Electrochemistry
Get insights from 145 questions on Electrochemistry, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Electrochemistry
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
Given:
2Fe3+ (aq) + 2I- (aq) → 2Fe2+ (aq) + I2 (s)
E0cell = 0.236V
n = moles of e- from balanced redox reaction = 2
F = Faraday's constant = 96,485 C/mol
T = 298 K.
Using the formula, we get
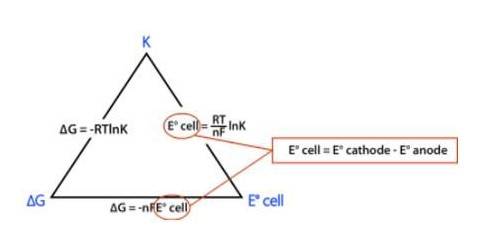
? rG0 = – nFE0cell
⇒? rG0 = – 2 * FE0cell
⇒? rG0 = −2 * 96485 C mol-1 * 0.236 V
⇒? rG0 = −45540 J mol-1
⇒? rG0 = −45.54 kJ mol-1
Now,
? rG0 = −2.303RT log Kc
Where, K is the equilibrium constant of the reaction
R is the gas constant; R = 8.314 J-mol-C-1
⇒ −45540 J mol-1 = –2.303* (8.314 J-mol-C-1)* (298 K) * (log Kc)
Solving for Kc we get,
⇒ logKc = 7.98
Taking antilog both side, we get
⇒ Kc = Antilog (7.98)
⇒ Kc = 9.6 * 1
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
Given:
[Ag+] = 0.002 M
[Ni2+] = 0.160 M
n = 2
(n = moles of e- from balanced redox reaction)
E0cell= 1.05 V
Now, using the Nernst equation, we get,

New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
Given:
For hydrogen electrode, pH = 10
n = 1
(n = moles of e- from balanced redox reaction)
On using the formula [H+] = 10– pH
⇒ [H+] = 10 − 10 M
We know,
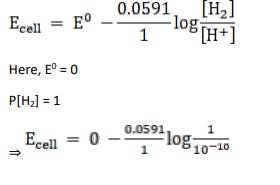
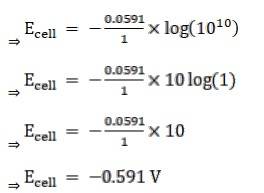
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
For a substance to oxidise Fe2+ to Fe3+ ion, it must have high reduction potential than Fe3+. The reduction potential of Fe3+ to Fe2+ reaction is 0.77V, the substances which have reduction potentials higher than this value will oxidise Fe2+ ions. Comparing the values, from the table:

New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
NO, because Zn is very reactive with Cu. It reacts with copper sulphate to form zinc sulphate i.e., Zn displaces Cu and metallic Cu is also formed.
The reaction is given as:
Zn + CuSO4 ⇒ ZnSO4 + Cu
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
To determine the standard electrode potential of the system Mg2+|Mg, connect it to the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE). Keep the Mg2+|Mg system as cathode and SHE as cathode. This is represented as shown below.
Pt (s) | H2 (g, 1 bar)| H+ (aq, 1 M) |Mg2+ (aq, 1M)| Mg
The electrode potential of a cell is given by
E? = E? R – E? L
Where,
E? R- Potential of the half-cell in the right side of the above representation
E? L- Potential of the half-cell in the left side of the above representation
It is to be noted that the potential of the standard hydrogen electrode is zero.
Therefore, E? L = 0
E? = E? R – 0
⇒ E? = E? R
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers