Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 11th
Get insights from 2k questions on Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) Dumas method: The nitrogen containing organic compound, when heated with copper oxide in an atmosphere of carbon dioxide, yields free nitrogen in addition to carbon dioxide and water
(ii)Kjeldahl's method: A known mass of the organic compound is heated strongly with conc. H2SO4, a little potassium sulphate and a little mercury (a catalyst). As a result, the nitrogen present in the organic compound is converted to ammonium sulphate.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Lassaigne's test: In organic compounds, nitrogen, sulphur and halogens are covalently bonded. Their detection in 'Lassaigne's test' is possible if they are in the ionic form. This can be achieved by fusing the organic compound with sodium metal.
Chemistry for test for nitrogen:
Sodium fusion extract is boiled with ferrous sulphate and acidified with sulphuric acid. Sodium cyanide reacts with ferrous sulphate and forms sodium hexacyanoferrate (II). On heating with sulphuric acid, some ferrous is oxidized to ferric hexacyanoferate (II) Fe4 [Fe (CN)6]3 which is prussian blue in colour.
Chemistry of the test for sulphur:
Aceti
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Distillation is used in case of volatile liquid mixed with non-volatile impurities.
Distillation under reduced pressure: This method is used to purify such liquids which have very high boiling points and which decompose at or below their boiling points.
Steam distillation is used to purify steam volatile liquids associated with water immiscible impurities.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Fractional crystallisation is the method that can be used to separate two compounds with different solubilities in a solvent S. A hot saturated solution of these two compounds is allowed to cool, the less soluble compound crystallises out while the more soluble remains in the solution. The crystals are separated from the mother liquor and the mother liquor is again concentrated and the hot solution again allowed cooling when the crystals of the second compound are obtained. These are again filtered and dried.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a) Crystallisation: In this process the impure solid is dissolved in the minimum volume of a suitable solvent. The soluble impurities pass into the solution while the insoluble ones left behind. The hot solution is then filtered and allowed to cool undisturbed till crystallisation is complete. The crystals are then separated from the mother liquor by filtration and dried.
Example: crystallisation of sugar.
(b) Distillation: The operation of distillation is employed for the purification of liquids from non-volatile impurities. The impure liquid is boiled in a flask and the vapours so formed are collected and condensed to give
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Inductive effect: The inductive effect refers to the polarity produced in a molecule as a result of higher electronegativity of one atom compared to another. Atoms or groups which lose electron towards a carbon atom are said to have +I Effect. Examples of +I effect are (Electron releasing)
(CH3)2C—, (CH3)2CH—, CH3CH2— CH3— etc.
Those atoms or groups which draw electron away from a carbon atom are said to have -I Effect. Examples of -I effect are:
NO2, F, Cl, Br, I, OH etc.
Electromeric effect: The electromeric effect refers to the polarity produced in a multiple bonded compound as it is approached by a reagent.
The atom A has lost
New question posted
6 months agoNew answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a) They are structural isomers. The given compounds have the same molecular formula but they differ in the position of the functional group (here ketone group: first one at C-3 and second one at C-2 positions).
(b) They are geometrical isomers. Compounds having the same molecular formula, the same constitution, and the sequence of covalent bonds, but with the different relative position of their atoms in space are called geometrical isomers.
(c) They are resonance contributors because they differ in the position of electrons but not atoms.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.32.
Sigma bond | Pi bond |
It is formed by axial overlap of the atomic orbitals. | It is formed by the sidewise overlap of the atomic orbitals. |
The bond is quite strong. | It is a comparatively weaker bond. |
Only one lobe of the p-orbitals is involved in the overlap. | Both lobes of the p-orbitals are involved in the overlap. |
Electron cloud of the molecular orbital is symmetrical around the inter-nuclear axis. | The electron cloud is not symmetrical |
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
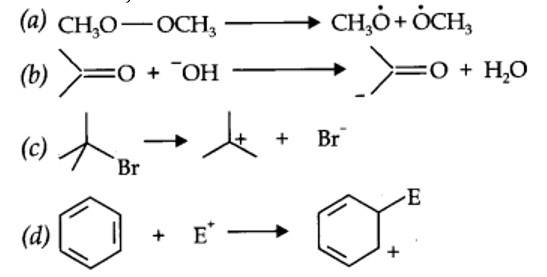
(a) Nucleophilic substitution (b) Electrophilic addition
(c) Bimolecular elimination (d) Nucleophilic substitution with rearrangement.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 65k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 679k Reviews
- 1800k Answers