliphatic and aromatic primary amines are heated with chloroform and ethanolic potassium hydroxide, they form isocyanides or carbylamines, which have a foul odor. This reaction does not occur in secondary or tertiary amines.
The reagents that can be used to convert benzenediazonium chloride to benzene are __________.
(i) SnCl2 /HCl
(ii) CH3CH2OH
(iii) H3 PO2
(iv) LiAlH4
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: option (B and C)
Certain mild reducing agents like hypophosphorous acid (phosphinic acid) or ethanol reduce diazonium salts to arenes and themselves get oxidised to phosphorous acid and ethanol, respectively.
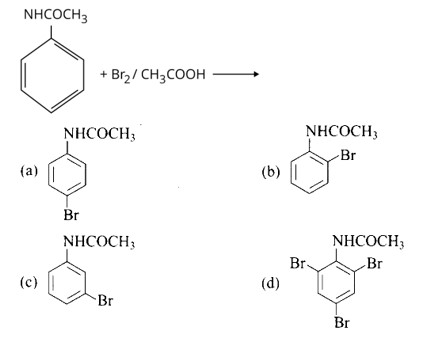
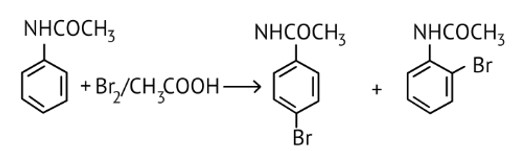
The Product of the following reaction is.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option a and b
NHCOCH3 is an ortho- para directing group so ortho-para products are formed.
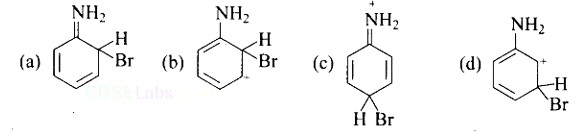
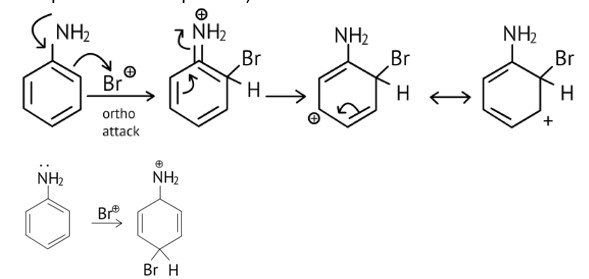
Arenium ion involved in the bromination of aniline is.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: A, B & C
As the NH2 group is Ortho para directing group, so Br+ attacks only at the o and p positions thus the products formed corresponds to the option A, B and C.
Which of the following amines can be prepared by Gabriel synthesis?
(a) Isobutyl amine
(b) 2-Phenylethylamine
(c) N-Methylbenzylamine
(d) Aniline
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (a and b)
Gabriel synthesis is a method for producing primary amines. When phthalimide is treated with ethanolic potassium hydroxide, it forms a potassium salt of phthalimide, which when heated with an alkyl halide and then alkaline hydrolyzed yields the corresponding primary amine.
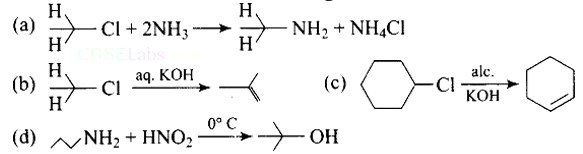
Which of the following reactions are correct?
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: option a and c
(a) Primary alkyl halides react with ammonia to give primary amines. Correct reaction.
(B) Elimination process doesn't occur with aq. KOH, hydrolysis process takes place. (B) is incorrect.
(c) Dehydrohalogenation I.e. elimination of HCl occurs which produces alkene as the product takes place with alc. KOH . (c) is correct.
(d) In this reaction, aliphatic primary amines, on treatment with nitrous acid, produce primary alcohol as a product.
Therefore (d) is incorrect.
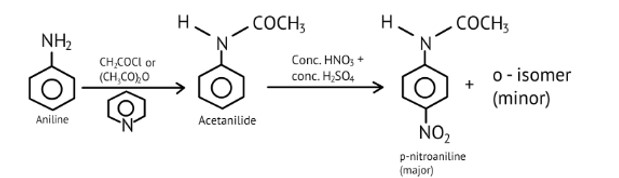
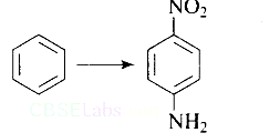
Under which of the following reaction conditions, aniline gives p-nitro derivative as the major product?
(A) Acetyl chloride/pyridine followed by reaction with conc. H2SO4+ conc. HNO3
(B) Acetic anhydride/pyridine followed by conc. H2SO4+ conc. HNO3
(C) Dil. HCl followed by reaction with conc. H2SO4+ conc. HNO3
(D) Reaction with conc. H2SO4+ conc. HNO3
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: a and b
In addition to the nitro derivatives, direct nitration of aniline produces tarry oxidation products. Furthermore, aniline is protonated in the strongly acidic medium to form the anilinium ion, which is meta directing. As a result, in addition to the ortho and para derivatives, a significant amount of meta derivative is formed.
However, by protecting the? NH2 group with an acetylation reaction with acetic anhydride, the nitration reaction can be controlled and the p-nitro derivative obtained as the main product.
Which of the following reactions belong to electrophilic aromatic substitution?
(A) Bromination of acetanilide
(B) Coupling reaction of aryldiazonium salts
(C) Diazotization of aniline
(D) Acylation of aniline
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (A and B)
Benzene diazonium chloride reacts with phenol to form p-hydroxy azobenzene by coupling the phenol molecule at its para position with the diazonium salt. This is referred to as a coupling reaction. This is an illustration of an electrophilic substitution reaction.
Amines Short Type Questions
| 1. Which is the role of HNO3 in the nitrating mixture used for nitration of benzene? |
| Ans: HNO3 acts as a base in the nitrating mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4) and provides the electrophile. |
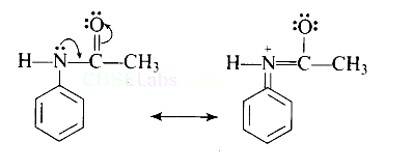
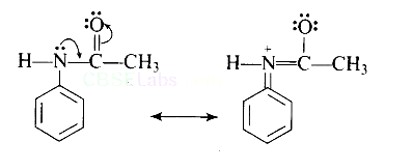
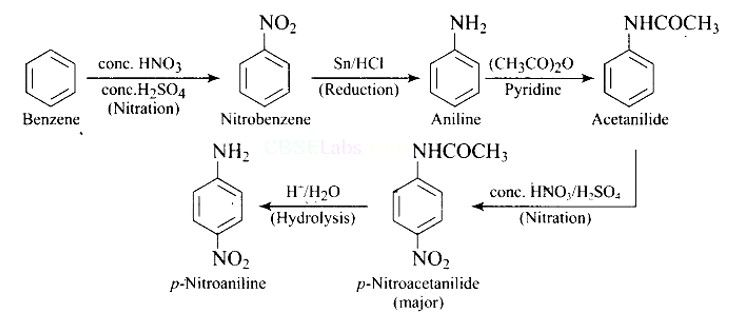
| 2. Why is −NH2 group of aniline acetylated before carrying out nitration? |
| Ans: Direct nitration of aniline is not possible on account of oxidation of -NH2 group. However, nitration can be carried after protecting the -NH2 group by acetylation to give acetanilide which is then nitrated and finally hydrolysed to give o- and p-nitroanilines. As a result, the activating effect -NH2 group is reduced i.e., the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen is less available for donation to benzene ring by resonance. Therefore, activating effect of —NHCOCH3 group is less than that of —NH2 group. |
Commonly asked questions
Which is the role of HNO3 in the nitrating mixture used for nitration of benzene?
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: HNO3 acts as a base in the nitrating mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4) and provides the electrophile.
Why is −NH2 group of aniline acetylated before carrying out nitration?
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans:
Direct nitration of aniline is not possible on account of oxidation of -NH2 group. However, nitration can be carried after protecting the -NH2 group by acetylation to give acetanilide which is then nitrated and finally hydrolysed to give o- and p-nitroanilines.
The acetyl group being electron withdrawing attracts the lone pair of electrons of the N-atom towards carbonyl group.
As a result, the activating effect -NH2 group is reduced i.e., the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen is less available for donation to benzene ring by resonance. Therefore, activating effect of —NHCOCH3 group is less than that of —NH2 group.
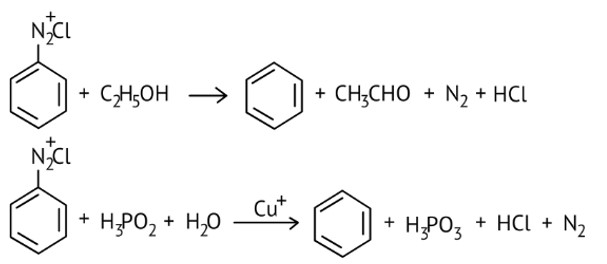
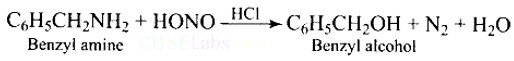
What is the product when C6H5CH2NH2 reacts with HNO2 ?
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: When Benzyl amine is treated with nitrous acid, firstly BDC is formed which is unstable and decomposes to Benzyl alcohol.
What is the best reagent to convert nitrile to primary amine?
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The best reagents for the conversion of nitrile to primary amine are LiAlH4 and Sodium/Alcohol. By reduction, the nitriles can be converted into a corresponding primary amine.
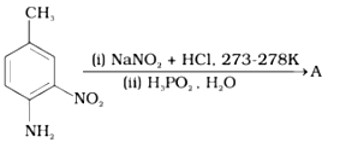
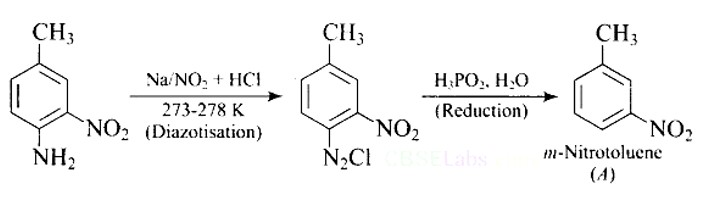
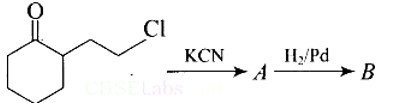
Give the structure of ‘A’ in the following reaction.
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans:
What is Hinsberg reagent?
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Hinsberg's reagent is also known as benzenesulphonyl chloride (C6H5SO2Cl). When it reacts with primary and secondary amines, it produces sulphonamides. Allowing secondary and tertiary amines to react with Hinsberg's reagent allows them to be distinguished (benzenesulphonyl chloride C6H5SO2Cl). Secondary amines react with Hinsberg's reagent to form an alkali-insoluble product. N, N-diethylamine, for example, reacts with Hinsberg's reagent to form N, N-diethylbenzenesulphonamide, which is insoluble in alkalis. Tertiary amines, on the other hand, are unaffected by Hinsberg's reagent.
