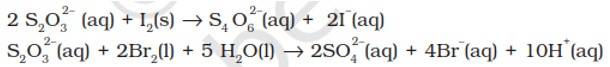Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 11th
Get insights from 2k questions on Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
5.23. (a) The dipole-dipole interaction between two HCl molecules is stronger than the London forces but is weaker than ion-ion interaction because only partial charges are involved.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Reactions (a) and (b) indicate that H3PO2 (hypophosphorous acid) is a reducing agent and thus reduces both AgNO3 and CuSO4 to Ag and Cu respectively. Conversely, both AgNO3 and CuSO4 act as oxidising agent and thus oxidise H3PO2to H3PO4 (orthophosphoric acid) Reaction (c) suggests that [Ag (NH3)2]+ oxidises C6H5CHO (benzaldehyde) to C6H5COO– (benzoate ion) but reaction (d) indicates that Cu2+ ions cannot oxidise C6H5CHO to C6H5COO–. Therefore, from the above reactions, we conclude that Ag+ ion is a strong deoxidising agent than Cu2+ ion.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
XeO64−? oxidizes F− and F− reduces XeO64−?
Hence, the given reaction occurs.
The oxidation number of Xe decreases from +8 to +6. The oxidation number of F increases from -1 to 0.
Thus, Na4? XeO6? is a stronger oxidising agent than F−.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Fluorine oxidizes chloride ion to chlorine, bromide ion to bromine and iodide ion to iodine respectively.
F2? + 2Cl− → 2F− + Cl2?
F2? + 2Br− → 2F− + Br2?
F2? + 2I− → 2F− + I2?
Chlorine oxidizes bromide ion to bromine and iodide ion to iodine.
Cl2? + Br− → 2Cl− + Br2?
Cl2? + I− → 2Cl− + I2?
Bromine oxidizes iodide ion to iodine.
Br2? + I− → 2Br− + I2?
But bromine and chlorine cannot oxidize fluoride to fluorine. Hence, fluorine is the best oxidizing agent amongst the halogens. The decreasing order of the oxidizing power of halogens is F2? >Cl2? >Br2? >I2?
HI and HBr can reduce sulphuric acid
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
The average O.N. of S in S2O32- is +2 while in S4O62- it is + 2.5. The O.N. of S in SO42- is +6. Since Br2 is a stronger oxidising agent than I2, it oxidises S of S2O32- to a higher oxidation state of +6 and hence forms SO42- ion. I2, however, being weaker oxidising agent oxidises S of S2O32- ion to a lower oxidation of +2.5 in S4O62- ion. It is because of this reason that thiosulphate reacts differently with Br2 and I2.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Substance oxidised | Substance reduced | Oxidising agent | Reducing agent |
(a) C6H12O6 | AgBr | C6H12O6 | |
(b) HCHO | [Ag (NH3)2]+ | [Ag (NH3)2]+ | HCHO |
(c) HCHO | Cu2+ | HCHO | |
(d) N2H4 | H2O2 | N2H4 | |
(e) Pb | PbO2 | Pb |
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
5.22. Higher the critical temperature, more easily the gas can be liquefied, i.e., greater are the intermolecular forces of attraction. Hence, CO2 has stronger intermolecular forces than CH4.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a) Toluene can be oxidised to benzoic acid in acidic, basic and neutral media according to the following redox equations:
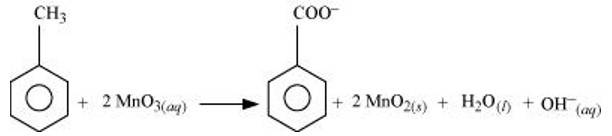
In the laboratory, benzoic acid is usually prepared by alcoholic KMnO4 oxidation of toluene. However, in industry alcoholic KMnO4 is preferred over acidic or alkaline KMnO4 because of the following reasons:
(i) The cost of adding an acid or the base is avoided because in the neutral medium, the base (OH- ions) are produced in the reaction itself.
(ii) Since reactions occur faster in homogeneous medium than in heterogeneous medium, therefore, alcohol helps in mixing the two reactants, i.e., KMnO4
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
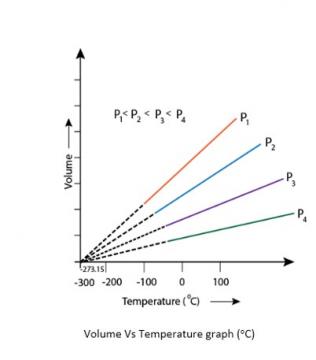
5.21. At -273°C, volume of the gas becomes equal to zero, i.e., the gas ceases to exist.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
The three examples are:
(i) When excess P4? (reducing agent) reacts with F2? (oxidizing agent), PF3? is produced in which P has +3 oxidation number.
P4? (excess) + F2? → PF3?
But if fluorine is in excess, PF5? is formed in which P has oxidation number of +5.
P4? ? + F2? (excess) → PF5?
(ii) Oxidizing agent is oxy
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 65k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 679k Reviews
- 1800k Answers