Physics
Get insights from 5.6k questions on Physics, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
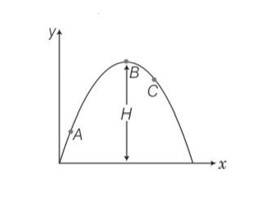
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- vsin = vertical component
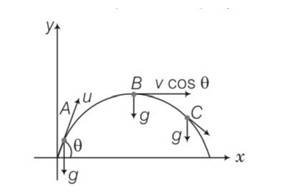
Vx= horizontal component of velocity =vcos = constant
Vy = vertical component of velocity =vsin
Velocity will always be tangential to the curve in the direction of motion and acceleration is always vertically downward and is equal to g.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- the cyclist covers OPRQO path.
As we know whenever an object performing circular motion, acceleration is called centripetal acceleration and is always directed towards the centre.
so there will be centripetal acceleration a= v2/r
So a= 100/1km= 100/1000=0.1m/s2 along RO.

New answer posted
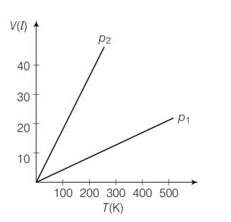
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) Pressure is inversely proportional to slope
So
So p1 > p2
New answer posted
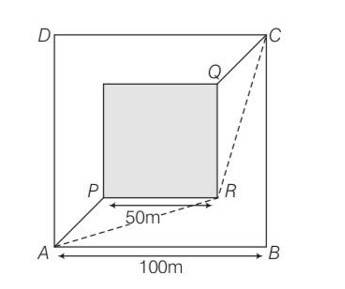
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation – Tsand=
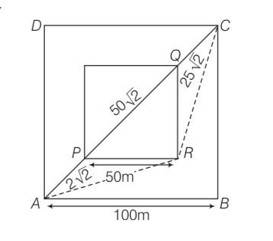
= 50
Time taken Toutside=
AR=
RC= AR=
Toutside= 2AR= 50
Tsand
New answer posted
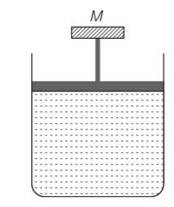
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) The pressure inside the gas will be
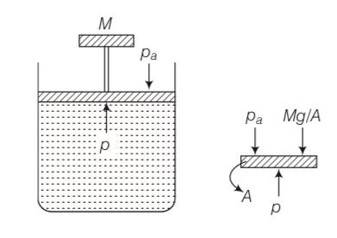
P= pa+Mg/A
A= area of piston
Pa= atmospheric pressure
Mg = weight of piston
When temperature is increases
pV=nRT so volume increases at constant pressure.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) Boyle's law is applicable when temperature is constant
PV=nRT=constant
PV= constant
So pressure is inversely proportional to volume.
So process is called isothermal process.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation – r=cos ?…….1
…….2
Multiplying eq1 by sin and 2 with cos and adding
Rsin
= ?( )=j
= rsin
n(rcos )=i
b)r
= -cos
c)r=cos
dr/dt=d/dt(cos )=w[-cos ]
d)L= MoLT0
e)a=1unit , r=
v= dr/dt=
v=
= w
a=
a=
=
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(d) In an ideal gas when a molecules collides elastically with a wall, the momentum transferred to each molecule will be twice the magnitude of its normal momentum. For the face EFGH, it transfer only half of that.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
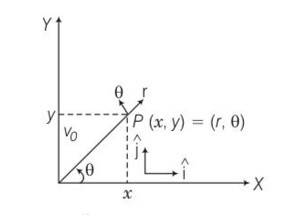
Explanation- a) for x direction ux= u+vocos
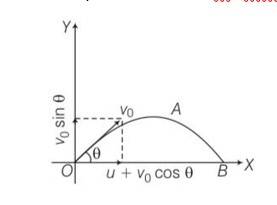
uy=velocity in y direction= v0sin
now tan
b) let t be the time flight y =0 uy=vosin
y= uyt+1/2 ayt2
0= vosin +
So T =
c) horizontal range R, = (u+vocos T= (u+vocos )
d) for range to be maximum dR/d
4vocos2
So cos =
e) cos =
so
f) if u=0 0
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) As the motion of the vessel as a whole does not affect the relative motion of the gas molecules with respect to the walls of the vessel, hence pressure of the gas inside the vessel, as conserved by us, on the ground remains the same.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 684k Reviews
- 1800k Answers