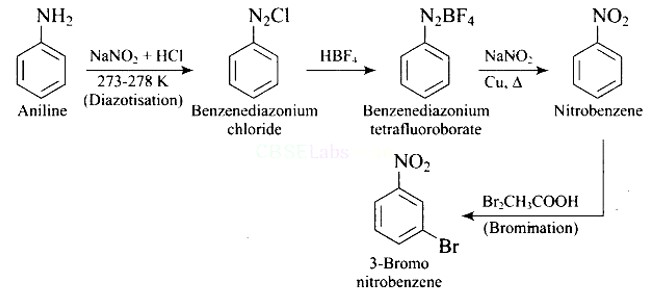
Why is benzene diazonium chloride not stored and is used immediately after its preparation?
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The reaction of aniline with nitrous acid at 273-278 K produces benzene diazonium chloride. The reaction of sodium nitrite with hydrochloric acid produces nitrous acid in the reaction mixture. Diazotisation is the process of converting primary aromatic amines into diazonium salts. Because of its instability, the diazonium salt is generally not stored or used immediately after preparation.
The crystalline solid benzene diazonium chloride is colorless.
It is easily soluble in water and stable at room temperature, but it reacts with water when warmed.
In the dry state, it decomposes easily.
Why does acetylation of −NH2 group of aniline reduce its activating effect?
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: As −NH2 is a strong activating group, the aniline will readily undergo electrophilic substitution reaction, and it is difficult to cease reaction at the mono substitution stage.
Therefore, the activating group −NH2 is protected by an acetylation process.
The acetylated complex formed utilizes the lone pair of nitrogen and are less available for donation, this helps to carry out the nitration reaction easily.
Explain why is MeNH2 stronger base than MeOH?
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: As the electronegativity of oxygen is more than the electronegativity of a nitrogen atom, the O−H bond is more polar than the N−H bond, therefore MeOH is stronger acid than MeNH2 or MeNH2 is stronger base than MeOH.
What is the role of pyridine in the acylation reaction of amines?
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Amides are the byproducts of the acylation reaction. The reaction is carried out in the presence of a stronger base than the amine, such as pyridine, which removes the formed HCl and shifts the equilibrium to the right.
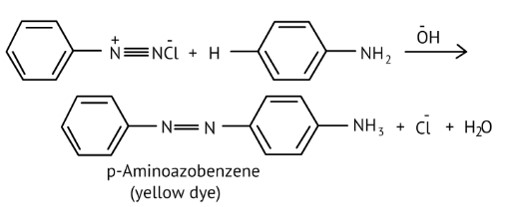
Under what reaction conditions (acidic/basic), the coupling reaction of aryl diazonium chloride with aniline is carried out?
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The azo products have an extended conjugate system with both aromatic rings linked by the –N=N- bond. These compounds are frequently colored and used as dyes. Benzene diazonium chloride reacts with phenol to form p-hydroxy azobenzene by coupling the phenol molecule in its para position with the diazonium salt. This is referred to as a coupling reaction.
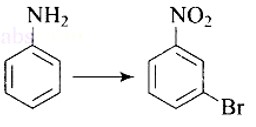
Predict the product of reaction of aniline with bromine in non-polar solvent such as CS2.
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: CS2 is a non-polar solvent which decreases the activating effect of? NH2. As a result, mono substitution occurs only at o- and p- positions giving a mixture of 2-bromoaniline (minor) and 4-bromoaniline (major) as products.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of dipole moment:
CH3CH2CH3,CH3CH2NH2,CH3CH2OH.
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: CH3CH2CH3 < CH3CH2NH2 < CH3CH2OH
As oxygen is more electronegative than nitrogen therefore, the O-H bond is more polar than the N-H bond. So ethanol has more dipole moments than ethylamine. Propane is non- polar in nature hence, had the least among all.
What is the structure and IUPAC name of the compound, allyl amine?
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans:
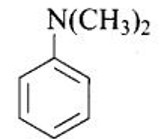
Write down the IUPAC name of
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: N, N-dimethylbenzenanmine
A compound Z with molecular formula C3H9N reacts with C6H5SO2Cl to give a solid, insoluble in alkali, identify Z.
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Z is an aliphatic amine that produces a solid that is insoluble in base. This means that the reaction with C6H5SO2Cl must produce a product with no replaceable hydrogen attached to nitrogen.
To put it another way, the amine must be a secondary amine.
Z stands for ethylmethylamine.
A primary amine, RNH2 can be reacted with CH3−X to get secondary amine, R−NHCH3 but the only disadvantage is that 3? amine and quaternary ammonium salts are also obtained as side products. Can you suggest a method where RNH2 forms only 2? amine?
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Carbylamine reaction is shown by primary amines only, primary amines react with chloroform in the presence of alcoholic KOH to form isocyanides which upon catalytic reduction gives secondary amines as the final product.
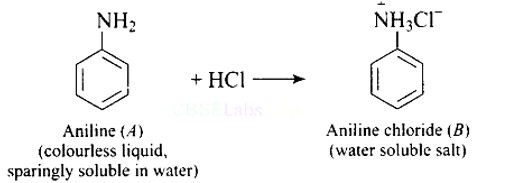
Why is aniline soluble in aqueous HCl?
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: On reaction with hydrochloric acid, aniline forms anilinium chloride ion which is water soluble. Therefore, the aniline solubility in aqueous HCl solution.
Suggest a route by which the following conversion can be accomplished.
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Identify A and B in the following reaction.
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
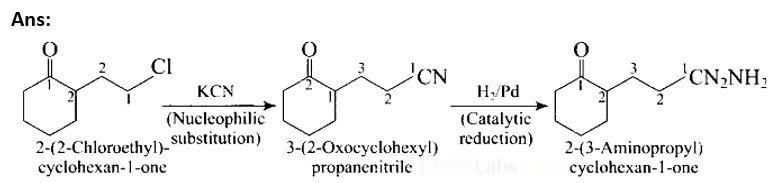
How will you carry out the following conversions?
(i) Toluene –> p-toIuidine
(ii) p-toluidine diazonium chloride –> p-toluic acid
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans:
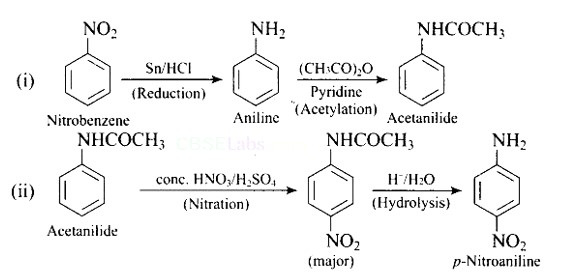
Write following conversions:
(i) Nitrobenzene → acetanilide
(ii) Acetanilide → p-nitroaniline
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans:
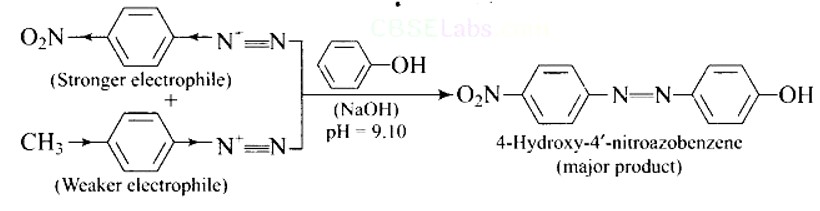
A solution contains 1 g mol each of p-toluene diazonium chloride and p-nitrophenyl diazonium chloride. To this 1 g mol of alkaline solution of phenol is added. Predict the major product. Explain your answer.
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans:
This is an example of an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. phenol generates phenoxide ion in alkaline medium, which is more electron-rich than phenol and thus more reactive to electrophilic attack. In this reaction, the electrophile is an aryldiazonium cation.
The faster the reaction, the stronger the electrophile.
The cation p-nitrophenyldiazonium is a stronger electrophile than the cation p-toluene diazonium.
As a result, it preferentially couples with phenol.
How will you bring out the following conversion?
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans:
How will you carry out the following conversion?
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans:
How will you carry out the following conversion?
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans:
How will you carry out the following conversion?
This is a Short Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans:
Amines Matching Type Questions
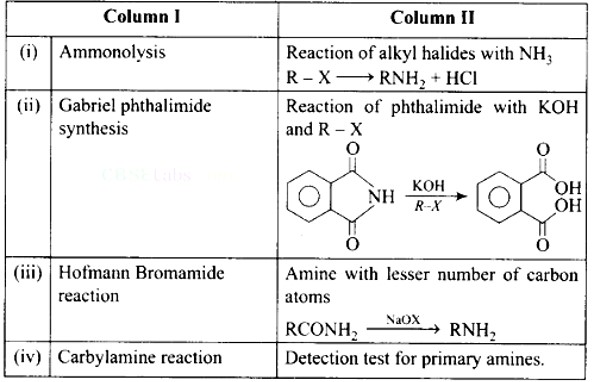
| Match the reactions given in Column I with the statements given in Column II.
|
||||||||||
| This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Ans: (i)- (d), (ii)- (c), (iii)- (a), (iv)- (b) |
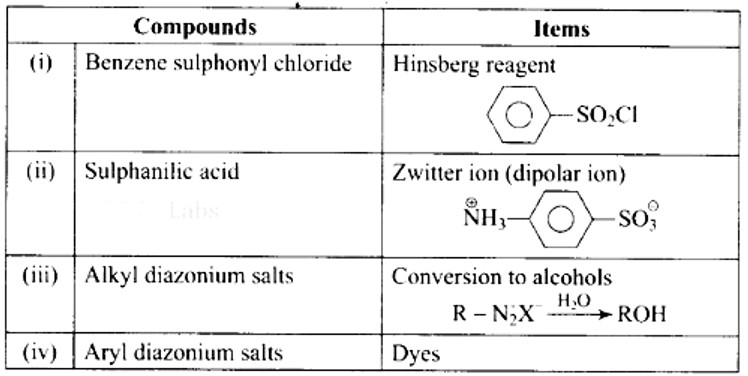
| Match the compounds given in Column I with the items given in Column II.
|
||||||||||
| This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Ans: (i)- (b), (ii)- (a), (iii)- (d), (iv)- (c) |
Commonly asked questions
Match the reactions given in Column I with the statements given in Column II.
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(i) Ammonolysis |
(a) Amine wth lesser number of carbon atoms |
|
(ii)Gabriel phthalimide synthesis |
(b) Detection test for primary amines. |
|
(iii) Hoffmann Bromide reaction |
(c) Reaction of phthalimide with KOH and R-X |
|
(iv) Carbylamine reaction |
(d) Reaction of aljylhalides with NH3 |
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (i)- (d), (ii)- (c), (iii)- (a), (iv)- (b)
Match the compounds given in Column I with the items given in Column II.
