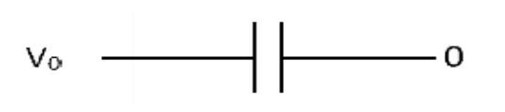Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Get insights from 131 questions on Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
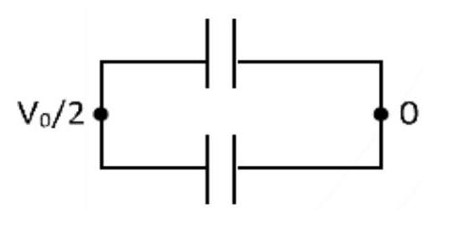
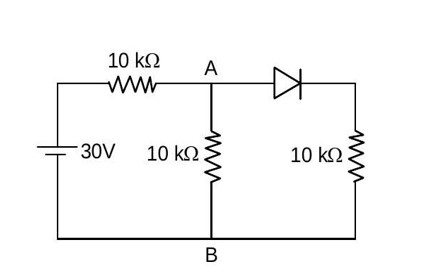
In forward bias diode act as a short circuit wire. Hence, the equivalent circuit is now.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
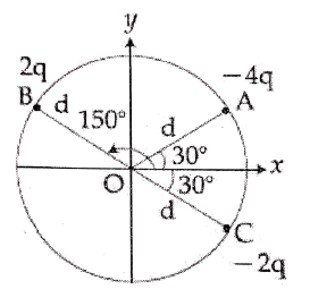
As charge remains same. So,
Initial total charge Q = (2C)V + CV = 3CV
When dielectric is inserted in C, its new capacitance is KC.
The capacitors 2C and KC are in parallel.
Equivalent capacitance C_eq = 2C + KC = (K+2)C
New potential Vc = Q/C_eq = 3CV/ (K+2)C) = 3V/ (K+2)
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
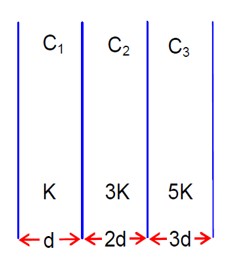
1/Ceq = 1/C? + 1/C? + 1/C?
1/Ceq = 1/ (K Aε? /d) + 1/ (3K Aε? /2d) + 1/ (5K Aε? /3d)
1/Ceq = d/ (K Aε? ) + 2d/ (3K Aε? ) + 3d/ (5K Aε? )
1/Ceq = (d/K Aε? ) * (1 + 2/3 + 3/5)
1/Ceq = (d/K Aε? ) * (15+10+9)/15) = 34d / (15K Aε? )
Ceq = 15K Aε? / 34d
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
V = E (1 - e? /τ)
Where τ = RC = 100 * 10? = 10? sec
50V = 100V (1 - e? /10? )
1/2 = 1 - e? ¹?
1/2 = e? ¹?
-ln2 = -10? t
t = ln2/10?
t = 0.693 * 10? sec
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 9
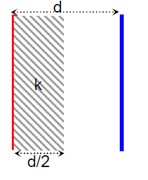
dC? = (ε? + kx)A / dx [For 0 < x < d/2]
1/C? = ∫ dx / (ε? + kx)A) from 0 to d/2
= (1/Ak) [ln (ε? + kx)] from 0 to d/2
= (1/kA) ln (1 + kd/ (2ε? )
C? = kA / ln (1 + kd/ (2ε? )
Similarly dC? = (ε? + k (d-x)A / dx [For d/2 ≤ x ≤ d]
C? = kA / ln (1 + kd/ (2ε? )
Clearly, C? = C? = C
For series combination:
C_eq = C? / (C? + C? ) = C/2 = kA / (2ln (2ε? + kd)/2ε? )
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers