Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism
Get insights from 108 questions on Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
As we know that radius of circular path in magnetic field is given as
Charged particle | Charge | Mass |
Deuteron | e | 2m |
Alpha particle | 2e | 4m |
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
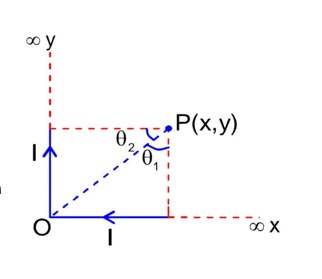
B due to OX wire
As in the diagram direction of B1 and B2 are in downward direction
So B = B1 + B2
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Using magnetic field due to straight wire :
So, magnetic field due to three wires
= 3 * 10-5 T
inside the plane
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
B due to OX wire
As in the diagram direction of B1 and B2 are in downward direction
So B = B1 + B2
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
for current
1 unit Area
Now, consider Amperian loop of radius small 'r' ln Amperian loop magnetic field will be tangential to the amperian loop.
(Ampere circuital law)
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