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(i) Benzene sulphonyl chloride |
(a) Zwitter ion |
|
(ii) Sulphanilic acid |
(B) Hinsberg reagent |
|
(iii) Alkyl diazonium salts |
(c) Dyes |
|
(iv) Aryl diazonium salts |
(d) Conversion to alcohols |
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (i)- (b), (ii)- (a), (iii)- (d), (iv)- (c)
Amines Assertion and Reason Type Questions
| In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices: (a) Both Assertion and Reason are wrong. (B) Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion. (c) Assertion is correct but Reason is wrong. (d) Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion. (e) Assertion is wrong but Reason is correct. Assertion (A): Acylation of amines gives a monosubstituted product, whereas alkylation of amines gives polysubstituted product. Reason (R): Acyl group sterically hinders the approach of further acyl groups. |
| This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Ans: (c) In the acryl derivative, the delocalisation of electrons of the nitrogen atom occur over the carbonyl group, this decreases the electron density on the nitrogen atom that it no more perform as nucleophile and don't react with next acylating alkaline molecule. Therefore, Assertion statement is correct but reason is incorrect. |
| In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices: Assertion (A): Hofmann’s bromamide reaction is given by primary amines. Reason (R): Primary amines are more basic than secondary amines. |
| This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Ans: (a) In Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction as in this reaction primary amide group is treated with halogen first bromine then the halogen substituted amide product is coverts to primary amine with the release of carbon dioxide gas. Both the statements assertion and reason are incorrect therefore the correct option is a. |
Commonly asked questions
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are wrong.
(B) Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct but Reason is wrong.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(e) Assertion is wrong but Reason is correct.
Assertion (A): Acylation of amines gives a monosubstituted product, whereas alkylation of amines gives polysubstituted product.
Reason (R): Acyl group sterically hinders the approach of further acyl groups.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (c)
In the acryl derivative, the delocalisation of electrons of the nitrogen atom occur over the carbonyl group, this decreases the electron density on the nitrogen atom that it no more perform as nucleophile and don't react with next acylating alkaline molecule.
Therefore, Assertion statement is correct but reason is incorrect.
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are wrong.
(B) Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct but Reason is wrong.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(e) Assertion is wrong but Reason is correct.
Assertion (A): Hofmann’s bromamide reaction is given by primary amines. Reason (R): Primary amines are more basic than secondary amines.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (a)
In Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction as in this reaction primary amide group is treated with halogen first bromine then the halogen substituted amide product is coverts to primary amine with the release of carbon dioxide gas. Both the statements assertion and reason are incorrect therefore the correct option is a.
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are wrong.
(B) Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct but Reason is wrong.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(e) Assertion is wrong but Reason is correct.
Assertion (A): N-Ethylbenzene sulphonamide is soluble in alkali.
Reason (R): Hydrogen attached to nitrogen in sulphonamide is strongly acidic.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (d)
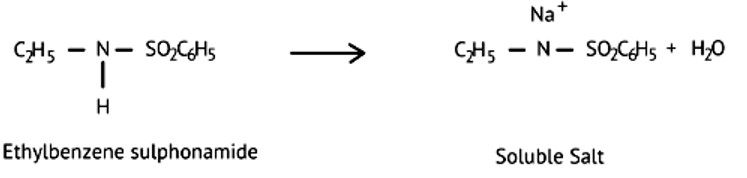
Ethylbenzene sulphonamide is soluble in alkali because it has acidic hydrogen.
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are wrong.
(B) Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct but Reason is wrong.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(e) Assertion is wrong but Reason is correct.
Assertion (A): N, N-diethylbenzene sulphonamide is insoluble in alkali.
Reason (R): Sulphonyl group attached to nitrogen atom is strong electron withdrawing group.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (b)
N, N-die ethyl benzene sulphonamide, there is no acidic hydrogen present on the N-atom which can make it soluble. Therefore, it is insoluble in alkali.
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are wrong.
(B) Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct but Reason is wrong.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(e) Assertion is wrong but Reason is correct.
Assertion (A): Only a small amount of HCl is required in the reduction of nitro compounds with iron scrap and HCl in the presence of steam.
Reason (R): FeCl2 formed gets hydrolysed to release HCl during the reaction.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (d)
Fe+2HCl→FeCl2+2 [H] FeCl2+H2O (g)→FeO+2HCl
The nascent hydrogen formed act as reducing agent for the reduction of nitro compounds.
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are wrong.
(B) Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct but Reason is wrong.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(e) Assertion is wrong but Reason is correct.
Assertion (A): Aromatic 1° amines can be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis.
Reason (R): Aryl halides undergo nucleophilic substitution with anion formed by phthalimide.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (a)
Aromatic primary amines cannot be prepared using Gabriel phthalimide synthesis as aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution with anion formed by phthalimide. Both the statement's assertion and reason are incorrect, hence the correct answer is a.
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are wrong.
(B) Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct but Reason is wrong.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(e) Assertion is wrong but Reason is correct.
Assertion (A): Acetanilide is less basic than aniline.
Reason (R): Acetylation of aniline results in decrease of electron density on nitrogen.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (d)
Acetanilide is less basic than aniline because electron density of nitrogen is lowered by acetyl group.
Animes Long Answer Type Questions
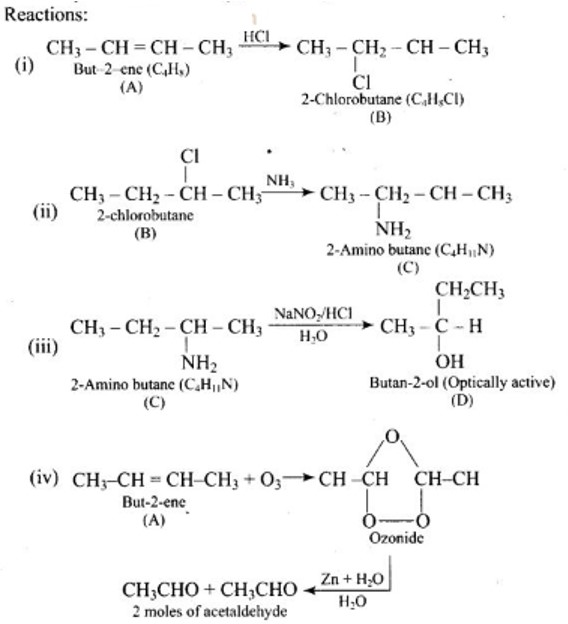
| A hydrocarbon ' A ', (C4H8) on reaction with HCl gives a compound ' B ' (C4H9Cl), which on reaction with 1 mol of NH3 gives compound ' C ', (C4H11 N). On reacting with NaNO2 and HCl followed by treatment with water, compound ' C ' yields an optically active alcohol, ' D '. Ozonolysis of ' A ' gives 2 moles of acetaldehyde. Identify compounds 'A' to 'D'. Explain the reactions involved. |
| This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Ans: |
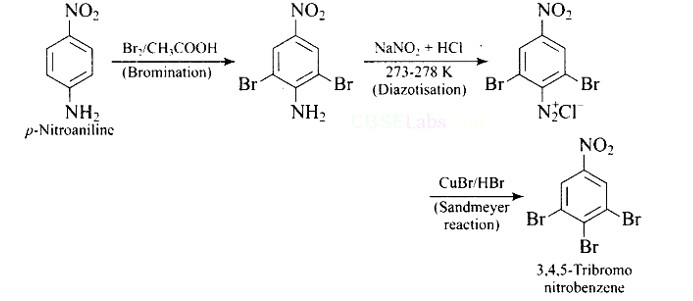
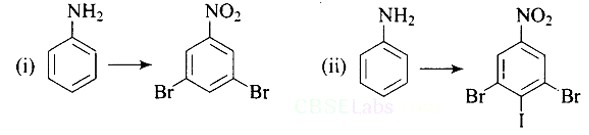
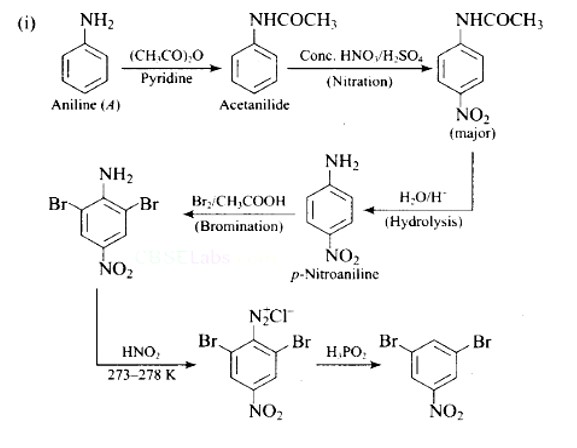
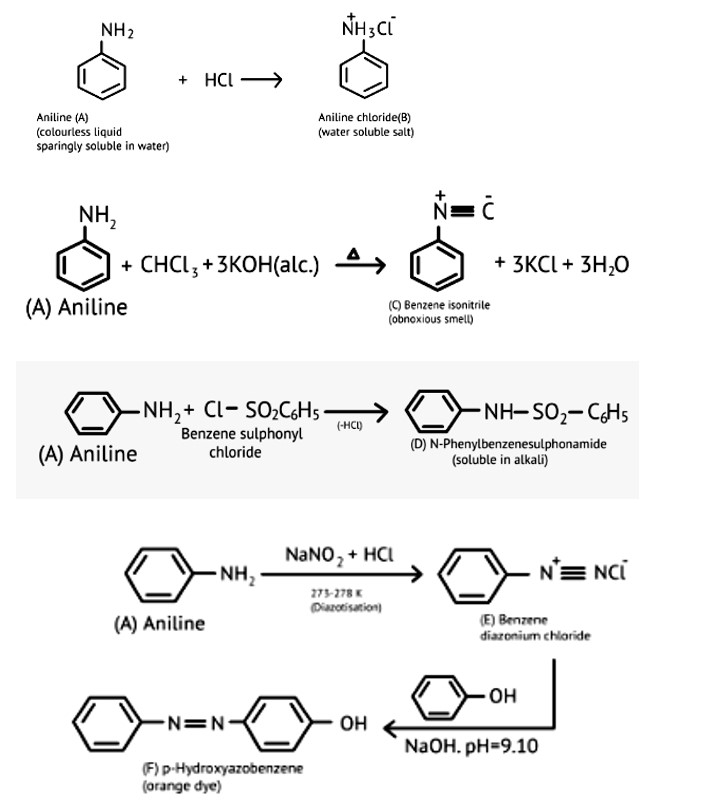
| A colourless substance ' A′(C6H7 N) is sparingly soluble in water and gives a water soluble compound ' B ' on treatment with mineral acid. On reacting with CHCl3 and alcoholic potash 'A' produces an obnoxious smell due to the formation of compound ' C '. Reaction of 'A' with benzenesulphonyl chloride gives compound ' D ' which is soluble in alkali. With NaNO2 and, ' A ' forms compound ' E ' which reacts with phenol in alkaline medium to give an orange dye ' F ' Identify compounds ' A ' to ' F '. |
| This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Ans: |
JEE Mains Solutions 2022, 26th july , chemistry, second shift
JEE Mains Solutions 2022, 26th july , chemistry, second shift
Commonly asked questions
Hemoglobin contains 0.34% of iron by mass. The number of Fe atoms in 3.3g of hemoglobin is (Given: Atomic mass of Fe is 56 u, NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1.)
Number of Fe atoms =
= 1.206 * 1020
Arrange the following in increasing order of heir covalent character.
(A). CaF2
(B). CaCl2
(C) CaBr2
(D) CaI2
According to Fajan’s rule,
Covalent character size of anion
At the half life for the decomposition of AB2 is 200s and is independent of the initial concentration of AB2. The time required for 80% of the AB2 to decompose is
t1/2 = 200 sec and it is 1st order reaction
Given below are two statements : one is labeled as Assertion A and the other is labeled as Reason R.
Assertion A: Finest gold is red in colour, as the size of the particles increase, it appears purple then blue and finally gold.
Reason R: The colour of the colloidal solution depends on the wavelength of light scattered by the dispersed particles.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
the finest gold sol is red in colour, as the size of particle increases, it appears purple then blue and finally gold. The colour of colloidal solution depends on the wavelength of light scattered by the dispersed particles. The wavelength of light further depends on size and nature of the particles. Hence, both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
The metal that has very low melting point and its periodic position is closer to a metalloid is
Element Melting Point
Al 933 K
Ga 303 K
ln 430 K
Se 490 K
The metal that is not extracted from its sulfide ore is
Al is extracted from Al2O3.2H2O i.e, Bauxite ore.
The products obtained from a reaction of hydrogen peroxide and acidified potassium permanganate are
Kindly go through the solution
Given below are two statements : one is labeled as Assertion A and the other is labeled as Reason R.
Assertion A: LiF is sparingly soluble in wate.
Reason R: The ionic radius of Li+ ion is smallest among its group members, hence has least hydration enthalpy.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
Due to high lattice energy, LiF is sparingly soluble in water. Li+ has high hydration energy among its group members due to the smallest size.
Given below are two statements : one is labeled as Assertion A and the other is labeled as Reason R.
Assertion A: Boric acid is a weak acid.
Reason R: Boric acid is not able to release H+ ion on its own. It receives OH- ion form water and releases H+ ion.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer form the option given below.
Kindly consider the following
The metal complex that is diamagnetic is (Atomic number; Fe, 26; Cu, 29)
K2 [Cu (CN)4]
Oxidation number of Cu is +1
Cu+ = [Ar]3d10 ® Diamagnetic
Match List I with List II.
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
Match list-I with list-II
List-I Pollutant | List-II Source | ||
(a) | Microorganisms | (i) | Domestic sewage |
(b) | Plant nutrients | (ii) | Chemical fertilizer |
(c) | Toxic heavy metals | (iii) | Chemical factory |
(d) | Sediment | (iv) | Strip mining |
The correct decreasing order of priority of functional groups in naming an organic compound as per IUPAC system of nomenclature is
Correct order of priority is
Which of the following is not an example of benzenoid compound?
The structure consisting benzene ring is called benzenoidal structure and options (A) and (B) do not contain benzene ring, so they are non benzenoidal.
Hydrolysis of which compound will give carbolic acid?
Kindly go through the solution
The correct sequential order fo the reagents for the given reaction is
Kindly go through the solution
Consider the reaction and predict the major product.
Kindly go through the solution
Vulcanization of rubber is carried out by heating a mixture of
Vulcanization of rubber is carried out by heating a mixture of isoprene and sulphur.
Animals starch is the other name of
Other name of animal starch is glycogen.
Given below are two statements : one is labeled as Assertion A and the other is labeled as Reason R.
Assertion A: Phenolphthalein is pH dependent indicator, remains colourless in acidic solution and gives pink colour in basic medium.
Reason R: Phenolphthalein is a weak acid. It doesn’t dissociate in basic medium.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
Phenolphtalein is a pH dependant indicator. It is a weak acid which is colourless in acidic medium but gives pink colour in basic medium. The pink colour is due to its conjugate form. Phenolphthalein dissociates in basic medium. Therefore, assertion is true but reason is false.
A 10g mixture of hydrogen and helium is contained in a vessel of capacity 0.0125 m3 at 6 bar ansd C. The mass of helium in the mixture is__________g. (nearest integer)
PV = nmixRT
Let moles of He is x
Moles of H2 = 3 – x
4x + 2 (3 – x) = 10
x = 2 mol
Mass of He = 8 gm
Consider an imaginary ion 
Number of electrons = 25
% of extra electrons =
For the reaction
H2F2(g) ® H2(g) + F2(g)
The enthalpy change for the above reaction is ()__________kJ mol-1. [nearest integer]
The elevation in boiling point for 1 molal solution of non-volatile solute A is 3K. The depression in freezing point for 2 molal solution of A in the same solvent is 6 K. The ratio of Kb and Kf i.e. Kb/Kf is 1 : X. The value of X is [nearest integer]
20mL of 0.02 M hypo solution is used for the titration of 10mL of copper sulphate solution, in the presence of excess of KI using starch as an indicator. The molarity of Cu2+ is found to be__________× 10-2 M. [nearest integer]
Given: 2Cu2+ + 4I- ® Cu2I2 + I2
I2 +
2 × mmol of l2 = 0.4
mmol of l2 = 0.2 mmol
mmol of Cu2+ = 0.2 × 2 × 10-3
The number of non-ionisable protons present in the product B obtained from the following reaction is______________.
C2H5OH + PCl3 ® C2H5Cl + A
A + PCl3 ® B
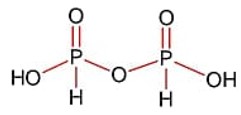
The spin-only magnetic moment value of the compound with strongest oxidizing ability among MnF4, MnF3 and MnF2 is_________B.M [nearest integer]
E.C = [Ar] 3d3 [Ar]3d4
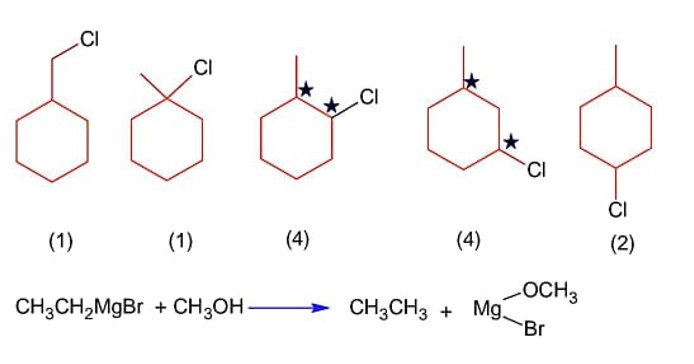
Total number of isomers (including stereoisomers) obtained on monochlorination of methylcyclohexane is_______________.
A 100 mL solution of CH3CH2MgBr on treatment with methanol produces 2.24 mL of a gas at STP. The weight of gas produced is __________ mg. [nearest integer]
Moles of C2H6 =
Weight of C2H6 = 10-4 × 30 = 3 mg
How many of the following drugs is/are example(s) of broad spectrum antibiotics?
Ofloxacin, Penicillin G, Terpineol, Salvarsan.
Ofloxacin is the only broad spectrum antibiotic given in the question.
Pencillin – G is narrow spectrum antibiotic.
Salvarsan is mainly active against spirochete, a bacteria that causes syphilis.
Terpineol is an antiseptic.
27th July 2022 first shift
27th July 2022 first shift
Commonly asked questions
20 mL of 0.02 M K2Cr2O7 solution is used for the titraction of 10 mL of Fe2+ solution in the acidic medium. The molarity of Fe2+ solution is ___________× 10-2 M. (Nearest Integer)
Meq of K2Cr2O7 = Meq of Fe2+
(Molarity × Volume × nf) of K2Cr2O7 = (molarity × volume × nf) of Fe2+
0.02 × 20 × 6 = M × 10 × 1
M = 0.24 M
Molarity = 24 × 10-2 M
2NO + 2H2 → N2 + 2H2O
The above reaction has been studied at 800°C. The related data are given in the table below.
|
Reaction serial number |
Initial Pressure of H2 / kPa |
Initial Pressure of NO / kPa |
Initial rate (-dP/dT)/(kPa/s) |
|
1 |
65.6 |
40.0 |
0.135 |
|
2 |
65.6 |
20.1 |
0.033 |
|
3. |
38.6 |
65.6 |
0.214 |
|
4. |
19.2 |
65.6 |
0.106 |
The order to the reaction with respect to NO is_______________.
On decreasing pressure of NO by a factor of ‘2’ the rate of reaction decreases by a factor of ‘4’
Order of reaction w.r.t ‘NO’ = 2
Amongst the following, the number of oxide(s) which are paramagnetic in nature is Na2O, KO2, NO2, N2O, ClO2, NO, SO2, Cl2O (Nearest Integer)
are paramagnetic.
The molar heat capacity for an ideal gas at constant pressure is 20.785JK-1 mol-1. The change in internal energy is 5000 J upon heating it from 300 K to 500 K. The number of moles of the gas at constant volume is __________. (Nearest Integer)
According to MO theory, number of species / ions from the following having identical bond order is___________.
CN-, NO+, O2,
have bond order = 3
At 310 K, the solubility of CaF2 in water is 2.34 × 10-3 g/ 100 mL. The solubility product of CaF2 is ____________× 10-8 (mol/L)3. (Give molar mass : CaF2 = 78 gmol-1)
Solubility of CaF2 = S mol/L
= 0.0108 × 10-8 (mol/L)3
The conductivity of a solution of complex with formula CoCl3(NH3)4 corresponds to 1 : 1 electrolyte, then the primary valency of central metal ion is__________________.
Complex is
Primary valency = No. of ionisable species = 1
In the titration of KMnO4 and oxalic acid in acidic medium, the change in oxidation number of carbon at the end point is____________.
Oxidation state of carbon changes from +3 to +4
change in O. S is 1
Optical activity of an enantiomeric mixture is + 12.6° and the specific rotation of (+) isomer is +30°. The optical purity is_____________%
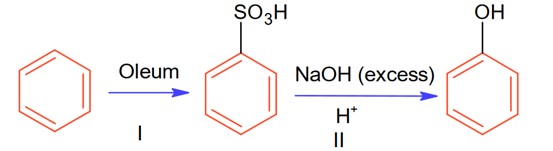
In the following reaction
The % yield for reaction I is 60% and that of reaction II is 50%. The overall yield of the complete reaction is___________% [Nearest integer]
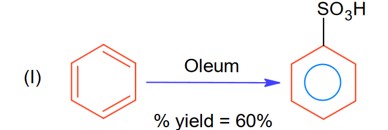
Let initial moles of reactant taken = n. Total moles obtained for benzene sulphonic acid = 0.6 n (with % yield = 60%)
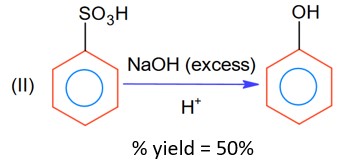
Moles of benzene sulphonic acid before reaction II = 0.6n
Moles obtained for phenol (with % yield 50%) = 0.6 × 0.5 n = 0.3 n
So, overall % age yield of complete reaction =
Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Thirteen Exam